The lumbar vertebrae are located between the thoracic vertebrae and pelvis. They form the lower part of the human back in humans, and the tail end of the back in quadrupeds. In humans, there are five lumbar vertebrae. The term is used to describe the anatomy of humans and quadrupeds, such as horses, pigs, or cattle. These bones are found in particular cuts of meat, including tenderloin or sirloin steak.

A laminectomy is a surgical procedure that removes a portion of a vertebra called the lamina, which is the roof of the spinal canal. It is a major spine operation with residual scar tissue and may result in postlaminectomy syndrome. Depending on the problem, more conservative treatments may be viable.

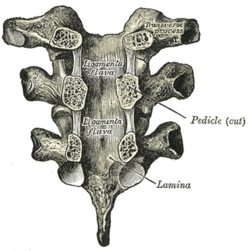
In human anatomy, the spinal canal, vertebral canal or spinal cavity is an elongated body cavity enclosed within the dorsal bony arches of the vertebral column, which contains the spinal cord, spinal roots and dorsal root ganglia. It is a process of the dorsal body cavity formed by alignment of the vertebral foramina. Under the vertebral arches, the spinal canal is also covered anteriorly by the posterior longitudinal ligament and posteriorly by the ligamentum flavum. The potential space between these ligaments and the dura mater covering the spinal cord is known as the epidural space. Spinal nerves exit the spinal canal via the intervertebral foramina under the corresponding vertebral pedicles.

Spondylosis is the degeneration of the vertebral column from any cause. In the more narrow sense it refers to spinal osteoarthritis, the age-related degeneration of the spinal column, which is the most common cause of spondylosis. The degenerative process in osteoarthritis chiefly affects the vertebral bodies, the neural foramina and the facet joints. If severe, it may cause pressure on the spinal cord or nerve roots with subsequent sensory or motor disturbances, such as pain, paresthesia, imbalance, and muscle weakness in the limbs.
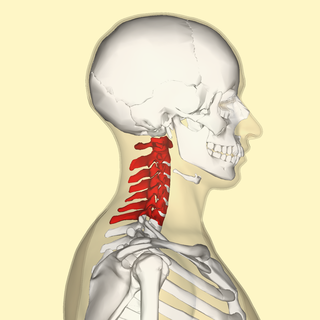
In tetrapods, cervical vertebrae are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull. Truncal vertebrae lie caudal of cervical vertebrae. In sauropsid species, the cervical vertebrae bear cervical ribs. In lizards and saurischian dinosaurs, the cervical ribs are large; in birds, they are small and completely fused to the vertebrae. The vertebral transverse processes of mammals are homologous to the cervical ribs of other amniotes. Most mammals have seven cervical vertebrae, with the only three known exceptions being the manatee with six, the two-toed sloth with five or six, and the three-toed sloth with nine.

Degenerative disc disease (DDD) is a medical condition typically brought on by the aging process in which there are anatomic changes and possibly a loss of function of one or more intervertebral discs of the spine. DDD can take place with or without symptoms, but is typically identified once symptoms arise. The root cause is thought to be loss of soluble proteins within the fluid contained in the disc with resultant reduction of the oncotic pressure, which in turn causes loss of fluid volume. Normal downward forces cause the affected disc to lose height, and the distance between vertebrae is reduced. The anulus fibrosus, the tough outer layers of a disc, also weakens. This loss of height causes laxity of the longitudinal ligaments, which may allow anterior, posterior, or lateral shifting of the vertebral bodies, causing facet joint malalignment and arthritis; scoliosis; cervical hyperlordosis; thoracic hyperkyphosis; lumbar hyperlordosis; narrowing of the space available for the spinal tract within the vertebra ; or narrowing of the space through which a spinal nerve exits with resultant inflammation and impingement of a spinal nerve, causing a radiculopathy.

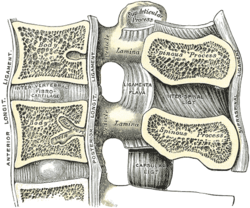
The anterior longitudinal ligament is a ligament that extends across the anterior/ventral aspect of the vertebral bodies and intervertebral discs the spine.

The supraspinous ligament is a ligament extending across the tips of the spinous processes of the vertebra of the vertebral column.

The intervertebral foramen is an opening between two pedicles of adjacent vertebra in the articulated spine. Each intervertebral foramen gives passage to a spinal nerve and spinal blood vessels, and lodges a posterior (dorsal) root ganglion. Cervical, thoracic, and lumbar vertebrae all have intervertebral foramina.

