The coccyx, commonly referred to as the tailbone, is the final segment of the vertebral column in all apes, and analogous structures in certain other mammals such as horses. In tailless primates since Nacholapithecus, the coccyx is the remnant of a vestigial tail. In animals with bony tails, it is known as tailhead or dock, in bird anatomy as tailfan. It comprises three to five separate or fused coccygeal vertebrae below the sacrum, attached to the sacrum by a fibrocartilaginous joint, the sacrococcygeal symphysis, which permits limited movement between the sacrum and the coccyx.

The sacrum, in human anatomy, is a large, triangular bone at the base of the spine that forms by the fusing of the sacral vertebrae (S1–S5) between ages 18 and 30.

The sacroiliac joint or SI joint (SIJ) is the joint between the sacrum and the ilium bones of the pelvis, which are connected by strong ligaments. In humans, the sacrum supports the spine and is supported in turn by an ilium on each side. The joint is strong, supporting the entire weight of the upper body. It is a synovial plane joint with irregular elevations and depressions that produce interlocking of the two bones. The human body has two sacroiliac joints, one on the left and one on the right, that often match each other but are highly variable from person to person.

The dimples of Venus are sagittally symmetrical indentations sometimes visible on the human lower back, just superior to the gluteal cleft. They are directly superficial to the two sacroiliac joints, the sites where the sacrum attaches to the ilium of the pelvis. An imaginary line joining both dimples of Venus passes over the spinous process of the second sacral vertebra.

The ischium forms the lower and back region of the hip bone.

In vertebrates, the pubis or pubic bone forms the lower and anterior part of each side of the hip bone. The pubis is the most forward-facing of the three bones that make up the hip bone. The left and right pubic bones are each made up of three sections; a superior ramus, an inferior ramus, and a body.
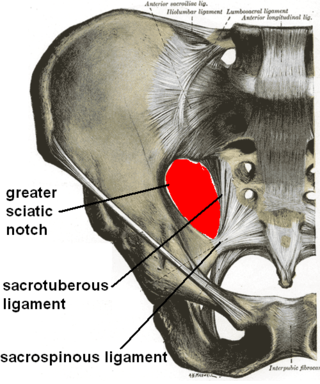
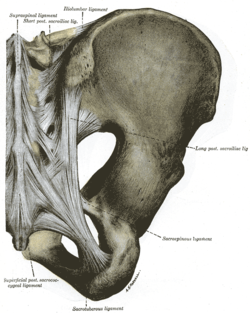
The sacrotuberous ligament is situated at the lower and back part of the pelvis. It is flat, and triangular in form; narrower in the middle than at the ends.
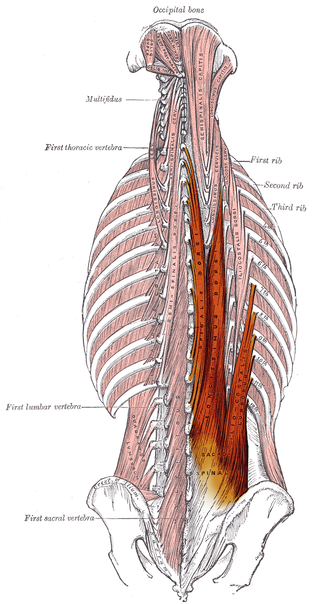
The erector spinae or spinal erectors is a set of muscles that straighten and rotate the back. The spinal erectors work together with the glutes to maintain stable posture standing or sitting.

The wing(ala)of ilium is the large expanded portion of the ilium, the bone which bounds the greater pelvis laterally. It presents for examination two surfaces—an external and an internal—a crest, and two borders—an anterior and a posterior.

The crest of the ilium is the superior border of the wing of ilium and the superiolateral margin of the greater pelvis.

The iliolumbar ligament is a strong ligament which attaches medially to the transverse process of the 5th lumbar vertebra, and laterally to back of the inner lip of the iliac crest.

The anterior sacroiliac ligament consists of numerous thin bands, which connect the anterior surface of the lateral part of the sacrum to the margin of the auricular surface of the ilium and to the preauricular sulcus.
The interosseous sacroiliac ligament, also known as the axial interosseous ligament, is a ligament of the sacroiliac joint that lies deep to the posterior ligament. It connects the tuberosities of the sacrum and the ilium of the pelvis.

The posterior sacrococcygeal ligament or dorsal sacrococcygeal ligament is a ligament which stretches from the sacrum to the coccyx and thus dorsally across the sacrococcygeal symphysis shared by these two bones.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:

The hip bone is a large flat bone, constricted in the center and expanded above and below. In some vertebrates it is composed of three parts: the ilium, ischium, and the pubis.

The term sacroiliac joint dysfunction refers to abnormal motion in the sacroiliac joint, either too much motion or too little motion, that causes pain in this region.

The pelvis is the lower part of an anatomical trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs, together with its embedded skeleton.

The gluteal lines are three curved lines outlined from three bony ridges on the exterior surface of the ilium in the gluteal region. They are the anterior gluteal line; the inferior gluteal line, and the posterior gluteal line.

Each vertebra is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, that make up the vertebral column or spine, of vertebrates. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spinal segment and the particular species.