Sinocyclocheilus is a genus of freshwater fish in the family Cyprinidae that is endemic to Guangxi, Guizhou and Yunnan in China. Almost all of its species live in or around caves and most of these have adaptions typical of cavefish such as a lack of scales, lack of pigmentation and reduced eyes. Several species have an unusual hunchbacked appearance and some of the cave-dwellers have a "horn" on the back, the function of which is unclear. In contrast, the Sinocyclocheilus species that live aboveground, as well as a few found underground, show no clear cavefish adaptions. They are relatively small fish reaching up to 23 cm (9.1 in) in length. The individual species have small ranges and populations, leading to the status of most of the evaluated species as threatened. Many species populations in the genus have yet to be evaluated by the IUCN.

Triplophysa is a genus of fish in the family Nemacheilidae found mainly in and around the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau in China, as well as inland waters of the larger part of central Asia. Currently, the genus is a mixed assemblage of species. Some lineages have been identified and treated as subgenera, but as Wikipedia follows Fishbase for fish species all but Hedinichthys have been treated as subgenera in Wikipedia, although Kottelat in his revision of the loaches did recognise them as valid. FishBase, however, includes these in Triplophysa without specifying subgenera and treats the names given by Kottelat as synonyms.

Potamidae is a family of freshwater crabs. It includes more than 650 species and nearly 100 genera, which are placed into two subfamilies: Potaminae and Potamiscinae.
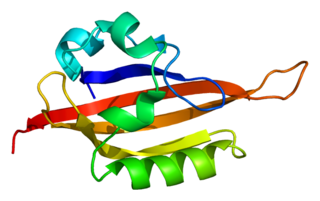
Endothelial PAS domain-containing protein 1 is a protein that is encoded by the EPAS1 gene in mammals. It is a type of hypoxia-inducible factor, a group of transcription factors involved in the physiological response to oxygen concentration. The gene is active under hypoxic conditions. It is also important in the development of the heart, and for maintaining the catecholamine balance required for protection of the heart. Mutation often leads to neuroendocrine tumors.

G/T mismatch-specific thymine DNA glycosylase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the TDG gene. Several bacterial proteins have strong sequence homology with this protein.

Ras-related protein Rab-27A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RAB27A gene.
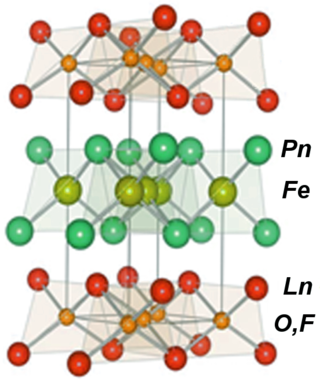
Iron-based superconductors (FeSC) are iron-containing chemical compounds whose superconducting properties were discovered in 2006. In 2008, led by recently discovered iron pnictide compounds, they were in the first stages of experimentation and implementation..

Dauricine is a plant metabolite, chemically classified as a phenol, an aromatic ether, and an isoquinoline alkaloid. It has been isolated from the Asian vine Menispermum dauricum, commonly known as Asian moonseed, and the North American vine Menispermum canadense, commonly known as Canadian moonseed. Scientists Tetsuji Kametani and Keiichiro Fukumoto of Japan are credited with being the first to synthesize dauricine in 1964, using both the Arndt-Eistert reaction and Bischler-Napieralski reaction to do so. Dauricine has been studied in vitro for its potential to inhibit cancer cell growth and to block cardiac transmembrane Na+, K+, and Ca2+ ion currents.
In molecular biology mir-605 microRNA is a short RNA molecule. MicroRNAs function to regulate the expression levels of other genes by several mechanisms.
In molecular biology mir-396 microRNA is a short RNA molecule. MicroRNAs function to regulate the expression levels of other genes by several mechanisms.
Huwentoxins (HWTX) are a group of neurotoxic peptides found in the venom of the Chinese bird spider Haplopelma schmidti. The species was formerly known as Haplopelma huwenum, Ornithoctonus huwena and Selenocosmia huwena. While structural similarity can be found among several of these toxins, HWTX as a group possess high functional diversity.
Triticum urartu, also known as red wild einkorn wheat, and a form of einkorn wheat, is a grass species related to wheat, and native to western Asia. It is a diploid species whose genome is the A genome of the allopolyploid hexaploid bread wheat Triticum aestivum, which has genomes AABBDD.

Chuan He is a Chinese-American chemical biologist. He currently serves as the John T. Wilson Distinguished Service Professor at the University of Chicago, and an Investigator of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute. He is best known for his work in discovering and deciphering reversible RNA methylation in post-transcriptional gene expression regulation. He was awarded the 2023 Wolf Prize in Chemistry for his work in discovering and deciphering reversible RNA methylation in post-transcriptional gene expression regulation in addition to his contributions to the invention of TAB-seq, a biochemical method that can map 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC) at base-resolution genome-wide, as well as hmC-Seal, a method that covalently labels 5hmC for its detection and profiling.
Indochinamon is a genus of freshwater crabs, typically found in the Indo-China region.
Lophopotamon is a genus of freshwater crab in the family Potamidae, containing only a single species, L. yenyuanense.
Kang Zhang is a Chinese-American ophthalmologist specializing in ophthalmic genetics and aging processes in the eye. He is currently a Professor of the Faculty of Medicine at Macau University of Science and Technology. He was previously a Professor of Ophthalmology and the Founding Director of the Institute for Genomic Medicine at the University of California, San Diego. Zhang is particularly known for his work on lanosterol, stem cell research, gene editing, and artificial intelligence.
The human identical sequence (HIS) is a sequence of RNA elements, 24-27 nucleotides in length, that coronavirus genomes share with the human genome. In pathogenic progression, HIS acts as a NamiRNA (nuclear activating miRNA) through the NamiRNA-enhancer network to activate neighboring host genes. The first HIS elements was identified in the SARS-CoV-2 genome, which has five HIS elements; other human coronaviruses have one to five. It has been suggested that these sequences can be more generally termed "host identical sequences" since similar correlations have been found between the genome of SARS-CoV-2 and multiple potential hosts (bats, pangolins, ferrets, and cats).







