
The Yucca Mountain Nuclear Waste Repository, as designated by the Nuclear Waste Policy Act amendments of 1987, is to be a deep geological repository storage facility within Yucca Mountain for spent nuclear fuel and other high-level radioactive waste in the United States. The site is located on federal land adjacent to the Nevada Test Site in Nye County, Nevada, about 80 mi (130 km) northwest of the Las Vegas Valley.

The Nevada National Security Site, previously the Nevada Test Site (NTS), is a United States Department of Energy reservation located in southeastern Nye County, Nevada, about 65 miles (105 km) northwest of the city of Las Vegas. Formerly known as the Nevada Proving Grounds, the site was established on January 11, 1951 for the testing of nuclear devices, covering approximately 1,360 square miles (3,500 km2) of desert and mountainous terrain. Nuclear weapons testing at the Nevada Test Site began with a 1-kiloton-of-TNT (4.2 TJ) bomb dropped on Frenchman Flat on January 27, 1951. Many of the iconic images of the nuclear era come from the NTS. NNSS is operated by Mission Support and Test Services, LLC.

Project Plowshare was the overall United States program for the development of techniques to use nuclear explosives for peaceful construction purposes. As part of the program, 31 nuclear warheads were detonated in 27 separate tests. Plowshare was the US portion of what are called Peaceful Nuclear Explosions (PNE); a similar Soviet program was carried out under the name Nuclear Explosions for the National Economy.

Operation Crosstie was a series of 48 nuclear tests conducted by the United States in 1967–1968 at the Nevada Test Site. These tests followed the Operation Latchkey series and preceded the Operation Bowline series.

Nuclear weapons tests are experiments carried out to determine the effectiveness, yield, and explosive capability of nuclear weapons. Throughout the twentieth century, most nations that developed nuclear weapons tested them. Testing nuclear weapons can yield information about how the weapons work, as well as how the weapons behave under various conditions and how personnel, structures, and equipment behave when subjected to nuclear explosions. Nuclear testing has often been used as an indicator of scientific and military strength, and many tests have been overtly political in their intention; most nuclear weapons states publicly declared their nuclear status by means of a nuclear test.
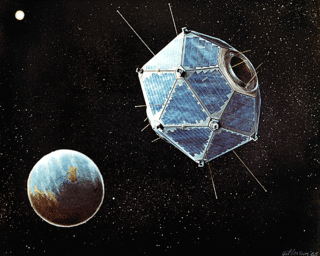
Project Vela was a project undertaken by the United States Department of Defense to develop and implement methods to monitor compliance with the 1963 Partial Test Ban Treaty. This treaty banned the testing of nuclear weapons in the atmosphere, in outer space, and underwater, effectively meaning nuclear tests were only to be permitted underground. The Vela Project started as a small budget research program within the DARPA Projects Agencies until 1961 when it was granted greater funding and resources through the authority of the Deputy Assistant Secretary of the Army. This was likely prompted by increased caution over Domestic Nuclear Affairs resulting from the 1961 Goldsboro B-52 crash as well as in anticipation of the 1963 PTB Treaty.

Amchitka is a volcanic, tectonically unstable island in the Rat Islands group of the Aleutian Islands in southwest Alaska. It is part of the Alaska Maritime National Wildlife Refuge. The island, with a land area of roughly 116 square miles (300 km2), is about 42 miles (68 km) long and 1 to 4 miles wide. The area has a maritime climate, with many storms, and mostly overcast skies.

Storax Sedan was a shallow underground nuclear test conducted in Area 10 of Yucca Flat at the Nevada National Security Site on July 6, 1962 as part of Operation Plowshare, a program to investigate the use of nuclear weapons for mining, cratering, and other civilian purposes. The radioactive fallout from the test contaminated more US residents than any other nuclear test. The Sedan Crater is the largest human-made crater in the United States, and is listed on the National Register of Historic Places.
Peaceful nuclear explosions (PNEs) are nuclear explosions conducted for non-military purposes. Proposed uses include excavation for the building of canals and harbours, electrical generation, the use of nuclear explosions to drive spacecraft, and as a form of wide-area fracking. PNEs were an area of some research from the late 1950s into the 1980s, primarily in the United States and Soviet Union.

Underground nuclear testing is the test detonation of nuclear weapons that is performed underground. When the device being tested is buried at sufficient depth, the explosion may be contained, with no release of radioactive materials to the atmosphere.

Project Gnome was the first nuclear test of Operation Plowshare and was the first continental nuclear weapon test since Trinity to be conducted outside of the Nevada Test Site. It was tested in southeastern New Mexico, approximately 40 km (25 mi) southeast of Carlsbad, New Mexico.

Pahute Mesa or Paiute Mesa is one of four major nuclear test regions within the Nevada National Security Site (NNSS). It occupies 243 square miles (630 km2) in the northwest corner of the NNSS in Nevada. The eastern section is known as Area 19 and the western section as Area 20.

Salmon Site is a 1,470-acre (5.9 km2) tract of land in Lamar County, Mississippi, near Baxterville. The tract is located over a geological formation known as the Tatum Salt Dome and is the location of the only nuclear weapons test detonations known to have been performed in the eastern United States.

Yucca Flat is a closed desert drainage basin, one of four major nuclear test regions within the Nevada Test Site (NTS), and is divided into nine test sections: Areas 1 through 4 and 6 through 10. Yucca Flat is located at the eastern edge of NTS, about ten miles (16 km) north of Frenchman Flat, and 65 miles (105 km) from Las Vegas, Nevada. Yucca Flat was the site for 739 nuclear tests – nearly four of every five tests carried out at the NTS.

Cannikin was an underground nuclear weapons test performed on November 6, 1971, on Amchitka island, Alaska, by the United States Atomic Energy Commission. The experiment, part of the Operation Grommet nuclear test series, tested the unique W71 warhead design for the LIM-49 Spartan anti-ballistic missile. With an explosive yield of almost 5 megatons of TNT (21 PJ), the test was the largest underground explosion ever detonated by the United States.
The World-Wide Standardized Seismograph Network (WWSSN) – originally the World-Wide Network of Seismograph Stations (WWNSS) – was a global network of about 120 seismograph stations built in the 1960s that generated an unprecedented collection of high quality seismic data. This data enabled seismology to become a quantitative science, elucidated the focal mechanisms of earthquakes and the structure of the earth's crust, and contributed to the development of plate tectonic theory. The WWSSN is credited with spurring a renaissance in seismological research.

The United States Department of Energy (DOE) is a cabinet-level department of the United States Government concerned with the United States' policies regarding energy and safety in handling nuclear material. Its responsibilities include the nation's nuclear weapons program, nuclear reactor production for the United States Navy, energy conservation, energy-related research, radioactive waste disposal, and domestic energy production. It also directs research in genomics; the Human Genome Project originated in a DOE initiative. DOE sponsors more research in the physical sciences than any other U.S. federal agency, the majority of which is conducted through its system of National Laboratories. The agency is administered by the United States Secretary of Energy, and its headquarters are located in Southwest Washington, D.C., on Independence Avenue in the James V. Forrestal Building, named for James Forrestal, as well as in Germantown, Maryland.

A geographic coordinate system is a coordinate system that enables every location on Earth to be specified by a set of numbers, letters or symbols. The coordinates are often chosen such that one of the numbers represents a vertical position and two or three of the numbers represent a horizontal position; alternatively, a geographic position may be expressed in a combined three-dimensional Cartesian vector. A common choice of coordinates is latitude, longitude and elevation. To specify a location on a plane requires a map projection.


















