Related Research Articles

Operation Tinderbox was a series of 14 nuclear tests conducted by the United States in 1979–1980 at the Nevada Test Site. These tests followed the Operation Quicksilver series and preceded the Operation Guardian series.

Operation Nougat was a series of 44 nuclear tests conducted at the Nevada Test Site in 1961 and 1962, immediately after the Soviet Union abrogated a testing moratorium, with the US' Mink test shot taking place the day before the Soviets test-detonated the Tsar Bomba. Most tests were limited-yield underground test shots. New designs would be further developed in atmospheric testing during Operation Dominic I and II.

Operation Storax was a series of 47 nuclear tests conducted by the United States in 1962–1963 at the Nevada Test Site. These tests followed the Operation Fishbowl series and preceded the Operation Roller Coaster series.
The United States's Niblick nuclear test series was a group of 41 nuclear tests conducted in 1963–1964. These tests followed the Operation Roller Coaster series and preceded the Operation Whetstone series.

The United States's Whetstone nuclear test series was a group of 46 nuclear tests conducted in 1964–1965. These tests followed the Operation Niblick series and preceded the Operation Flintlock series.

The United States's Mandrel nuclear test series was a group of 52 nuclear tests conducted in 1969–1970. These tests followed the Operation Bowline series and preceded the Operation Emery series.
Operation Quicksilver was a series of 16 nuclear tests conducted by the United States in 1978–1979 at the Nevada Test Site. These tests followed the Operation Cresset series and preceded the Operation Tinderbox series.
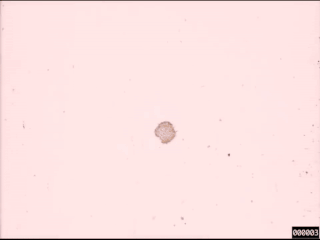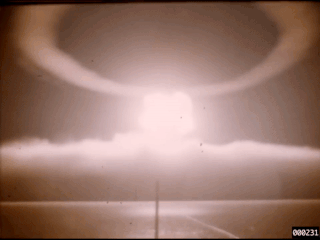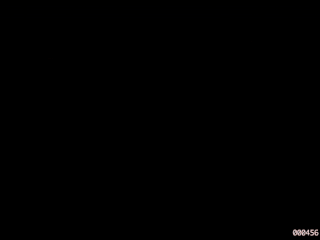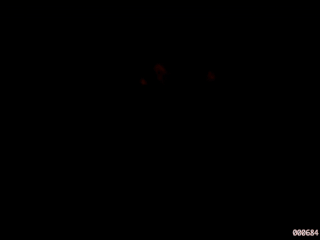
Operation Hardtack II was a series of 37 nuclear tests conducted by the United States in 1958 at the Nevada Test Site. These tests followed the Operation Argus series and preceded the Operation Nougat series.

Operation Tumbler–Snapper was a series of nuclear weapons tests conducted by the United States in early 1952 at the Nevada Test Site. The Tumbler–Snapper series of tests followed Operation Buster–Jangle and preceded Operation Ivy.

Operation Sunbeam was a series of four nuclear tests conducted at the United States's Nevada Test Site in 1962. Operation Sunbeam tested tactical nuclear warheads; the most notable was the Davy Crockett.
The United States's Praetorian nuclear test series was a group of 19 nuclear tests conducted in 1981–1982. These tests followed the Operation Guardian series and preceded the Operation Phalanx series.
Operation Fusileer was a series of 16 nuclear tests conducted by the United States in 1983–1984 at the Nevada Test Site. These tests followed the Operation Phalanx series and preceded the Operation Grenadier series.
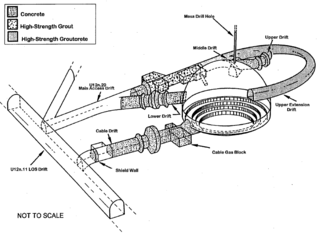
Operation Charioteer was a series of 16 nuclear tests conducted by the United States in 1985–1986 at the Nevada Test Site. These tests followed the Operation Grenadier series and preceded the Operation Musketeer series.
The United States's Musketeer nuclear test series was a group of 14 nuclear tests conducted in 1986–1987. These tests followed the Operation Charioteer series and preceded the Operation Touchstone series.

