Related Research Articles

The Ichneumonidae, also known as the ichneumon wasps or ichneumonids, is a parasitoid wasp family within the insect order Hymenoptera. This insect family is among the most species-rich branches of the tree of life. At the same time, it is one of the groups for which our knowledge most severely lags behind their actual diversity. The roughly 25,000 species described today probably represent less than a quarter of their true richness, but reliable estimates are lacking, as is much of the most basic knowledge about their ecology, distribution and evolution. Ichneumonid wasps, with very few exceptions, attack the immature stages of holometabolous insects and spiders, eventually killing their hosts. They thus fulfill an important role as regulators of insect populations, both in natural and semi-natural systems, making them promising agents for biological control.

Alexandr Pavlovich Rasnitsyn is a Russian entomologist, expert in palaeoentomology, and Honored Scientist of the Russian Federation (2001). His scientific interests are centered on the palaeontology, phylogeny, and taxonomy of hymenopteran insects and insects in general. He has also studied broader biological problems such as evolutionary theory, the principles of phylogenetics, taxonomy, nomenclature, and palaeoecology. He has published over 300 articles and books in several languages. In August 2008 he was awarded the Distinguished Research Medal of the International Society of Hymenopterists.

Phuwiangosaurus is a genus of titanosaur dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous (Valanginian-Hauterivian) Sao Khua Formation of Thailand. The type species, P. sirindhornae, was described by Martin, Buffetaut, and Suteethorn in a 1993 press release and was formally named in 1994. The species was named to honor Princess Maha Chakri Sirindhorn of Thailand, who was interested in the geology and palaeontology of Thailand, while the genus was named after the Phu Wiang area, where the fossil was discovered.

Cephoidea is a small superfamily within the Symphyta, commonly referred to as stem sawflies, containing some 100 species in 10 genera in the living family, Cephidae, plus another 17 genera in the extinct family Sepulcidae. Most species occur in the Northern Hemisphere, especially in Eurasia. The larvae are stem borers in various plants, especially grasses, but sometimes other herbaceous plants, shrubs, or trees. A few are pests of cereal grains. They are exceptionally slender for symphytans, often resembling other types of wasps, and they are the only Symphyta which lack cenchri. They are sometimes postulated to be the sister taxon to the Apocrita, though the Orussidae are more commonly considered such.
Enaliornis is a genus of hesperornithine birds which lived in the early Late Cretaceous, making them the oldest known hesperornithines. Fossils have been found near Cambridge, England. Due to its lack of certain hesperornithid apomorphies, they were much more "conventional" birds and were initially held to be Gaviiformes (loons/divers).
Elosuchus is an extinct genus of neosuchian crocodyliform that lived during the Middle Cretaceous of what is now Africa.
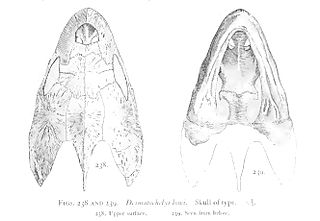
Desmatochelys is an extinct genus of sea turtles belonging to the family Protostegidae. This genus contains two known species, D. lowii and D. padillai. D. lowii was first discovered in 1895, followed by D. padillai in 2015. Having been estimated at over 120 million years old, D. padillai is currently the oldest known species of sea turtle.

Dorsetochelys is an extinct genus of turtle from the Early Cretaceous of southern England and northwestern Germany.

The Dabeigou Formation is a palaeontological formation located in Hebei, China. It dates from the mid Valanginian to Hauterivian age of the Cretaceous period, approximately 135 to 130 Ma.

The Andaikhudag Formation, in older literature referred to as Unduruh Formation or Ondorukhaa Formation, is an Early Cretaceous geologic formation in Mongolia. Dinosaur remains diagnostic to the genus level are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation.