The posterior longitudinal ligament is a ligament connecting the posterior surfaces of the vertebral bodies of all of the vertebrae of humans. It weakly prevents hyperflexion of the vertebral column. It also prevents posterior spinal disc herniation, although problems with the ligament can cause it.
Microsurgical lumbar laminoplasty is a minimally invasive technique for decompressing pinched nerves in the lumbar spine. Pinched or compressed nerves may result from herniated discs, lumbar spinal stenosis, or spondylolisthesis.

Neurogenic claudication (NC), also known as pseudoclaudication, is the most common symptom of lumbar spinal stenosis (LSS) and describes intermittent leg pain from impingement of the nerves emanating from the spinal cord. Neurogenic means that the problem originates within the nervous system. Claudication, from Latin claudicare 'to limp', refers to painful cramping or weakness in the legs. NC should therefore be distinguished from vascular claudication, which stems from a circulatory problem rather than a neural one.
A laminotomy is an orthopaedic neurosurgical procedure that removes part of the lamina of a vertebral arch in order to relieve pressure in the vertebral canal. A laminotomy is less invasive than conventional vertebral column surgery techniques, such as laminectomy because it leaves more ligaments and muscles attached to the spinous process intact and it requires removing less bone from the vertebra. As a result, laminotomies typically have a faster recovery time and result in fewer postoperative complications. Nevertheless, possible risks can occur during or after the procedure like infection, hematomas, and dural tears. Laminotomies are commonly performed as treatment for lumbar spinal stenosis and herniated disks. MRI and CT scans are often used pre- and post surgery to determine if the procedure was successful.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:

Laminoplasty is an orthopaedic/neurosurgical surgical procedure for treating spinal stenosis by relieving pressure on the spinal cord. The main purpose of this procedure is to provide relief to patients who may have symptoms of numbness, pain, or weakness in arm movement. The procedure involves cutting the lamina on both sides of the affected vertebrae and then "swinging" the freed flap of bone open thus relieving the pressure on the spinal cord. The spinous process may be removed to allow the lamina bone flap to be swung open. The bone flap is then propped open using small wedges or pieces of bone such that the enlarged spinal canal will remain in place.
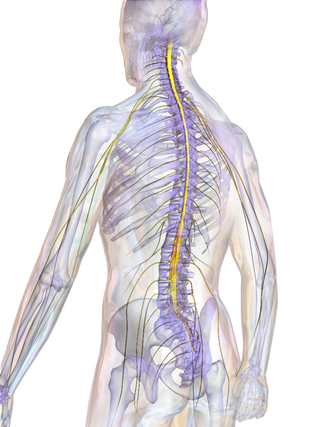
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the lower brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal cord is hollow and contains a structure called the central canal, which contains cerebrospinal fluid. The spinal cord is also covered by meninges and enclosed by the neural arches. Together, the brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system.

Spinal stenosis is an abnormal narrowing of the spinal canal or neural foramen that results in pressure on the spinal cord or nerve roots. Symptoms may include pain, numbness, or weakness in the arms or legs. Symptoms are typically gradual in onset and improve with leaning forward. Severe symptoms may include loss of bladder control, loss of bowel control, or sexual dysfunction.

Denticulate ligaments are lateral projections of the spinal pia mater forming triangular-shaped ligaments that anchor the spinal cord along its length to the dura mater on each side. There are usually 21 denticulate ligaments on each side, with the uppermost pair occurring just below the foramen magnum, and the lowest pair occurring between spinal nerve roots of T12 and L1. The denticulate ligaments are traditionally believed to provide stability for the spinal cord against motion within the vertebral column.

The vertebral column, also known as the spinal column, spine or backbone, is the core part of the axial skeleton in vertebrate animals. The vertebral column is the defining and eponymous characteristic of the vertebrate endoskeleton, where the notochord found in all chordates has been replaced by a segmented series of mineralized irregular bones called vertebrae, separated by fibrocartilaginous intervertebral discs. The dorsal portion of the vertebral column houses the spinal canal, an elongated cavity formed by alignment of the vertebral neural arches that encloses and protects the spinal cord, with spinal nerves exiting via the intervertebral foramina to innervate each body segments.

Each vertebra is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, that make up the vertebral column or spine, of vertebrates. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spinal segment and the particular species.