Related Research Articles

The foot is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is a separate organ at the terminal part of the leg made up of one or more segments or bones, generally including claws or nails.

The human leg, in the general word sense, is the entire lower limb of the human body, including the foot, thigh or sometimes even the hip or gluteal region. However, the definition in human anatomy refers only to the section of the lower limb extending from the knee to the ankle, also known as the crus or, especially in non-technical use, the shank. Legs are used for standing, and all forms of locomotion including recreational such as dancing, and constitute a significant portion of a person's mass. Female legs generally have greater hip anteversion and tibiofemoral angles, but shorter femur and tibial lengths than those in males.

In humans and other primates, the knee joins the thigh with the leg and consists of two joints: one between the femur and tibia, and one between the femur and patella. It is the largest joint in the human body. The knee is a modified hinge joint, which permits flexion and extension as well as slight internal and external rotation. The knee is vulnerable to injury and to the development of osteoarthritis.

The tibia, also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates, and it connects the knee with the ankle bones. The tibia is found on the medial side of the leg next to the fibula and closer to the median plane or centre-line. The tibia is connected to the fibula by the interosseous membrane of leg, forming a type of fibrous joint called a syndesmosis with very little movement. The tibia is named for the flute tibia. It is the second largest bone in the human body next to the femur. The leg bones are the strongest long bones as they support the rest of the body.

The fibula or calf bone is a leg bone on the lateral side of the tibia, to which it is connected above and below. It is the smaller of the two bones and, in proportion to its length, the most slender of all the long bones. Its upper extremity is small, placed toward the back of the head of the tibia, below the knee joint and excluded from the formation of this joint. Its lower extremity inclines a little forward, so as to be on a plane anterior to that of the upper end; it projects below the tibia and forms the lateral part of the ankle joint.
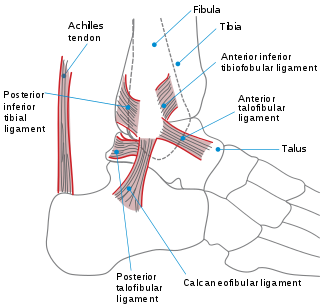
The ankle, or the talocrural region, or the jumping bone (informal) is the area where the foot and the leg meet. The ankle includes three joints: the ankle joint proper or talocrural joint, the subtalar joint, and the inferior tibiofibular joint. The movements produced at this joint are dorsiflexion and plantarflexion of the foot. In common usage, the term ankle refers exclusively to the ankle region. In medical terminology, "ankle" can refer broadly to the region or specifically to the talocrural joint.
The Maisonneuve fracture is a spiral fracture of the proximal third of the fibula associated with a tear of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis and the interosseous membrane. There is an associated fracture of the medial malleolus or rupture of the deep deltoid ligament of the ankle. This type of injury can be difficult to detect.

The talus, talus bone, astragalus, or ankle bone is one of the group of foot bones known as the tarsus. The tarsus forms the lower part of the ankle joint. It transmits the entire weight of the body from the lower legs to the foot.

An ankle fracture is a break of one or more of the bones that make up the ankle joint. Symptoms may include pain, swelling, bruising, and an inability to walk on the injured leg. Complications may include an associated high ankle sprain, compartment syndrome, stiffness, malunion, and post-traumatic arthritis.
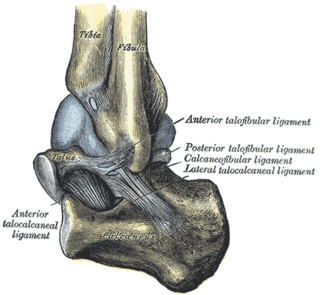
The distal tibiofibular joint is formed by the rough, convex surface of the medial side of the distal end of the fibula, and a rough concave surface on the lateral side of the tibia.
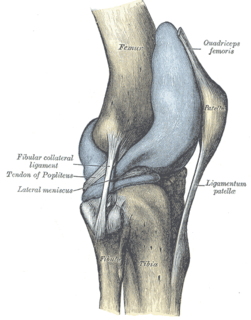
The proximal tibiofibular articulation is an arthrodial joint between the lateral condyle of the tibia and the head of the fibula.

The anterior ligament of the lateral malleolus is a flat, trapezoidal band of fibers, broader below than above, which extends obliquely downward and lateralward between the adjacent margins of the tibia and fibula, on the front aspect of the syndesmosis.
The inferior transverse ligament of the tibiofibular syndesmosis is a connective tissue structure in the lower leg that lies in front of the posterior ligament. It is a strong, thick band, of yellowish fibers which passes transversely across the back of the ankle joint, from the lateral malleolus to the posterior border of the articular surface of the tibia, almost as far as its malleolar process.

The lateral collateral ligament of ankle joint are ligaments of the ankle which attach to the fibula.
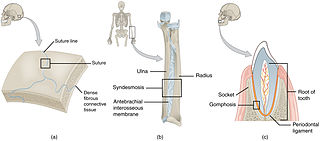
In anatomy, fibrous joints are joints connected by fibrous tissue, consisting mainly of collagen. These are fixed joints where bones are united by a layer of white fibrous tissue of varying thickness. In the skull the joints between the bones are called sutures. Such immovable joints are also referred to as synarthroses.

A malleolus is the bony prominence on each side of the human ankle.

A trimalleolar fracture is a fracture of the ankle that involves the lateral malleolus, the medial malleolus, and the distal posterior aspect of the tibia, which can be termed the posterior malleolus. The trauma is sometimes accompanied by ligament damage and dislocation.
A high ankle sprain, also known as a syndesmotic ankle sprain (SAS), is a sprain of the syndesmotic ligaments that connect the tibia and fibula in the lower leg, thereby creating a mortise and tenon joint for the ankle. High ankle sprains are described as high because they are located above the ankle. They comprise approximately 15% of all ankle sprains. Unlike the common lateral ankle sprains, when ligaments around the ankle are injured through an inward twisting, high ankle sprains are caused when the lower leg and foot externally rotates.

The Danis–Weber classification is a method of describing ankle fractures. It has three categories:
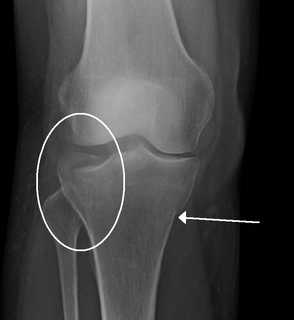
A crus fracture is a fracture of the lower legs bones meaning either or both of the tibia and fibula.
References
- ↑ Hunter, T., Peltier, L.F. Lund, P. J. (2000). Radiographics. 20:819-736 .
- 1 2 Moore and Agur. Essential Clinical Anatomy. Lippincotts Williams and Wilkins. 2007
- ↑ Moore and Dalley. Clinically Oriented Anatomy. 2006
- ↑ Wilson FC (2000). "Fractures of the ankle: pathogenesis and treatment". Journal of the Southern Orthopaedic Association. 9 (2): 105–15. PMID 10901648.
- ↑ Pott, P. (1769). Some Few General Remarks on Fractures and Dislocations. London, Howes. Clarke. Collins.
- ↑ synd/1126 at Who Named It?
- ↑ Sartoris DJ (1993). "Eponymic fractures of the ankle". The Journal of Foot and Ankle Surgery. 32 (2): 239–41. PMID 8318982.
- ↑ Dupuytren, G. (1819). Mémoire sur la fracture de l’extremité inferieure du peroné, les luxations et les accidents qui en sont la suite. Ann med.-chir Hôp. Paris, 1: 2-212.