
Podocnemididae is a family of pleurodire (side-necked) turtles, once widely distributed. Most of its 41 genera and 57 species are now extinct. Seven of its eight surviving species are native to South America: the genus Peltocephalus, with two species, only one of which is extant ; and the genus Podocnemis, with six living species of South American side-necked river turtles and four extinct. There is also one genus native to Madagascar: Erymnochelys, the Madagascan big-headed turtle, whose single species E. madagascariensis.

The Arrau turtle, also known as the South American river turtle, giant South American turtle, giant Amazon River turtle, Arrau sideneck turtle, Amazon River turtle or simply the Arrau, is the largest of the side-neck turtles (Pleurodira) and the largest freshwater turtle in Latin America. The species primarily feeds on plant material and typically nests in large groups on beaches. Due to hunting of adults, collecting of their eggs, pollution, habitat loss, and dams, the Arrau turtle is seriously threatened.

Podocnemis is a genus of aquatic turtles, commonly known as South American river turtles, in the family Podocnemididae. The genus consists of six extant species occurring in tropical South America. Four additional species are known only from fossils. These turtles have pig-like noses but are not closely related to the pig-nosed turtle.

The yellow-spotted Amazon river turtle, also known commonly as the yellow-headed sideneck turtle and the yellow-spotted river turtle, and locally as the taricaya, is one of the largest South American river turtles.

Peter Charles Howard Pritchard was a leading turtle zoologist. Pritchard was educated at Oxford University and the University of Florida, where he received a Ph.D. and specialized in Zoology. He was most commonly known for his career of almost 40 years for the conservation of turtles.

Stupendemys is an extinct genus of freshwater side-necked turtle, belonging to the family Podocnemididae. It is the largest freshwater turtle known to have existed, with a carapace over 2 meters long. Its fossils have been found in northern South America, in rocks dating from the Middle Miocene to the very start of the Pliocene, about 13 to 5 million years ago. Male specimens are known to have possessed bony horns growing from the front edges of the shell and the discovery of the fossil of a young adult shows that the carapace of these turtles flattens with age. A fossil skull described in 2021 indicates that Stupendemys was a generalist feeder.
La Venta is a fossil locality located in the modern departments of Tolima and Huila in Colombia. This site is one of the richest Neogene fossil assemblages in South America and represents the best-known Cenozoic fossil site outside of Argentina. It provides a glimpse of what life in the region was like before the main wave of the Great American Interchange.

The red-headed Amazon side-necked turtle, red-headed river turtle or red-headed sideneck is a species of turtle in the family Podocnemididae. It is found in the Amazon basin in Brazil, Colombia, and Venezuela. The red-headed river turtle is considered a small turtle with a size of less than 32 cm, making it easily distinguishable from other species in the area. Identifying factors of this turtle include colors ranging from dark brown to black, barbels under the chin, and a bright red strip that goes from behind its head to the tympanum.

The Magdalena River turtle or Rio Magdalena river turtle is a species of turtle in the family Podocnemididae, which diverged from other turtles in the Cretaceous Period, 100 million years ago. It is endemic to northern Colombia, where its home range consists of the Sinú, San Jorge, Cauca, and Magdalena river basins.

The six-tubercled Amazon River turtle or six-tubercled river turtle is a species of turtle in the family Podocnemididae.

Granastrapotherium is an extinct genus of ungulate mammals, described from remains found in rocks of the Honda Group in the Tatacoa Desert, in the Colombian departments of Huila and Tolima, at the Miocene fossil site La Venta. The only species formally recognized is Granastrapotherium snorki. Remains found in Bolivia and Peru, seem to belong to Granastrapotherium or a very similar animal.

Xenastrapotherium is an extinct genus of astrapothere, a type of hoofed herbivorous mammal, native to South America, which lived in the Middle to Late Miocene period, typically during the Laventan stage. It is a member of the family Astrapotheriidae in the subfamily Uruguaytheriinae, large astrapotheres, equipped with a trunk-like nose and protruding teeth, similar to the elephants, but their tusks were the canine teeth, not the incisors. Xenastrapotherium was a genus widely distributed in northern South America, in contrast to other species of astrapotheres which lived in the area of the Southern Cone of the continent. It differed from other astrapotheres by having two lower incisors on each side of the jaw and the tusks have a pronounced longitudinal curvature, although their general shape and size are probably very similar to Astrapotherium, whose weight would be 900 to 1,500 kilograms, comparable to the current black rhinoceros.

The savanna side-necked turtle, also commonly known as the Llanos side-necked turtle, is a species of turtle in the family Podocnemididae. The species is endemic to South America.
Patasola is an extinct genus of New World monkeys from the Middle Miocene. Its remains have been found at the Konzentrat-Lagerstätte of La Venta in the Honda Group of Colombia. The type species is Patasola magdalenae.

Miocochilius is an extinct genus of small notoungulate mammals (typotheres) native to South America. The genus lived during the Middle Miocene epoch. The genus contains two described species, the type species M. anomopodus described in 1953 by Ruben Arthur Stirton and M. federicoi, described and included in the genus by Darin A. Croft.
Canaanimico is an extinct genus of medium-sized New World monkeys from the Late Oligocene fossiliferous fluvio-lacustrine Chambira Formation of the Ucayali Basin in Amazonian Peru. The genus was described by Marivaux et al. in 2016 and the type species is C. amazonensis.
Bairdemys is an extinct genus of side-necked turtles in the family Podocnemididae. The genus existed from the Late Oligocene to Late Miocene and its fossils have been found in South Carolina, Puerto Rico, Panama and Venezuela. The genus was described in 2002 by Gaffney & Wood and the type species is B. hartsteini.
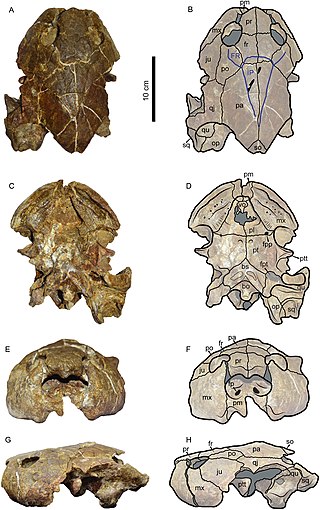
Caninemys is an extinct genus of large freshwater side-necked turtle, belonging to the family Podocnemididae. Its fossils have been found in Brazil and Colombia, in rocks dating back from the middle to late Miocene.
Pericotoxodon is an extinct genus of toxodontid notoungulate, from the Miocene period. Fossils of Pericotoxodon were found near Río Inuya and Mapuya in Peru, and in La Venta, Colombia and Bolivia, in deposits dated to the Middle Miocene.

Magdalenabradys is an extinct genus of mylodontid ground sloths that lived during the Middle Miocene and Early Pliocene of what is now Colombia and Venezuela. Fossils have been found in the Villavieja Formation of the Honda Group in Colombia, and the Codore and Urumaco Formations of Venezuela.














