
Threatened species are any species which are vulnerable to extinction in the near future. Species that are threatened are sometimes characterised by the population dynamics measure of critical depensation, a mathematical measure of biomass related to population growth rate. This quantitative metric is one method of evaluating the degree of endangerment without direct reference to human activity.

The Endangered Species Act of 1973 is the primary law in the United States for protecting and conserving imperiled species. Designed to protect critically imperiled species from extinction as a "consequence of economic growth and development untempered by adequate concern and conservation", the ESA was signed into law by President Richard Nixon on December 28, 1973. The Supreme Court of the United States described it as "the most comprehensive legislation for the preservation of endangered species enacted by any nation". The purposes of the ESA are two-fold: to prevent extinction and to recover species to the point where the law's protections are not needed. It therefore "protect[s] species and the ecosystems upon which they depend" through different mechanisms. For example, section 4 requires the agencies overseeing the Act to designate imperiled species as threatened or endangered. Section 9 prohibits unlawful ‘take,’ of such species, which means to "harass, harm, hunt..." Section 7 directs federal agencies to use their authorities to help conserve listed species. The Act also serves as the enacting legislation to carry out the provisions outlined in The Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES). The Supreme Court found that "the plain intent of Congress in enacting" the ESA "was to halt and reverse the trend toward species extinction, whatever the cost." The Act is administered by two federal agencies, the United States Fish and Wildlife Service (FWS) and the National Marine Fisheries Service (NMFS). FWS and NMFS have been delegated by the Act with the authority to promulgate any rules and guidelines within the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) to implement its provisions.

The Blanding's turtle is a semi-aquatic turtle of the family Emydidae. This species is native to central and eastern parts of Canada and the United States. It is considered to be an endangered species throughout much of its range. The Blanding's turtle is of interest in longevity research, as it shows few or no common signs of aging and is physically active and capable of reproduction into eight or nine decades of life.

Driftless Area National Wildlife Refuge is a United States National Wildlife Refuge in northeastern Iowa, southwestern Wisconsin and northwestern Illinois. It is a collection of non-contiguous parcels in the vicinity of the Upper Mississippi River National Wildlife and Fish Refuge.

Calla is a genus of flowering plant in the family Araceae, containing the single species Calla palustris.

Wolf Lake is an 804-acre (325.4 ha) lake that straddles the Indiana and Illinois state line near Lake Michigan. It is smaller than it was prior to settlement by European colonizers because of infilling for development around the edges. Despite years of environmental damage caused by heavy industries, transportation infrastructure, urban runoff and filling of wetlands, it is one of the most important biological sites in the Chicago region.

An IUCN Red List Critically Endangered species is one that has been categorized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature as facing an extremely high risk of extinction in the wild. As of December 2023, of the 157,190 species currently on the IUCN Red List, 9,760 of those are listed as Critically Endangered, with 1,302 being possibly extinct and 67 possibly extinct in the wild.

Allium cernuum, known as nodding onion or lady's leek, is a perennial plant in the genus Allium. It grows in open areas in North America.

Heteranthera limosa is an annual flowering plant in the water hyacinth family known by the common names ducksalad and blue mudplantain. It grows in shallow water or on mud. It is considered a threatened species in parts of the central United States, and an invasive species weed in California, where it is a nuisance in rice paddies. It is also occasional in Florida waterways.
William W. Powers State Recreation Area is an Illinois state park administered by the Illinois Department of Natural Resources on 580 acres (230 ha) in the Hegewisch community area of the City of Chicago in Cook County, Illinois, United States. The area includes 419 acres (170 ha) of water in Wolf Lake that provides about 6 miles (10 km) of shoreline to fishermen. The park hosts about half a million visitors annually. The park contains numerous species, and is one of the most important biological sites in the Chicago region.

Carex jamesii, known as James's sedge or grass sedge, is a species of sedge native to North America from Minnesota east to New York and south to Oklahoma and South Carolina. It occurs in mesic hardwood forests and produces fruits from early May to mid July. It has two to four perigynia that are subtended by leaf-like pistillate scales. Its seeds are dispersed by ants.

Cypripedium candidum, known as the small white lady's slipper or white lady's slipper, is a rare orchid of the genus Cypripedium. It is native to eastern North America across the northern United States and southern Canada.

Hammarbya paludosa is a small orchid commonly known as bog orchid, bog adder's-mouth or bog adder's-mouth orchid. It grows in bogs in temperate and subarctic regions of the Northern Hemisphere.

Polanisia dodecandra is a species of flowering plant in the Cleomaceae family, known by the common name redwhisker clammyweed or clammyweed, and there are three subspecies of Polanisia. Usually annual, occasionally perennial, Polanisia is native to North America, and is found throughout much of Canada and the United States. It favors full sun, mesic to dry conditions, and barren, sandy or gravelly soils, even highly disturbed areas where there is little other ground vegetation. It looks similar to a close relative, the spider flower (Cleome).

Polanisia is a genus of flowering plants in the family Cleomaceae. Members of the genus are commonly known as clammyweeds. Polanisia jamesii is listed as locally endangered in Minnesota, while P. dodecandra is widespread through much of North America.
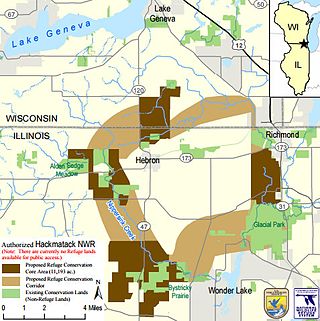
The Hackmatack National Wildlife Refuge is a newly established United States national wildlife refuge that will include noncontiguous properties, especially tallgrass prairie patches, wetland properties, and oak savanna parcels, located in the northwestern region of the Chicago metropolitan area and the southern part of the Milwaukee area. The refuge's boundaries encompass parts of McHenry County, Illinois, and Walworth County, Wisconsin. The refuge will be operated by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service, known as USFWS. 85 percent of the refuge will be in Illinois, and 15 percent in Wisconsin.

Astragalus neglectus, or Cooper's milkvetch, is a species of flowering plant in the family Fabaceae native to northeastern North America.

Over 22,500 species of wildlife have been recorded in North Macedonia. Over 10,000 of these are insects, which include 3,000 beetle species and large numbers of Lepidoptera, flies, and Hymenoptera. Aside from insects, other large arthropod groups include Chelicerata and crustaceans. Among vertebrates, more than 300 species of birds recorded, although not all nest in the country. There are over 80 species of both fish and mammals, 32 reptiles, and 14 amphibians.

Chionophila tweedyi, or Tweedy's snowlover, is a perennial herb in the plantain family. It is native to Idaho and Montana in the western United States.

Asclepias stenophylla is a species of flowering plant in the dogbane family (Apocynaceae) commonly called slimleaf milkweed and narrow-leaved green milkweed.



















