Related Research Articles

An intervertebral disc lies between adjacent vertebrae in the vertebral column. Each disc forms a fibrocartilaginous joint, to allow slight movement of the vertebrae, to act as a ligament to hold the vertebrae together, and to function as a shock absorber for the spine.

The sacrum, in human anatomy, is a large, triangular bone at the base of the spine that forms by the fusing of sacral vertebrae S1–S5 between 18 and 30 years of age.

A spinal nerve is a mixed nerve, which carries motor, sensory, and autonomic signals between the spinal cord and the body. In the human body there are 31 pairs of spinal nerves, one on each side of the vertebral column. These are grouped into the corresponding cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral and coccygeal regions of the spine. There are eight pairs of cervical nerves, twelve pairs of thoracic nerves, five pairs of lumbar nerves, five pairs of sacral nerves, and one pair of coccygeal nerves. The spinal nerves are part of the peripheral nervous system.

The lumbar vertebrae are, in human anatomy, the five vertebrae between the rib cage and the pelvis. They are the largest segments of the vertebral column and are characterized by the absence of the foramen transversarium within the transverse process and by the absence of facets on the sides of the body. They are designated L1 to L5, starting at the top. The lumbar vertebrae help support the weight of the body, and permit movement.

Kyphosis is an abnormally excessive convex curvature of the spine as it occurs in the thoracic and sacral regions. Abnormal inward concave lordotic curving of the cervical and lumbar regions of the spine is called lordosis. It can result from degenerative disc disease; developmental abnormalities, most commonly Scheuermann's disease; osteoporosis with compression fractures of the vertebra; multiple myeloma; or trauma. A normal thoracic spine extends from the 1st to the 12th vertebra and should have a slight kyphotic angle, ranging from 20° to 45°. When the "roundness" of the upper spine increases past 45° it is called kyphosis or "hyperkyphosis". Scheuermann's kyphosis is the most classic form of hyperkyphosis and is the result of wedged vertebrae that develop during adolescence. The cause is not currently known and the condition appears to be multifactorial and is seen more frequently in males than females.

Schmorl's nodes are protrusions of the nucleus pulposus of the intervertebral disc through the vertebral body endplate and into the adjacent vertebra.

Back injuries result from damage, wear, or trauma to the bones, muscles, or other tissues of the back. Common back injuries include sprains and strains, herniated discs, and fractured vertebrae. The lumbar spine is often the site of back pain. The area is susceptible because of its flexibility and the amount of body weight it regularly bears. It is estimated that low-back pain may affect as much as 80 to 90 percent of the general population in the United States.
Neuromeres are morphologically or molecularly defined transient segments of the early developing brain. Rhombomeres are such segments that make up the rhombencephalon or hindbrain. More controversially, some argue that there exist early developmental segments that give rise to structures of the midbrain (mesomeres) and forebrain (prosomeres).

Spondylolisthesis is the displacement of one spinal vertebra compared to another. While some medical dictionaries define spondylolisthesis specifically as the forward or anterior displacement of a vertebra over the vertebra inferior to it, it is often defined in medical textbooks as displacement in any direction. Spondylolisthesis is graded based upon the degree of slippage of one vertebral body relative to the subsequent adjacent vertebral body. Spondylolisthesis is classified as one of the six major etiologies: degenerative, traumatic, dysplastic, isthmic, pathologic, or post-surgical, which are discussed in further detail below. Spondylolisthesis most commonly occurs in the lumbar spine, primarily at the L5-S1 level with the L5 vertebral body anteriorly translating over the S1 vertebral body.
Congenital vertebral anomalies are a collection of malformations of the spine. Most, around 85%, are not clinically significant, but they can cause compression of the spinal cord by deforming the vertebral canal or causing instability. This condition occurs in the womb. Congenital vertebral anomalies include alterations of the shape and number of vertebrae.

Bertolotti's syndrome is a commonly missed cause of back pain which occurs due to lumbosacral transitional vertebrae (LSTV). It is a congenital condition but is not usually symptomatic until one's later twenties or early thirties. However, there are a few cases of Bertolotti's that become symptomatic at a much earlier age.

Spinal disc herniation is an injury to the cushioning and connective tissue between vertebrae, usually caused by excessive strain or trauma to the spine. It may result in back pain, pain or sensation in different parts of the body, and physical disability. The most conclusive diagnostic tool for disc herniation is MRI, and treatment may range from painkillers to surgery. Protection from disc herniation is best provided by core strength and an awareness of body mechanics including posture.

Radiculopathy, also commonly referred to as pinched nerve, refers to a set of conditions in which one or more nerves are affected and do not work properly. This can result in pain, weakness, numbness, or difficulty controlling specific muscles.
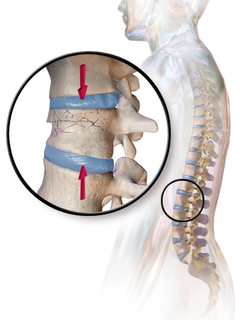
A compression fracture is a collapse of a vertebra. It may be due to trauma or due to a weakening of the vertebra. This weakening is seen in patients with osteoporosis or osteogenesis imperfecta, lytic lesions from metastatic or primary tumors, or infection. In healthy patients, it is most often seen in individuals suffering extreme vertical shocks, such as ejecting from an ejection seat. Seen in lateral views in plain x-ray films, compression fractures of the spine characteristically appear as wedge deformities, with greater loss of height anteriorly than posteriorly and intact pedicles in the anteroposterior view.
The lumbar fascia is an anatomic structure of the lumbar region. It consists of a band or sheet of connective tissue fibres, primarily collagen, that attaches, stabilizes, encloses and separates muscles not limited to the lumbar region as the name suggests, but extending upwards over the thorax to the neck and downwards over the muscles covering the sacrum. The upper thoracic portion is thin while the lumbar and sacral regions are thicker and stronger.

Facet syndrome is a syndrome in which the facet joints cause painful symptoms. In conjunction with degenerative disc disease, a distinct but functionally related condition, facet arthropathy is believed to be one of the most common causes of lower back pain.

Sacroiliac joint dysfunction generally refers to pain in the sacroiliac joint region that is caused by abnormal motion in the sacroiliac joint, either too much motion or too little motion. It typically results in inflammation of the sacroiliac joint, and can be debilitating.

The pelvis is either the lower part of the trunk of the human body between the abdomen and the thighs or the skeleton embedded in it.

The vertebral column, also known as the backbone or spine, is part of the axial skeleton. The vertebral column is the defining characteristic of a vertebrate in which the notochord found in all chordates has been replaced by a segmented series of bone: vertebrae separated by intervertebral discs. The vertebral column houses the spinal canal, a cavity that encloses and protects the spinal cord.

In the vertebrate spinal column, each vertebra is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, the proportions of which vary according to the segment of the backbone and the species of vertebrate.
References
- ↑ Lin YH, Chen CS, Cheng CK, Chen YH, Lee CL, Chen WJ (November 2001). "Geometric parameters of the in vivo tissues at the lumbosacral joint of young Asian adults". Spine. 26 (21): 2362–7. doi:10.1097/00007632-200111010-00013. PMID 11679822.
- ↑ Lu X, Hou C, Yuan W, Zhang Z, Chen A (June 2009). "Complete traumatic anterior dislocation of the lumbosacral joint: a case report". Spine. 34 (14): E488–92. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181a8cdad. PMID 19525828.
| This human musculoskeletal system article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |