| Operation Mandrel | |
|---|---|
 Mandrel Mirlow, 1Mt. | |
| Information | |
| Country | United States |
| Test site |
|
| Period | 1969–1970 |
| Number of tests | 52 |
| Test type | underground shaft, tunnel |
| Max. yield | 1.9 megatonnes of TNT (7.9 PJ) |
| Test series chronology | |
The United States's Mandrel nuclear test series [1] was a group of 52 nuclear tests conducted in 1969–1970. These tests [note 1] followed the Operation Bowline series and preceded the Operation Emery series.
| Name [note 2] | Date time (UT) | Local time zone [note 3] [3] | Location [note 4] | Elevation + height [note 5] | Delivery [note 6] Purpose [note 7] | Device [note 8] | Yield [note 9] | Fallout [note 10] | References | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ildrim | July 16, 1969 13:02:30.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U2au 37°07′10″N116°03′22″W / 37.11939°N 116.05599°W | 1,256 m (4,121 ft) – 410.26 m (1,346.0 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 20 kt | [1] [4] [5] [6] [7] | |||
| Hutch | July 16, 1969 14:55:00.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U2df 37°08′22″N116°05′18″W / 37.13953°N 116.08822°W | 1,300 m (4,300 ft) – 548.64 m (1,800.0 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 120 kt | Venting detected, 1.1 kCi (41 TBq) | [1] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] | ||
| Spider - 1 | August 14, 1969 14:30:00.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U2bp1 37°09′37″N116°03′52″W / 37.1602°N 116.06448°W | 1,292 m (4,239 ft) – 207.26 m (680.0 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 1 kt | Venting detected, 2 Ci (74 GBq) | [1] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] | Simultaneous, separate holes. | |
| Spider - 2 | August 14, 1969 14:30:00.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U2bp2 37°09′30″N116°03′53″W / 37.1582°N 116.06467°W | 1,291 m (4,236 ft) – 213 m (699 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 1 kt | [1] [6] [7] [8] | Simultaneous, separate holes. | ||
| Horehound | August 27, 1969 13:45:00.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U3gm 36°59′34″N115°59′47″W / 36.99267°N 115.99637°W | 1,174 m (3,852 ft) – 331.83 m (1,088.7 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | less than 20 kt | [1] [6] [7] | |||
| Pliers | August 27, 1969 13:45:00.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U3gn 37°01′17″N116°02′20″W / 37.02146°N 116.03884°W | 1,187 m (3,894 ft) – 238.87 m (783.7 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 10 kt | Venting detected on site | [1] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] | ||
| Rulison | September 10, 1969 21:00:00.01 | MST (–7 hrs) | near Parachute, Colorado 39°24′19″N107°56′55″W / 39.40535°N 107.94857°W | 2,498 m (8,196 ft) – 2,570 m (8,430 ft) | underground shaft, peaceful research | 40 kt | Venting detected off site | [1] [7] [9] | Plowshare – gas stimulation experiment. | |
| Minute Steak | September 12, 1969 18:02:20.42 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U11f 36°52′38″N115°55′46″W / 36.87718°N 115.92936°W | 1,007 m (3,304 ft) – 264.26 m (867.0 ft) | underground shaft, weapon effect | 5 kt | Venting detected on site, 8.4 kCi (310 TBq) | [1] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] | ||
| Jorum | September 16, 1969 14:30:00.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U20e - 37°18′51″N116°27′42″W / 37.31408°N 116.46156°W | 1,898 m (6,227 ft) – 1,158.24 m (3,800.0 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 800 kt | [1] [4] [6] [7] [10] | |||
| Kyack - 1 | September 20, 1969 14:30:00.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U2bq1 37°09′31″N116°04′07″W / 37.15874°N 116.06863°W | 1,296 m (4,252 ft) – 192.02 m (630.0 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 800 t | Venting detected on site | [1] [4] [6] [7] [8] [11] | Simultaneous, separate holes. | |
| Kyack - 2 | September 20, 1969 14:30:00.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U2bq2 37°09′26″N116°04′00″W / 37.15729°N 116.06677°W | 1,293 m (4,242 ft) – 192 m (630 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 1 kt | Venting detected on site, 510 Ci (19,000 GBq) | [1] [6] [7] [8] [9] [11] | Simultaneous, separate holes. | |
| Seaweed - 1 | October 1, 1969 14:30:00.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U3hk3 37°00′41″N115°59′58″W / 37.01141°N 115.99935°W | 1,184 m (3,885 ft) – 118.43 m (388.5 ft) | underground shaft, safety experiment | less than 20 kt | Venting detected on site, 0.00000005 Ci (1.9×10−6 GBq) | [1] [6] [7] [8] | Simultaneous, separate holes. | |
| Seaweed - 2 | October 1, 1969 14:30:00.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U3hkf 37°00′38″N116°00′01″W / 37.01048°N 116.0003°W | 1,183 m (3,881 ft) – 118 m (387 ft) | underground shaft, safety experiment | less than 20 kt | Venting detected on site | [1] [6] [7] [8] [9] | Simultaneous, separate holes. | |
| Seaweed - 3 | October 1, 1969 14:30:00.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U3hkc 37°00′49″N115°59′58″W / 37.01371°N 115.99935°W | 1,184 m (3,885 ft) + | underground shaft, safety experiment | less than 20 kt | Venting detected on site | [1] [6] [7] [8] | Simultaneous, separate holes. | |
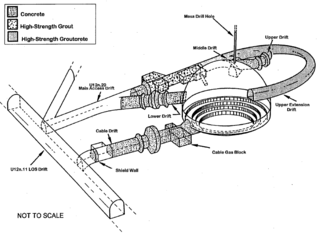
| Milrow | October 2, 1969 22:06:00.04 | BST (–11 hrs) | Amchitka Island, Alaska 51°24′57″N179°10′46″E / 51.41572°N 179.17939°E | 40 m (130 ft) – 1,220 m (4,000 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 1 Mt | [1] [5] [7] | Calibration for Grommet Cannikin test. Was initially named "Ganja", until someone in the DoE got wise to it. | ||
| Pipkin | October 8, 1969 14:30:00.14 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U20b 37°15′24″N116°26′30″W / 37.25667°N 116.44164°W | 1,965 m (6,447 ft) – 624.84 m (2,050.0 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 200 kt | Venting detected, 6 Ci (220 GBq) | [1] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] | ||
| Seaweed B | October 16, 1969 14:00:00.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U3hkd 37°00′45″N115°59′56″W / 37.01255°N 115.99901°W | 1,185 m (3,888 ft) – 118.55 m (388.9 ft) | underground shaft, safety experiment | less than 20 kt | Venting detected on site, 0.0000002 Ci (7.4×10−6 GBq) | [1] [6] [7] [8] | ||
| Cruet | October 29, 1969 19:30:00.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U2cn 37°07′17″N116°07′42″W / 37.12138°N 116.12829°W | 1,372 m (4,501 ft) – 263.65 m (865.0 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 11 kt | [1] [5] [6] [7] | |||
| Pod - 1 | October 29, 1969 20:00:00.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U2ch 37°08′25″N116°07′53″W / 37.14015°N 116.13136°W | 1,397 m (4,583 ft) – 266.7 m (875 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 16.7 kt | Venting detected on site, 3.9 kCi (140 TBq) | [1] [6] [7] [8] [9] | Simultaneous, separate holes. | |
| Pod - 2 | October 29, 1969 20:00:00.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U2ci 37°08′25″N116°08′34″W / 37.1404°N 116.1427°W | 1,464 m (4,803 ft) + | underground shaft, weapons development | 16.7 kt | Venting detected on site | [1] [6] [7] [8] | Simultaneous, separate holes. | |
| Pod - 3 | October 29, 1969 20:00:00.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U2dj 37°08′11″N116°08′27″W / 37.13628°N 116.14083°W | 1,448 m (4,751 ft) + | underground shaft, weapons development | 16.7 kt | Venting detected on site | [1] [6] [7] [8] | Simultaneous, separate holes. | |
| Pod - 4 | October 29, 1969 20:00:00.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U2ck 37°08′07″N116°08′13″W / 37.13532°N 116.13694°W | 1,424 m (4,672 ft) – 312 m (1,024 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 16.7 kt | Venting detected on site | [1] [6] [7] [8] [9] | Simultaneous, separate holes. | |
| Calabash | October 29, 1969 22:01:51.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U2av 37°08′36″N116°03′54″W / 37.14326°N 116.06501°W | 1,283 m (4,209 ft) – 624.84 m (2,050.0 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 110 kt | [1] [5] [6] [7] [10] | |||
| Scuttle | November 13, 1969 15:15:00.13 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U2bh 37°09′53″N116°04′33″W / 37.16462°N 116.07576°W | 1,312 m (4,304 ft) – 164.59 m (540.0 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 1.7 kt | Venting detected, 210 Ci (7,800 GBq) | [1] [6] [7] [8] [9] | ||
| Piccalilli | November 21, 1969 14:52:00.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U3fc 37°01′52″N116°00′10″W / 37.03118°N 116.00276°W | 1,195 m (3,921 ft) – 393.8 m (1,292 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 22 kt | [1] [5] [6] [7] [10] | |||
| Planer | November 21, 1969 14:52:00.08 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U3ei 37°00′53″N116°01′24″W / 37.01481°N 116.02347°W | 1,183 m (3,881 ft) – 377.84 m (1,239.6 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 20 kt | [1] [6] [7] [10] | |||
| Diesel Train | December 5, 1969 17:00:00.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U12e.11 37°10′48″N116°12′42″W / 37.17992°N 116.21174°W | 2,207 m (7,241 ft) – 419.15 m (1,375.2 ft) | tunnel, weapon effect | 20 kt | [1] [4] [6] [7] [10] | |||
| Culantro - 1 | December 10, 1969 15:00:00.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U3hia 37°00′53″N116°00′13″W / 37.01469°N 116.00362°W | 1,181 m (3,875 ft) – 134.13 m (440.1 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | less than 20 kt | [1] [6] [7] | Simultaneous, separate holes. | ||
| Culantro - 2 | December 10, 1969 15:00:00.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U3hib 37°00′54″N116°00′07″W / 37.01489°N 116.0019°W | 1,182 m (3,878 ft) + | underground shaft, weapons development | less than 20 kt | [1] [6] [7] | Simultaneous, separate holes. | ||
| Tun - 1 | December 10, 1969 15:30:00.07 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U10am1 37°10′04″N116°04′49″W / 37.16771°N 116.08023°W | 1,323 m (4,341 ft) – 193.55 m (635.0 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 2.5 kt | Venting detected on site | [1] [4] [6] [7] [8] [11] | Simultaneous, separate holes. | |
| Tun - 2 | December 10, 1969 15:30:00.07 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U10am2 37°10′10″N116°04′49″W / 37.16945°N 116.08019°W | 1,324 m (4,344 ft) – 194 m (636 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 2 kt | Venting detected on site, 72 Ci (2,700 GBq) | [1] [6] [7] [8] [9] [11] | Simultaneous, separate holes. | |
| Tun - 3 | December 10, 1969 15:30:00.07 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U10am3 37°10′04″N116°04′41″W / 37.16769°N 116.07797°W | 1,319 m (4,327 ft) – 194 m (636 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 2 kt | Venting detected on site | [1] [6] [7] [8] [9] [11] | Simultaneous, separate holes. | |
| Tun - 4 | December 10, 1969 15:30:00.07 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U10am4 37°10′10″N116°04′41″W / 37.16947°N 116.07796°W | 1,320 m (4,330 ft) – 256 m (840 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 3 kt | Venting detected on site | [1] [6] [7] [8] [9] [11] | Simultaneous, separate holes. | |
| Grape A | December 17, 1969 15:00:00.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U7s 37°05′00″N116°00′10″W / 37.08333°N 116.00266°W | 1,274 m (4,180 ft) – 550.67 m (1,806.7 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 89 kt | [1] [5] [6] [7] [10] | |||
| Lovage | December 17, 1969 15:15:00.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U3fe 37°00′24″N116°01′25″W / 37.00661°N 116.02356°W | 1,181 m (3,875 ft) – 378.05 m (1,240.3 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 16 kt | [1] [5] [6] [7] [10] | |||
| Terrine-White - 1 | December 18, 1969 19:00:00.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U9bi1 37°07′14″N116°02′08″W / 37.12044°N 116.03551°W | 1,264 m (4,147 ft) – 461.77 m (1,515.0 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 38 kt | Venting detected, 48 Ci (1,800 GBq) | [1] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] | Simultaneous, separate holes. | |
