Related Research Articles

Mycology is the branch of biology concerned with the study of fungi, including their genetic and biochemical properties, their taxonomy and their use to humans, including as a source for tinder, traditional medicine, food, and entheogens, as well as their dangers, such as toxicity or infection.

The Russulales are an order of the Agaricomycetes,. According to the Dictionary of the Fungi, the order consists of 12 families, 80 genera, and 1767 species. According to Species Fungorum, the order contains 13 families, 117 genera, and 3,060 species.

Ostreola is a genus of fungi in the family Mytilinidiaceae. This is a monotypic genus, containing the single species Ostreola consociata.

The Eurotiomycetes are a class of ascomycetes within the subphylum Pezizomycotina.

Craterellus is a genus of generally edible fungi similar to the closely related chanterelles, with some new species recently moved from the latter to the former. Both groups lack true gills on the underside of their caps, though they often have gill-like wrinkles and ridges.

The Hypocreales are an order of fungi within the class Sordariomycetes. In 2008, it was estimated that it contained some 237 genera, and 2647 species in seven families. Since then, a considerable number of further taxa have been identified, including an additional family, the Stachybotryaceae. According to the Catalog of Life, As of April 2021 the Hypocreales contains 6 families, 137 genera, and 1411 species.
Index Fungorum is an international project to index all formal names in the fungus kingdom. As of 2015 the project is based at the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, one of three partners along with Landcare Research and the Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences.

The Dermateaceae is a family of cup fungi in the order Helotiales. Most species in this family are plant pathogens but some are saprobes.

The Venturiaceae are a family of fungi in the order Pleosporales. Several of the species in this family are plant pathogens.

The Phanerochaetaceae are a family of mostly crust fungi in the order Polyporales.
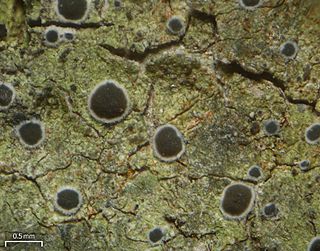
The Pilocarpaceae are a family of crustose lichens in the order Lecanorales. The species of this family have a cosmopolitan distribution and have been found in a variety of climatic regions. Pilocarpaceae was circumscribed by Alexander Zahlbruckner in Adolf Engler's influential 1905 work Die Natürlichen Pflanzenfamilien.

The Stereocaulaceae are a family of lichen-forming fungi in the order Lecanorales. It contains five genera. Species of this family are widely distributed in temperate boreal and austral regions.

Podosphaera is a genus of fungi in the family Erysiphaceae. Species in this genus are plant pathogens, causing powdery mildew.
Allophylaria is a genus of fungi in the family Helotiaceae. As of February 2015, the nomenclatural database Index Fungorum lists 14 species in the genus.

The Umbilicariales are an order of lichenized fungi in the subclass Umbilicariomycetidae, class Lecanoromycetes. It contains five families: Elixiaceae, Fuscideaceae, Ophioparmaceae, Ropalosporaceae, and Umbilicariaceae. Umbilicariales was proposed as a new order in 2007, while the subclass Umbilicariomycetidae was proposed in 2013.

Hypocenomyce is a genus of lichen-forming fungi in the family Ophioparmaceae. Species in the genus grow on bark and on wood, especially on burned tree stumps and trunks in coniferous forest. Hypocenomyce lichens are widely distributed in the northern hemisphere.
The Chaetomiaceae are a family of fungi in the Ascomycota, order Sordariales, class Sordariomycetes. Chaetomiaceae are usually saprobic or parasitic. Cheatomiaceae are a great source of enzymes with diverse biotechnological and industrial applications such as PMO, L-methioninase, β-1,3-glucanase, laccase, dextranase, lipolytic, pectinolytic, amylolytic, chitinolytic, and proteolytic enzymes. The production of such compounds can be taken into account as candidates for the development of effective and novel lead compounds for medicine, biological control and production of bioactive secondary metabolites. Chaetomiaceae furthermore contains some of the most well known thermophilic fungi, an interesting feature carrying many biological applications, but that is found only in few fungal genera.

The Trypetheliales are an order of fungi in the class Dothideomycetes. Most of the species in the order form lichens, although some are lichenicolous fungi. Trypetheliales contains two families, Polycoccaceae and Trypetheliaceae. The order was circumscribed in 2008 by lichenologists Robert Lücking, André Aptroot, and Harrie Sipman.

Haematomma is a genus of crustose lichens established by Abramo Bartolommeo Massalongo in 1852. It is the sole genus in the Haematommataceae, a family circumscribed by Josef Hafellner in 1984. Commonly called bloodstain lichens, the species assigned to this genus are widely distributed in tropical and temperate areas.
References
- ↑ "Synonymy: Porosphaerella E. Müll. & Samuels". Species Fungorum. CAB International. Retrieved 2016-04-13.
- ↑ "Porosphaerella". www.gbif.org. Retrieved 7 August 2022.
- ↑ Lumbsch TH, Huhndorf SM (December 2007). "Outline of Ascomycota – 2007". Myconet. Chicago, USA: The Field Museum, Department of Botany. 13: 1–58.