
In vertebrate anatomy, ribs are the long curved bones which form the rib cage, part of the axial skeleton. In most tetrapods, ribs surround the chest, enabling the lungs to expand and thus facilitate breathing by expanding the chest cavity. They serve to protect the lungs, heart, and other internal organs of the thorax. In some animals, especially snakes, ribs may provide support and protection for the entire body.

The rib cage is an endoskeletal enclosure in the thorax of most vertebrate animals that comprises the ribs, vertebral column and sternum, which protects vital organs such as the heart, lungs and great vessels. The circumferential enclosure formed by left and right rib cages, together known as the thoracic cage, is a semi-rigid bony and cartilaginous structure which surrounds the thoracic cavity and supports the shoulder girdles to form the core part of the axial skeleton.
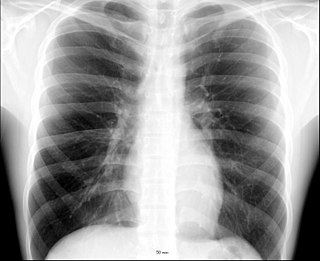
The thorax or chest is a part of the anatomy of mammals and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen. In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main divisions of the creature's body, each of which is in turn composed of multiple segments.

Tietze syndrome is a benign inflammation of one or more of the costal cartilages. It was first described in 1921 by German surgeon Alexander Tietze and was subsequently named after him. The condition is characterized by tenderness and painful swelling of the anterior (front) chest wall at the costochondral, sternocostal, or sternoclavicular junctions. Tietze syndrome affects the true ribs and has a predilection for the 2nd and 3rd ribs, commonly affecting only a single joint.

The axial skeleton is the part of the skeleton that consists of the bones of the head and trunk of a vertebrate. In the human skeleton, it consists of 80 bones and is composed of six parts; the skull, also the ossicles of the middle ear, the hyoid bone, the rib cage, sternum and the vertebral column. The axial skeleton together with the appendicular skeleton form the complete skeleton. Another definition of axial skeleton is the bones including the vertebrae, sacrum, coccyx, skull, ribs, and sternum.

Hyaline cartilage is the glass-like (hyaline) and translucent cartilage found on many joint surfaces. It is also most commonly found in the ribs, nose, larynx, and trachea. Hyaline cartilage is pearl-gray in color, with a firm consistency and has a considerable amount of collagen. It contains no nerves or blood vessels, and its structure is relatively simple.
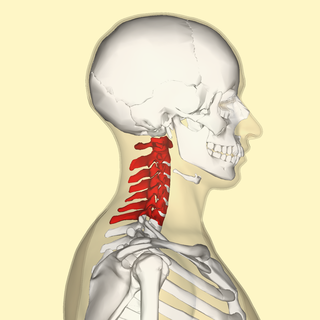
In tetrapods, cervical vertebrae are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull. Truncal vertebrae lie caudal of cervical vertebrae. In sauropsid species, the cervical vertebrae bear cervical ribs. In lizards and saurischian dinosaurs, the cervical ribs are large; in birds, they are small and completely fused to the vertebrae. The vertebral transverse processes of mammals are homologous to the cervical ribs of other amniotes. Most mammals have seven cervical vertebrae, with the only three known exceptions being the manatee with six, the two-toed sloth with five or six, and the three-toed sloth with nine.
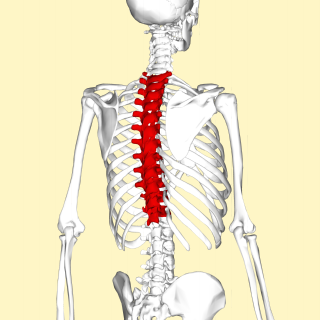
In vertebrates, thoracic vertebrae compose the middle segment of the vertebral column, between the cervical vertebrae and the lumbar vertebrae. In humans, there are twelve thoracic vertebrae and they are intermediate in size between the cervical and lumbar vertebrae; they increase in size going towards the lumbar vertebrae, with the lower ones being much larger than the upper. They are distinguished by the presence of facets on the sides of the bodies for articulation with the heads of the ribs, as well as facets on the transverse processes of all, except the eleventh and twelfth, for articulation with the tubercles of the ribs. By convention, the human thoracic vertebrae are numbered T1–T12, with the first one (T1) located closest to the skull and the others going down the spine toward the lumbar region.