Khurendukhosaurus is a genus of choristodere, a type of amphibious reptile. It is known from Lower Cretaceous rocks of Mongolia and Russia. Two species have been named. The type species, K. orlovi, was named in 1984 by Sigogneau–Russell and Efimov for the fragmentary postcranial skeleton PIN 3386/3. This specimen was discovered in the Albian-age Lower Cretaceous Khuren Dukh Formation Formation at Hüren Dukh, central Mongolia. The lake deposits at this site also contain fossils of the choristoderes Irenosaurus and Tchoiria. Other postcranial bones of K. orlovi have been found at this site as well.
Labenopimplinae are an extinct subfamily of the parasitic wasp family Ichneumonidae. Labenopimplinae are known from the Cenomanian of the Russian Far East and Turonian of Orapa, Botswana. The subfamily includes five genera with 13 species. The subfamily is highly polymorphic and combines features of the Labeninae and Pimplinae.

Hemiphlebiidae is a family of damselflies, it contains only one extant species, the ancient greenling, native to Southern Australia and Tasmania. The fossil record of the group extends back to the Late Jurassic, making them the oldest known crown group damselflies.
Rugocaudia is a potentially dubious genus of basal titanosauriform sauropod dinosaur known from the Early Cretaceous of Montana, United States.
Brodavis is a genus of freshwater hesperornithiform birds known from the Late Cretaceous of North America and Asia. It was first described and named by Larry D. Martin, Evgeny N. Kurochkin and Tim T. Tokaryk in 2012 and assigned to a new monogeneric family, Brodavidae. Four species were described and assigned to Brodavis.

Omma is a genus of beetles in the family Ommatidae. Omma is an example of a living fossil. The oldest species known, O. liassicum, lived during the final stage of the Triassic (Rhaetian), over 200 million years ago, followed by several other species from Europe and Asia until after O. attenuatum from the Lower Cretaceous, the genus then reappears in the Burmese amber during the Cenomanian, then disappears from the fossil record for the remaining 100 million years until today, with one species endemic to Australia, three other extant species that were formerly part of this genus were moved to the separate genus Beutelius in 2020. The extant Omma stanleyi is strongly associated with wood, being found under Eucalyptus bark and exhibiting thanatosis when disturbed. Its larval stage and many other life details are unknown due to its rarity. Males are typically 14-20 mm in length, while females are 14.4-27.5 mm. Omma stanleyi occurs throughout eastern Australia from Victoria to Central Queensland.

Yurgovuchia is a genus of dromaeosaurid theropod dinosaurs that lived in North America during the Early Cretaceous period in what is now the Cedar Mountain Formation. It contains a single species, Yurgovuchia doellingi. The remains were discovered in Utah, United States.
Amplicella is a genus of extinct hymenopteran.
Tengrisaurus is a genus of lithostrotian sauropod, from the Early Cretaceous (Barremian-Aptian) Murtoi Formation, Russia. It was described in 2017 by Averianov & Skutschas. The type species is T. starkovi. New remains were described in 2021 by Averianov, Sizov & Skutschas.

Cretophasmomima is an extinct genus of stem-stick insect from the Cretaceous of Eurasia and is one of the oldest and most basal stick insects known. The type species, Cretophasmomima vitimica, was described in 1985 from the Aptian aged Zaza Formation in Russia. A second species, Cretophasmomima burjatica was described from the same formation in 1988. A third and fourth species, Cretophasmomima clara and Cretophasmomima arkagalica were also described in 1988 in the same paper from the Ola Formation and the Arkagalinskaya Formation respectively, both formations are Lower Campanian in age. A fifth species Cretophasmomima melanogramma was described in 2014 off the basis of three specimens from the Aptian Yixian Formation in China. In 2020 a sixth species Cretophasmomima traceyae was described based on a forewing with preserved colouration from the Barremian aged Weald Clay Formation in England.
References
- ↑ D. S. Kopylov (2012). "New species of Praeichneumonidae (Hymenoptera, Ichneumonoidea) from the Lower Cretaceous of Transbaikalia". Paleontological Journal . 46 (1): 66–72. doi:10.1134/S0031030112010078.