
Podocarpus totara is a species of podocarp tree endemic to New Zealand. It grows throughout the North Island and northeastern South Island in lowland, montane and lower subalpine forest at elevations of up to 600 m.

Mount Cameroon is an active volcano in the South West region of Cameroon next to the city of Buea near the Gulf of Guinea. Mount Cameroon is also known as Cameroon Mountain or Fako or by its indigenous name Mongo ma Ndemi. Mount Cameroon is ranked 22nd by topographic isolation.

Abies lasiocarpa, the subalpine fir or Rocky Mountain fir, is a western North American fir tree.

Mount Giluwe is the second highest mountain in Papua New Guinea at 4,367 metres (14,327 ft), and the fifth highest peak on the island of New Guinea. It is located in the Southern Highlands province and is an old shield volcano with vast alpine grasslands. Ancient volcanic plugs form its two summits, with the central peak the highest and an east peak about 2 kilometres (1.2 mi) away at 4,300 m (14,108 ft). Giluwe has the distinction of being the highest volcano on the Australian continent and Oceania, and is thus one of the Volcanic Seven Summits.
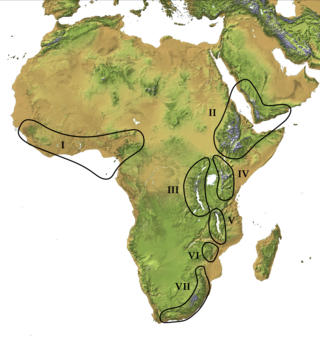
The Afromontane regions are subregions of the Afrotropical realm, one of the Earth's eight biogeographic realms, covering the plant and animal species found in the mountains of Africa and the southern Arabian Peninsula. The Afromontane regions of Africa are discontinuous, separated from each other by lower-lying areas, and are sometimes referred to as the Afromontane archipelago, as their distribution is analogous to a series of sky islands.

The Talamancan montane forests ecoregion, in the tropical moist broadleaf forest biome, are in montane Costa Rica and western Panama in Central America.

The Sierra Nevada subalpine zone refers to a biotic zone below treeline in the Sierra Nevada mountain range of California, United States. This subalpine zone is positioned between the upper montane zone at its lower limit, and tree line at its upper limit.

Phyllocladus hypophyllus is a species of conifer in the family Podocarpaceae. It a tree native to Borneo, Sulawesi and the Maluku Islands (Indonesia), the Philippines, and New Guinea.
Podocarpus borneensis is a species of conifer in the family Podocarpaceae. It native to the island of Borneo, which is divided between Indonesia and Malaysia.

The Eastern Himalayan alpine shrub and meadows is a montane grasslands and shrublands ecoregion of Bhutan, China, India, Myanmar, and Nepal, which lies between the tree line and snow line in the eastern portion of the Himalaya Range.

The Ecology of the North Cascades is heavily influenced by the high elevation and rain shadow effects of the mountain range. The North Cascades is a section of the Cascade Range from the South Fork of the Snoqualmie River in Washington, United States, to the confluence of the Thompson and Fraser Rivers in British Columbia, Canada, where the range is officially called the Cascade Mountains but is usually referred to as the Canadian Cascades. The North Cascades Ecoregion is a Level III ecoregion in the Commission for Environmental Cooperation's classification system.

The flora and fauna of Mount Kenya are diverse, due to the variation in altitude, rainfall, aspect and temperature. The mountain slopes can be divided into vegetation zones, with each zone having different dominant plant species. Although many plants on Mount Kenya have local names, here they are reported only with their English and scientific names.

Ilex mitis is a tall, dense, evergreen tree that is indigenous to Sub-Saharan Africa and Madagascar. It makes an excellent fast-growing hedge for gardens - growing tall, straight and dense.

Montane ecosystems are found on the slopes of mountains. The alpine climate in these regions strongly affects the ecosystem because temperatures fall as elevation increases, causing the ecosystem to stratify. This stratification is a crucial factor in shaping plant community, biodiversity, metabolic processes and ecosystem dynamics for montane ecosystems. Dense montane forests are common at moderate elevations, due to moderate temperatures and high rainfall. At higher elevations, the climate is harsher, with lower temperatures and higher winds, preventing the growth of trees and causing the plant community to transition to montane grasslands and shrublands or alpine tundra. Due to the unique climate conditions of montane ecosystems, they contain increased numbers of endemic species. Montane ecosystems also exhibit variation in ecosystem services, which include carbon storage and water supply.
The ecology of the Himalayas varies with climate, rainfall, altitude, and soils. The climate ranges from tropical at the base of the mountains to permanent ice and snow at the highest elevations. The amount of yearly rainfall increases from west to east along the southern front of the range. This diversity of climate, altitude, rainfall and soil conditions supports a variety of distinct plant and animal species, such as the Nepal gray langur

Pterophylla fraxinea, formerly known as Weinmannia fraxinea, is a tree in the family Cunoniaceae. It grows up to 40 metres (130 ft) tall. The bark is grey to dark brown. Inflorescences bear up to three pairs of flowers. The specific epithet fraxinea is from the Latin meaning "ash tree", referring to the leaves' resemblance to those of the genus Fraxinus.

The flora of the U.S. Sierra Nevada alpine zone is characterized by small, low growing, cushion and mat forming plants that can survive the harsh conditions in the high-altitude alpine zone above the timber line. These flora often occur in alpine fell-fields. The Sierra Nevada alpine zone lacks a dominant plant species that characterizes it, so may or may not be called a vegetation type. But it is found above the subalpine forest, which is the highest in a succession of recognized vegetation types at increasing elevations.

Rhododendron rugosum is a species of rhododendron native to Borneo. It is found in the high mountains, including Mount Kinabalu, in Sabah state of northeastern Borneo.
Nothofagus brassii is a species of tree in the family Nothofagaceae. It is endemic to New Guinea. It is commonly known as Sagé, sagé hitam, sahé, and kayu sagé, kayu sagé hitam (Indonesian).
Nothofagus starkenborghiorum is a species of tree in the family Nothofagaceae. It is native to New Guinea and New Britain. It grows in montane rain forests, and occasionally in lowland rain forests.
