| Terrine-Yellow - 2 | December 18, 1969 19:00:00.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U9bi2 37°07′14″N116°01′47″W / 37.12044°N 116.0297°W | 1,277 m (4,190 ft) – 417 m (1,368 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | unknown yield | Venting detected | [1] [6] [7] [8] [9] | Simultaneous, separate holes. | |
| Fob-Blue - 3 | January 23, 1970 16:30:00.21 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U9iy27 37°08′26″N116°02′01″W / 37.14063°N 116.03351°W | 1,273 m (4,177 ft) + | underground shaft, weapons development | less than 20 kt | [1] [6] [7] | Simultaneous, separate holes. | ||
| Fob-Green - 1 | January 23, 1970 16:30:00.21 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U9iv27 37°08′26″N116°02′16″W / 37.14066°N 116.03764°W | 1,266 m (4,154 ft) – 266.7 m (875 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 8 kt | [1] [5] [6] [7] | Simultaneous, separate holes. | ||
| Fob-Red - 2 | January 23, 1970 16:30:00.21 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U9iv24 37°08′15″N116°02′16″W / 37.13737°N 116.03765°W | 1,263 m (4,144 ft) + | underground shaft, weapons development | less than 20 kt | [1] [6] [7] | Simultaneous, separate holes. | ||
| Ajo | January 30, 1970 17:00:00.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U3gd 37°01′51″N116°02′08″W / 37.03079°N 116.03562°W | 1,191 m (3,907 ft) – 304.11 m (997.7 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 20 kt | [1] [4] [5] [6] [7] | |||
| Belen | February 4, 1970 17:00:00.07 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U3br 37°03′18″N116°02′23″W / 37.05497°N 116.03971°W | 1,206 m (3,957 ft) – 420.8 m (1,381 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 97 kt | [1] [6] [7] [10] [11] | |||
| Grape B | February 4, 1970 17:00:00.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U7v 37°05′53″N116°01′39″W / 37.09804°N 116.02737°W | 1,269 m (4,163 ft) – 554.46 m (1,819.1 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 120 kt | [1] [5] [6] [7] [10] | |||
| Labis | February 5, 1970 15:00:00.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U10an 37°09′50″N116°02′23″W / 37.16392°N 116.0397°W | 1,286 m (4,219 ft) – 441.96 m (1,450.0 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 25 kt | [1] [5] [6] [7] | |||
| Diana Mist | February 11, 1970 19:15:00.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U12n.06 37°12′04″N116°12′22″W / 37.20123°N 116.2061°W | 2,229 m (7,313 ft) – 402.02 m (1,319.0 ft) | tunnel, weapon effect | 12 kt | [1] [4] [6] [7] [10] | |||
| Cumarin | February 25, 1970 14:28:38.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U3gz 37°02′12″N116°00′00″W / 37.03655°N 116.00013°W | 1,206 m (3,957 ft) – 408.51 m (1,340.3 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 51 kt | [1] [5] [6] [7] [10] | |||
| Yannigan-Blue - 2 | February 26, 1970 15:30:00.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U2ay3 37°06′50″N116°04′00″W / 37.11375°N 116.06664°W | 1,258 m (4,127 ft) – 394 m (1,293 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 20 kt | Venting detected | [1] [6] [7] [8] [9] [11] | Simultaneous, separate holes. | |
| Yannigan-Red - 1 | February 26, 1970 15:30:00.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U2ay1 37°06′59″N116°03′44″W / 37.11631°N 116.06232°W | 1,258 m (4,127 ft) – 388.62 m (1,275.0 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 70 kt | Venting detected, 320 Ci (12,000 GBq) | [1] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] | Simultaneous, separate holes. | |
| Yannigan-White - 3 | February 26, 1970 15:30:00.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U2ay2 37°07′05″N116°04′01″W / 37.11793°N 116.06708°W | 1,261 m (4,137 ft) – 363 m (1,191 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 30 kt | Venting detected | [1] [6] [7] [8] [9] [11] | Simultaneous, separate holes. | |
| Cyathus | March 6, 1970 14:24:00.94 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U8b 37°10′23″N116°05′34″W / 37.17311°N 116.09266°W | 1,353 m (4,439 ft) – 289.56 m (950.0 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 8.7 kt | Venting detected, less than 46 Ci (1,700 GBq) | [1] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] | ||
