| Polygonum fowleri | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Order: | Caryophyllales |
| Family: | Polygonaceae |
| Genus: | Polygonum |
| Species: | P. fowleri |
| Binomial name | |
| Polygonum fowleri | |
| Synonyms [1] | |
| |
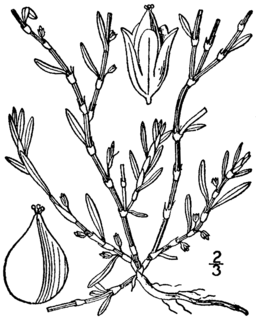
Polygonum fowleri, commmonly called Fowler's knotweed or Hudsonian knotweed, is a plant species native to the seashores of the northern part of North America. It has been reported from every Canadian province and territory except Alberta and Saskatchewan, as well as from Maine, Alaska, Washington, Oregon, California, and St. Pierre & Miquelon. It is usually found in gravelly locations along the seacoast. [2] [3]

The provinces and territories of Canada are sub-national governments within the geographical areas of Canada under the authority of the Canadian Constitution. In the 1867 Canadian Confederation, three provinces of British North America—New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and the Province of Canada —were united to form a federated colony, becoming a sovereign nation in the next century. Over its history, Canada's international borders have changed several times, and the country has grown from the original four provinces to the current ten provinces and three territories. Together, the provinces and territories make up the world's second-largest country by area.

Alberta is a western province of Canada. With an estimated population of 4,067,175 as of 2016 census, it is Canada's fourth most populous province and the most populous of Canada's three prairie provinces. Its area is about 660,000 square kilometres (250,000 sq mi). Alberta and its neighbour Saskatchewan were districts of the Northwest Territories until they were established as provinces on September 1, 1905. The premier is Jason Kenney as of April 30, 2019.

Saskatchewan is a prairie and boreal province in western Canada, the only province without a natural border. It has an area of 651,900 square kilometres (251,700 sq mi), nearly 10 percent of which is fresh water, composed mostly of rivers, reservoirs, and the province's 100,000 lakes.
Polygonum fowleri is a prostrate to ascending herb, often with zigzagged stems. Inflorescences are in the axils of the leaves, each with up to 10 white or pink flowers. [2] [4]
- Subspecies
Two subspecies are recognized, treated by some botanists as distinct species: [2]
- Polygonum fowleri subsp. fowleri – shores of Atlantic, Pacific, and Arctic Oceans
- Polygonum fowleri subsp. hudsonianum(S. J. Wolf & McNeill) Costea & Tardif (= P. hudsonianum(S. J. Wolf & McNeill) H. R. Hinds) – shores of Hudson Bay, the Canadian Arctic Islands, and the Atlantic coast of Labrador, Newfoundland, and Nova Scotia

The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south and is bounded by Asia and Australia in the west and the Americas in the east.

The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, although some oceanographers call it the Arctic Mediterranean Sea or simply the Arctic Sea, classifying it a mediterranean sea or an estuary of the Atlantic Ocean. It is also seen as the northernmost part of the all-encompassing World Ocean.
Hudson Bay is a large body of saltwater in northeastern Canada with a surface area of 1,230,000 km2 (470,000 sq mi). It drains a very large area, about 3,861,400 km2 (1,490,900 sq mi), that includes parts of southeastern Nunavut, Saskatchewan, most of Manitoba, Ontario, Quebec and indirectly through smaller passages of water to parts of North Dakota, South Dakota, Minnesota, and Montana. Hudson Bay's southern arm is called James Bay.