Operation Anvil was a series of 21 nuclear tests conducted by the United States in 1975–1976 at the Nevada Test Site. These tests followed the Operation Bedrock series and preceded the Operation Fulcrum series.
Operation Roller Coaster was a series of four nuclear tests conducted jointly by the United States and the United Kingdom in 1963, at the Nevada Test Site. The tests did not involve the detonation of any nuclear weapons. Instead, their purpose was to evaluate the distribution of radioactive particles in a "dirty bomb" scenario, or an inadvertent, non-nuclear detonation of a nuclear weapon, as well as to evaluate the effectiveness of storage structures in containing the explosion and the particles released. The tests followed the Operation Storax series and preceded the Operation Niblick series.
Operation Project 56 was a series of 4 nuclear tests conducted by the United States in 1955–1956 at the Nevada Test Site. These tests followed the Operation Wigwam series and preceded the Operation Redwing series.

Operation Project 58/58A was a series of 4 nuclear tests conducted by the United States in 1957–1958 at the Nevada Test Site. These tests followed the Operation Plumbbob series and preceded the Operation Hardtack I series.
Project 57 was an open-air nuclear test conducted by the United States at the Nellis Air Force Range in 1957, following Operation Redwing, and preceding Operation Plumbbob. The test area, also known as Area 13, was a 10 miles (16 km) by 16 miles (26 km) block of land abutting the northeast boundary of the Nevada National Security Site.

Operation Dominic was a series of 31 nuclear test explosions ("shots") with a 38.1 Mt (159 PJ) total yield conducted in 1962 by the United States in the Pacific. This test series was scheduled quickly, in order to respond in kind to the Soviet resumption of testing after the tacit 1958–1961 test moratorium. Most of these shots were conducted with free fall bombs dropped from B-52 bomber aircraft. Twenty of these shots were to test new weapons designs; six to test weapons effects; and several shots to confirm the reliability of existing weapons. The Thor missile was also used to lift warheads into near-space to conduct high-altitude nuclear explosion tests; these shots were collectively called Operation Fishbowl.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Yang, Xiaoping; North, Robert; Romney, Carl (August 2000), CMR Nuclear Explosion Database (Revision 3), SMDC Monitoring Research
- ↑ "Time Zone Historical Database". iana.com. Retrieved March 8, 2014.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Estimated exposures and thyroid doses received by the American people from Iodine-131 in fallout following Nevada atmospheric nuclear bomb tests, Chapter 2 (PDF), National Cancer Institute, 1997, retrieved January 5, 2014
- 1 2 3 4 5 Radiological Effluents Released from U.S. Continental Tests 1961 Through 1992 (DOE/NV-317 Rev. 1) (PDF), DOE Nevada Operations Office, August 1996, archived from the original (PDF) on November 3, 2013, retrieved October 31, 2013
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Official list of underground nuclear explosions, Sandia National Laboratories, July 1, 1994, retrieved December 18, 2013
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 United States Nuclear Tests: July 1945 through September 1992 (PDF) (DOE/NV-209 REV15), Las Vegas, NV: Department of Energy, Nevada Operations Office, December 1, 2000, archived from the original (PDF) on October 12, 2006, retrieved December 18, 2013
- 1 2 Broad, William J. (1985). Star warriors : a penetrating look into the lives of the young scientists behind our space age weaponry. New York: Simon and Schuster. p. 116. ISBN 0671545663.
- ↑ Hansen, Swords of Armageddon, p. VII-204.
- ↑ Hechanova, Anthony E.; O'Donnell, James E. (September 25, 1998), Estimates of yield for nuclear tests impacting the groundwater at the Nevada Test Site, Nuclear Science and Technology Division
- 1 2 3 4 Operation Argus, 1958 (DNA6039F), Washington, DC: Defense Nuclear Agency, Department of Defense, 1982, retrieved November 26, 2013
- ↑ "Lists of motion picture films and videos at The National. Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA), 2014" (PDF). Government Attic. p. 77. Retrieved December 2, 2020.
BASEBALL stockpile Confidence Test
- ↑ Hansen, Swords of Armageddon, p. VI-121.