| Arabis-Blue - 3 | March 6, 1970 15:00:00.21 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U9itsz26 37°08′22″N116°02′16″W / 37.13956°N 116.03764°W | 1,265 m (4,150 ft) + | underground shaft, safety experiment | less than 20 kt | [1] [6] [7] | Simultaneous, separate holes. | ||
| Arabis-Green - 2 | March 6, 1970 15:00:00.21 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U9itsx28 37°08′30″N116°02′06″W / 37.14174°N 116.03488°W | 1,270 m (4,170 ft) + | underground shaft, weapons development | less than 20 kt | [1] [6] [7] | Simultaneous, separate holes. | ||
| Arabis-Red - 1 | March 6, 1970 15:00:00.21 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U9itsv26 37°08′22″N116°01′56″W / 37.13955°N 116.03218°W | 1,276 m (4,186 ft) – 249.94 m (820.0 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 3.5 kt | [1] [5] [6] [7] | Simultaneous, separate holes. | ||
| Jal | March 19, 1970 14:03:30.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U3hh 37°00′04″N116°01′25″W / 37.00104°N 116.02359°W | 1,178 m (3,865 ft) – 301.39 m (988.8 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 6 kt | [1] [4] [5] [6] [7] | |||
| Shaper | March 23, 1970 23:05:00.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U7r 37°05′10″N116°01′19″W / 37.08618°N 116.02198°W | 1,252 m (4,108 ft) – 560.44 m (1,838.7 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 89 kt | [1] [5] [6] [7] [10] | |||
| Handley | March 26, 1970 19:00:00.2 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U20m 37°18′02″N116°32′06″W / 37.30042°N 116.535°W | 1,772 m (5,814 ft) – 1,209.14 m (3,967.0 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 1.9 Mt | [1] [4] [5] [6] [7] | |||
| Snubber | April 21, 1970 14:30:00.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U3ev2s 37°03′16″N115°59′21″W / 37.05451°N 115.98926°W | 1,253 m (4,111 ft) – 343.5 m (1,127 ft) | underground shaft, weapon effect | 12.7 kt | Venting detected off site, 55 kCi (2,000 TBq) | [1] [4] [6] [7] [8] [9] | ||
| Can-Green - 1 | April 21, 1970 15:00:00.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U2dd1 37°06′44″N116°04′58″W / 37.11236°N 116.08281°W | 1,266 m (4,154 ft) – 274.32 m (900.0 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 20 kt | [1] [4] [5] [6] [7] | Simultaneous, separate holes. | ||
| Can-Red - 2 | April 21, 1970 15:00:00.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U2dd4 37°06′56″N116°04′52″W / 37.11554°N 116.08098°W | 1,268 m (4,160 ft) + | underground shaft, weapons development | 20 kt | [1] [6] [7] | Simultaneous, separate holes. | ||
| Beebalm | May 1, 1970 14:13:00.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U3fn 37°03′33″N116°01′44″W / 37.0592°N 116.02892°W | 1,209 m (3,967 ft) – 390.21 m (1,280.2 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 1 kt | [1] [4] [6] [7] [10] | |||
| Hod-C (Blue) - 3 | May 1, 1970 14:25:00.0 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U9iz25 37°08′18″N116°01′56″W / 37.13843°N 116.03216°W | 1,276 m (4,186 ft) + | underground shaft, safety experiment | less than 20 kt | [1] [7] [8] | |||
| Hod-A (Green) - 1 | May 1, 1970 14:40:00.17 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U9itsx23 37°08′10″N116°02′06″W / 37.13625°N 116.03492°W | 1,268 m (4,160 ft) – 265.18 m (870.0 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 9 kt | Venting detected on site, 1 Ci (37 GBq) | [1] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] | Simultaneous, separate holes. | |
| Hod-B (Red) - 2 | May 1, 1970 14:40:00.17 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U9itsx20 37°07′59″N116°02′06″W / 37.13295°N 116.03495°W | 1,266 m (4,154 ft) – 241 m (791 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 4 kt | Venting detected | [1] [6] [7] [8] [9] [11] | ||
| Mint Leaf | May 5, 1970 15:30:00.17 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U12t.01 37°12′59″N116°11′04″W / 37.21649°N 116.18441°W | 2,094 m (6,870 ft) – 396.24 m (1,300.0 ft) | tunnel, weapon effect | 20 kt | Venting detected off site, 960 kCi (36,000 TBq) | [1] [4] [6] [7] [8] [9] | ||
