
Nesohedyotis is a genus of flowering plants endemic to the island of Saint Helena in the South Atlantic Ocean. It in the family Rubiaceae.

Oculina is a genus of colonial stony coral in the family Oculinidae. These corals are mostly found in the Caribbean Sea, the Gulf of Mexico and Bermuda but some species occur in the eastern Pacific Ocean. They occur at depths down to 1000 metres.

Favia is a genus of reef-building stony corals in the family Mussidae. Members of the genus are massive or thickly encrusting colonial corals, either dome-shaped or flat, and a few are foliaceous. There is a great diversity of form even among individuals of the same species. The corallites project slightly above the surface of the coral and each has its own wall. In most species, the corallites are plocoid and in some, monocentric. The septa and costae linked to the corallite wall are well developed and covered by fine teeth. The polyps only extend and feed during the night. Each one has a small number of tapering tentacles which often have a darker coloured tip; these are called stinger tentacles, or sweeper tentacles. They use these to sweep the water to see if any other coral is in its area; if so, then they begin to sting the other coral. This is commonly known as coral war. Each coral is trying to make sure it has enough room around it so it can continue to grow and have more surface area for its offspring. The columella is parietal and spongy, and there are vesicles on both the endotheca and exotheca. Members of this genus are widespread in both the Atlantic Ocean and the Indo-Pacific.

Balanophyllia is a genus of solitary corals in the order of stony corals.

Polycyathus is a genus of small corals in the order Scleractinia, the stony corals. Most species occur in the Pacific Ocean.

Caryophyllia is a genus of solitary corals in the family Caryophylliidae. Members of this genus are azooxanthellate and are found in the North Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea at depths down to 2,670 metres (8,760 ft).
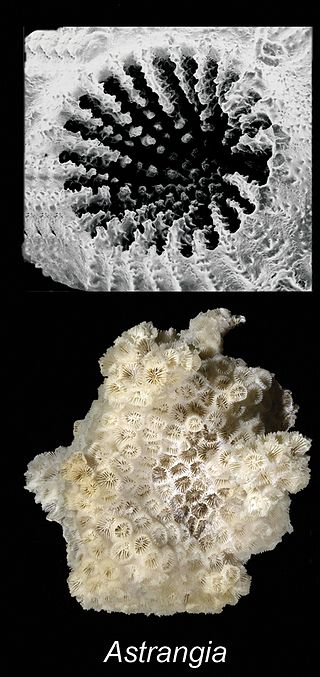
Astrangia is a genus of stony corals in the family Rhizangiidae. Members of this genus are non-reef building corals and are found in the Atlantic and Indo-Pacific Oceans. They are solitary corals with large polyps and are found in clumps. They reproduce from stolons. The corallites are small with simple toothed septa.

Turbinaria is a genus of colonial stony corals in the family Dendrophylliidae. Common names for this genus include disc coral, scroll coral, cup coral, vase coral, pagoda coral and ruffled ridge coral. These corals are native to the Red Sea, Indian Ocean, Japan and the south Central Pacific Ocean.

Dactylotrochus is a genus of large polyp stony corals from the Red Sea and western Pacific Ocean. It is monotypic with a single species, Dactylotrochus cervicornis. It inhabits the deep sea and is believed to be azooxanthellate.
Callogorgia is a genus of deep sea corals that are ideally suited to be habitats for different organisms. They reproduce both sexually and asexually, clinging to the hard substrate of the ocean during their maturation process. Callogorgia are found at depths ranging from 750-8200 feet in the Gulf of Mexico, Pacific Ocean and the Caribbean Sea. An array of organisms have relationships with Callogorgia, including brittle stars, cat sharks, and copepods. The nature of these relationships are often commensal, with Callogorgia providing a habitat for the organisms.
Callogorgia elegans is a species of soft corals in the family Primnoidae. It is found in the north-western Pacific Ocean. Like other coral species, C. elegans is bottom-dwelling and sessile, or immobile.
Janaria is a genus of commensal athecate hydroids in the family Hydractiniidae. It is a monotypic genus and the only species is Janaria mirabilis, commonly known as staghorn hydrocoral. It is a colonial species and lives on a shell occupied by a hermit crab. It is native to the tropical and semitropical eastern Pacific Ocean.

Heterocyathus is a genus of coral of the family Caryophylliidae.

Narella is a genus of deep-sea soft corals in the family Primnoidae (Milne Edwards, 1857). They are sessile, bottom-dwelling organisms that can be found in all ocean basins, having cosmopolitan distribution. They have a branching appearance.
Paracalyptrophora is a genus of corals belonging to the family Primnoidae.

Endopachys is a genus of corals belonging to the family Dendrophylliidae.

Distichopora is a genus of hydrozoans belonging to the family Stylasteridae.

Letepsammia is a genus of corals belonging to the family Micrabaciidae.

Parastenella is a genus of cnidarians belonging to the family Primnoidae.

Trochocyathus is a genus of corals in the family Caryophylliidae. Living species are found in waters near Hawai'i at depths of 64 to 1,020 meters. Fossil species are found as far back as the latest Paleocene in the Dilwyn Formation of Australia, in the late Cretaceous in the Woodbury Formation of New Jersey, and in Suffolk.

















