
Odobenidae is a family of pinnipeds, of which the only extant species is the walrus. In the past, however, the group was much more diverse, and includes more than a dozen fossil genera.

The walrus is a large pinniped marine mammal with discontinuous distribution about the North Pole in the Arctic Ocean and subarctic seas of the Northern Hemisphere. It is the only extant species in the family Odobenidae and genus Odobenus. This species is subdivided into two subspecies: the Atlantic walrus, which lives in the Atlantic Ocean, and the Pacific walrus, which lives in the Pacific Ocean.

Pinnipeds, commonly known as seals, are a widely distributed and diverse clade of carnivorous, fin-footed, semi-aquatic, and mostly marine mammals. They comprise the extant families Odobenidae, Otariidae, and Phocidae, with 34 extant species and more than 50 extinct species described from fossils. While seals were historically thought to have descended from two ancestral lines, molecular evidence supports them as a monophyletic lineage. Pinnipeds belong to the clade Caniformia of the order Carnivora; their closest living relatives are musteloids, having diverged about 50 million years ago.

Caniformia is a suborder within the order Carnivora consisting of "dog-like" carnivorans. They include dogs, bears, raccoons, and mustelids. The Pinnipedia are also assigned to this group. The center of diversification for the Caniformia is North America and northern Eurasia. Caniformia stands in contrast to the other suborder of Carnivora, the Feliformia, the center of diversification of which was in Africa and southern Asia.
Potamotherium an extinct genus of caniform carnivoran from the Miocene epoch of France and Germany. It has historically been assigned to the family Mustelidae, but more recent studies suggest that it represents a primitive relative of pinnipeds

Enaliarctos is an extinct genus of pinnipedimorph, and may represent the ancestor to all pinnipeds. Prior to the discovery of Puijila, the five species in the genus Enaliarctos represented the oldest known pinnipedimorph fossils, having been recovered from late Oligocene and early Miocene strata of California and Oregon.

Desmatophoca is an extinct genus of early pinniped that lived during the Miocene, and is named from the Greek "phoca", meaning seal. A taxon of the family Desmatophocidae, it shares some morphological similarities with modern true seals. Two species are recognized: Desmatophoca oregonensis and Desmatophoca brachycephala. Little information exists regarding Desmatophoca, due to the small number of fossil samples obtained and identified.

Imagotaria is an extinct monotypic genus of walrus with the sole species Imagotaria downsi. Fossils of Imagotaria are known from the early late Miocene of California.

Ontocetus is an extinct genus of walrus, an aquatic carnivoran of the family Odobenidae, endemic to coastal regions of the southern North Sea and the southeastern coastal regions of the U.S. during the Miocene-Pleistocene. It lived from 13.6 mya—300,000 years ago, existing for approximately 13.3 million years.
Neotherium mirum is an extinct species of basal walrus. It was smaller than living forms and it did not have long tusks. Males were larger than females.

Pontolis is an extinct genus of large walrus. It contained three species, P. magnus, P. barroni, and P. kohnoi. Like all pinnipeds, Pontolis was a heavily built amphibious carnivore. Pontolis lived along the Pacific coast of North America along what is now the western coasts of California and Oregon between 11.608 and 5.332 million years ago, during the Miocene and Pliocene.
Pteronarctos is a genus of basal pinnipediform from middle Miocene marine deposits in Oregon.
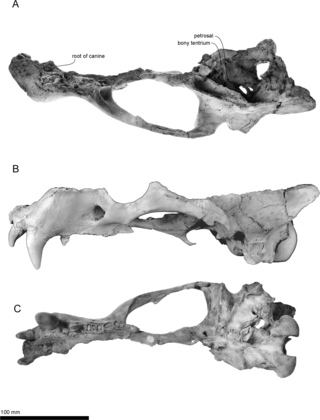
Archaeodobenus is an extinct genus of pinniped that lived during the Late Miocene of what is now Japan. It belonged to the Odobenidae family, which is today only represented by the walrus, but was much more diverse in the past, containing at least 16 genera.

Proneotherium is an extinct genus of pinniped that lived approximately 20.43 to 15.97 mya during the Early Miocene in what is now Oregon, U.S. It belonged to the family Odobenidae, the only extant species of which is the walrus.

Nanodobenus is an extinct genus of pinniped that lived approximately 15.97 to 7.246 mya during the Miocene in what is now Baja California Sur, Mexico. It belonged to the family Odobenidae, the only extant species of which is the walrus.

Pinnipedimorpha is a clade of arctoid carnivorans that is defined to include the last common ancestor of Phoca and Enaliarctos, and all descendants of that ancestor. Scientists still debate on which lineage of arctoid carnivorans are the closest relatives to the pinnipedimorphs, being more closely related to musteloids.

Otarioidea is a superfamily of pinnipeds that includes the families Odobenidae, Otariidae and their stem-relatives. In the past when the pinnipeds were considered to be a diphyletic group of marine mammals, a few points of cranial and dental morphology suggested that the otarioids originated from a line of bears. One extinct family, Enaliarctidae, was postulated to be otarioids that were a transitional clade between Hemicyoninae and Otariidae. Recent comprehensive studies have, however, since the 1990s found pinnipeds to be a monophyletic clade of aquatic arctoids. There are a few authorities that place desmatophocids and odobenids as sister taxa to Phocidae in the clade Phocomorpha based on a few minor physiological features.


