| Diamond Dust | May 12, 1970 14:00:00.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U16a.05 37°00′37″N116°12′10″W / 37.0104°N 116.20277°W | 1,899 m (6,230 ft) – 221.89 m (728.0 ft) | tunnel, joint verification | less than 20 kt | Venting detected, 5 Ci (180 GBq) | [1] [6] [7] [8] [9] | Designed to test detection of underground nuclear tests; see Vela Uniform. | |
| Cornice-Green - 2 | May 15, 1970 13:30:00.17 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U10ap3 37°09′43″N116°02′23″W / 37.16186°N 116.03981°W | 1,286 m (4,219 ft) + | underground shaft, weapons development | 40 kt | [1] [6] [7] | Simultaneous, separate holes. | ||
| Cornice-Yellow - 1 | May 15, 1970 13:30:00.17 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U10ap1 37°09′57″N116°02′11″W / 37.16588°N 116.03636°W | 1,293 m (4,242 ft) – 390.14 m (1,280.0 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 45 kt | [1] [4] [5] [6] [7] | Simultaneous, separate holes. | ||
| Manzanas | May 21, 1970 14:00:00.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U3gr 37°00′44″N115°59′34″W / 37.01214°N 115.99265°W | 1,194 m (3,917 ft) – 240.65 m (789.5 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 1 kt | Venting detected on site, less than 0.2 Ci (7.4 GBq) | [1] [4] [6] [7] [8] [9] | ||
| Morrones | May 21, 1970 14:15:00.03 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U3ei 37°04′15″N116°00′50″W / 37.07076°N 116.01387°W | 1,237 m (4,058 ft) – 482.72 m (1,583.7 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 29 kt | [1] [6] [7] [10] | |||
| Hudson Moon | May 26, 1970 14:16:00.17 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U12e.12 37°10′57″N116°12′51″W / 37.18256°N 116.21427°W | 2,274 m (7,461 ft) – 422.45 m (1,386.0 ft) | tunnel, weapon effect | 9 kt | Venting detected on site, 1.3 kCi (48 TBq) | [1] [4] [6] [7] [8] [9] | ||
| Flask-Green - 1 | May 26, 1970 15:00:00.05 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U2az1 37°06′48″N116°03′49″W / 37.11336°N 116.06354°W | 1,251 m (4,104 ft) – 529 m (1,736 ft) | underground shaft, peaceful research | 105 kt | Venting detected, 63 Ci (2,300 GBq) | [1] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] | Simultaneous, Separate holes. Project Plowshare – develop clean devices for hard rock excavation. | |
| Flask-Red - 3 | May 26, 1970 15:00:00.05 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U2az3 37°06′58″N116°04′03″W / 37.11615°N 116.06757°W | 1,259 m (4,131 ft) – 152.4 m (500 ft) | underground shaft, peaceful research | 35 t | Venting detected | [1] [6] [7] [8] [9] | Simultaneous, Separate holes. Project Plowshare – develop clean devices for hard rock excavation. | |
| Flask-Yellow - 2 | May 26, 1970 15:00:00.05 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U2az2 37°07′05″N116°03′49″W / 37.11799°N 116.06364°W | 1,259 m (4,131 ft) – 335 m (1,099 ft) | underground shaft, peaceful research | 90 t | Venting detected | [1] [6] [7] [8] [9] | Simultaneous, Separate holes. Project Plowshare – develop clean devices for hard rock excavation. | |
| Piton C | May 28, 1970 11:45:00.2 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U9itsaa2 37°08′18″N116°01′51″W / 37.13842°N 116.03079°W | 1,279 m (4,196 ft) – 100.58 m (330.0 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 2.5 kt | Venting detected on site, 25 kCi (920 TBq) | [1] [6] [7] [8] [9] | ||
| Piton - 1 | May 28, 1970 12:00:00.164 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U9itsy30 37°08′38″N116°02′01″W / 37.14393°N 116.03349°W | 1,274 m (4,180 ft) – 236.22 m (775.0 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 800 t | Venting detected on site, more than 10 Ci (370 GBq) | [1] [4] [6] [7] [8] [9] | Simultaneous, separate holes. | |
| Piton - 2 | May 28, 1970 12:00:00.164 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U9itsx27 37°08′26″N116°02′06″W / 37.14056°N 116.03497°W | 1,270 m (4,170 ft) + | underground shaft, weapons development | less than 20 kt | Venting detected on site | [1] [6] [7] [8] | Simultaneous, separate holes. | |