The transverse plane is an anatomical plane that divides the body into superior and inferior sections. It is perpendicular to the coronal and sagittal planes.

Pork ribs are a cut of pork popular in Western and Asian cuisines. The ribcage of a domestic pig, meat and bones together, is cut into usable pieces, prepared by smoking, grilling, or baking – usually with a sauce, often barbecue – and then served.

The sternal angle is the projecting angle formed between the manubrium and body of a sternum at their junction at the manubriosternal joint.
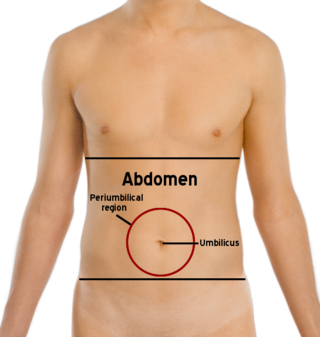
The abdomen is the part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis, in humans and in other vertebrates. The abdomen is the front part of the abdominal segment of the torso. The area occupied by the abdomen is called the abdominal cavity. In arthropods, it is the posterior tagma of the body; it follows the thorax or cephalothorax.

The shoulder girdle or pectoral girdle is the set of bones in the appendicular skeleton which connects to the arm on each side. In humans it consists of the clavicle and scapula; in those species with three bones in the shoulder, it consists of the clavicle, scapula, and coracoid. Some mammalian species have only the scapula.
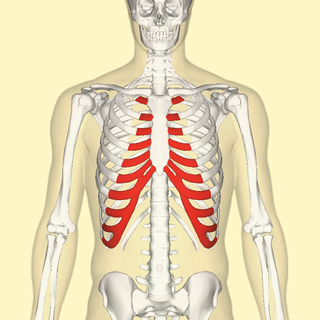
The costal cartilages are bars of hyaline cartilage that serve to prolong the ribs forward and contribute to the elasticity of the walls of the thorax. Costal cartilage is only found at the anterior ends of the ribs, providing medial extension.

The sternoclavicular joint or sternoclavicular articulation is a synovial saddle joint between the manubrium of the sternum, and the clavicle, and the first costal cartilage. The joint possesses a joint capsule, and an articular disc, and is reinforced by multiple ligaments.
Unlike the other two intercostal muscles, the external intercostal muscle does not retain its muscular character all the way to the sternum, and so the tissue in this location is called the external intercostal membrane.

The curvatures of the stomach refer to the long, convex, lateral suface and the shorter, concave, medial surface of the organ, which are referred to as the greater and lesser curvatures, respectively. The greater curvature, which begins at the cardiac notch, and arches backwards, passing inferiorly to the left, is four or five times as long as the lesser curvature, which attaches to the hepatogastric ligament and is supplied by the left gastric artery and right gastric branch of the hepatic artery.

The sternum or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the central part of the chest. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels from injury. Shaped roughly like a necktie, it is one of the largest and longest flat bones of the body. Its three regions are the manubrium, the body, and the xiphoid process. The word sternum originates from Ancient Greek στέρνον (stérnon) 'chest'.

Each vertebra is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, that make up the vertebral column or spine, of vertebrates. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spinal segment and the particular species.

Slipping rib syndrome (SRS) is a condition in which the interchondral ligaments are weakened or disrupted and have increased laxity, causing the costal cartilage tips to subluxate. This results in pain or discomfort due to pinched or irritated intercostal nerves, straining of the intercostal muscles, and inflammation. The condition affects the 8th, 9th, and 10th ribs, referred to as the false ribs, with the 10th rib most commonly affected.

