| Arnica-Violet - 2 | June 26, 1970 13:00:00.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U2dd3 37°07′02″N116°05′06″W / 37.11716°N 116.08495°W | 1,272 m (4,173 ft) – 264 m (866 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 2 kt | Venting detected, 73 Ci (2,700 GBq) | [1] [6] [7] [8] [9] [11] | Simultaneous, separate holes. | |
| Arnica-Yellow - 1 | June 26, 1970 13:00:00.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U2dd2 37°06′50″N116°05′14″W / 37.11391°N 116.08709°W | 1,270 m (4,170 ft) – 309.37 m (1,015.0 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 3.5 kt | [1] [5] [6] [7] [8] | Simultaneous, separate holes. |
- ↑ A bomb test may be a salvo test, defined as two or more explosions "where a period of time between successive individual explosions does not exceed 5 seconds and where the burial points of all explosive devices can be connected by segments of straight lines, each of them connecting two burial points and does not exceed 40 kilometers in length". [2]
- ↑ The US, France and Great Britain have code-named their test events, while the USSR and China did not, and therefore have only test numbers (with some exceptions – Soviet peaceful explosions were named). Word translations into English in parentheses unless the name is a proper noun. A dash followed by a number indicates a member of a salvo event. The US also sometimes named the individual explosions in such a salvo test, which results in "name1 – 1(with name2)". If test is canceled or aborted, then the row data like date and location discloses the intended plans, where known.
- ↑ To convert the UT time into standard local, add the number of hours in parentheses to the UT time; for local daylight saving time, add one additional hour. If the result is earlier than 00:00, add 24 hours and subtract 1 from the day; if it is 24:00 or later, subtract 24 hours and add 1 to the day. Historical time zone data obtained from the IANA time zone database.
- ↑ Rough place name and a latitude/longitude reference; for rocket-carried tests, the launch location is specified before the detonation location, if known. Some locations are extremely accurate; others (like airdrops and space blasts) may be quite inaccurate. "~" indicates a likely pro-forma rough location, shared with other tests in that same area.
- ↑ Elevation is the ground level at the point directly below the explosion relative to sea level; height is the additional distance added or subtracted by tower, balloon, shaft, tunnel, air drop or other contrivance. For rocket bursts the ground level is "N/A". In some cases it is not clear if the height is absolute or relative to ground, for example, Plumbbob/John. No number or units indicates the value is unknown, while "0" means zero. Sorting on this column is by elevation and height added together.
- ↑ Atmospheric, airdrop, balloon, gun, cruise missile, rocket, surface, tower, and barge are all disallowed by the Partial Nuclear Test Ban Treaty. Sealed shaft and tunnel are underground, and remained useful under the PTBT. Intentional cratering tests are borderline; they occurred under the treaty, were sometimes protested, and generally overlooked if the test was declared to be a peaceful use.
- ↑ Include weapons development, weapon effects, safety test, transport safety test, war, science, joint verification and industrial/peaceful, which may be further broken down.
- ↑ Designations for test items where known, "?" indicates some uncertainty about the preceding value, nicknames for particular devices in quotes. This category of information is often not officially disclosed.
- ↑ Estimated energy yield in tons, kilotons, and megatons. A ton of TNT equivalent is defined as 4.184 gigajoules (1 gigacalorie).
- ↑ Radioactive emission to the atmosphere aside from prompt neutrons, where known. The measured species is only iodine-131 if mentioned, otherwise it is all species. No entry means unknown, probably none if underground and "all" if not; otherwise notation for whether measured on the site only or off the site, where known, and the measured amount of radioactivity released.