| Operation Emery | |
|---|---|
 Unexpected venting from the Baneberry nuclear test | |
| Information | |
| Country | United States |
| Test site |
|
| Period | 1970–1971 |
| Number of tests | 16 |
| Test type | underground shaft, tunnel |
| Max. yield | 220 kilotonnes of TNT (920 TJ) |
| Test series chronology | |
The United States's Emery nuclear test series [1] was a group of 16 nuclear weapons tests conducted in 1970 and 1971. These tests [note 1] followed the Operation Mandrel series and preceded the Operation Grommet series.
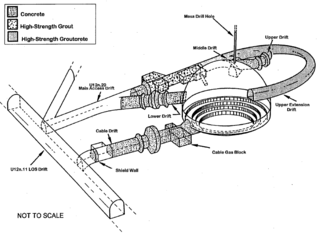
The underground Baneberry test vented into the atmosphere. For descriptions, see Yucca Flat#Baneberry and List of military nuclear accidents#1970s
| Name [note 2] | Date time (UT) | Local time zone [note 3] [2] | Location [note 4] | Elevation + height [note 5] | Delivery [note 6] Purpose [note 7] | Device [note 8] | Yield [note 9] | Fallout [note 10] | References | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scree-Acajou - 1 | October 13, 1970 15:05:00.02 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U9itsx24 37°08′15″N116°02′06″W / 37.1374°N 116.03491°W | 1,269 m (4,163 ft) – 249.33 m (818.0 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 1 kt | Venting detected on site, 11 Ci (410 GBq) | [1] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] | Simultaneous, separate holes. | |
| Scree-Alhambra - 2 | October 13, 1970 15:05:00.02 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U9itsz21 37°08′03″N116°01′57″W / 37.13406°N 116.0324°W | 1,273 m (4,177 ft) – 192 m (630 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 2 kt | Venting detected on site | [1] [3] [4] [6] [7] [8] | Simultaneous, separate holes. | |
| Scree-Chamois - 3 | October 13, 1970 15:05:00.02 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U9itsz24 37°08′14″N116°01′56″W / 37.13733°N 116.03217°W | 1,275 m (4,183 ft) + | underground shaft, safety experiment | less than 20 kt | Venting detected on site | [1] [3] [6] [7] | Simultaneous, separate holes. | |
| Tijeras | October 14, 1970 14:30:00.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U7y 37°04′15″N116°00′20″W / 37.07085°N 116.00566°W | 1,249 m (4,098 ft) – 560.62 m (1,839.3 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 89 kt | [1] [6] [7] [9] [10] | |||
| Truchas-Chacon - 1 | October 28, 1970 14:30:00.03 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U3hn 37°00′50″N116°01′07″W / 37.01401°N 116.01867°W | 1,182 m (3,878 ft) – 118.38 m (388.4 ft) | underground shaft, safety experiment | unknown yield | Venting detected on site | [1] [3] [6] [7] | Simultaneous, separate holes. | |
| Truchas-Chamisal - 2 | October 28, 1970 14:30:00.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U3ho 37°00′50″N116°01′05″W / 37.01398°N 116.01799°W | 1,182 m (3,878 ft) – 118 m (387 ft) | underground shaft, safety experiment | unknown yield | Venting detected on site, 3 Ci (110 GBq) | [1] [3] [4] [6] [7] | Simultaneous, separate holes. | |
| Truchas-Rodarte - 3 | October 28, 1970 14:30:00.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U3hm 37°00′53″N116°01′12″W / 37.01479°N 116.02007°W | 1,183 m (3,881 ft) + | underground shaft, weapons development | 8 kt | Venting detected on site | [1] [3] [6] [7] | Simultaneous, separate holes. | |
| Abeytas | November 5, 1970 15:00:00.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U3gx 37°01′46″N116°00′45″W / 37.02947°N 116.01244°W | 1,188 m (3,898 ft) – 393.46 m (1,290.9 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 20 kt | [1] [6] [7] [9] [10] | |||
| Penasco | November 19, 1970 15:00:00.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U3hl 37°00′53″N116°01′00″W / 37.01474°N 116.01665°W | 1,183 m (3,881 ft) – 270.92 m (888.8 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 2 kt | [1] [5] [6] [7] [8] | |||
| Carrizozo - 1 (with Corazon) | December 3, 1970 15:07:00.0 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U3hr 37°00′22″N116°02′27″W / 37.00608°N 116.04079°W | 1,183 m (3,881 ft) + | underground shaft, weapons development | less than 20 kt | [1] [6] [7] | |||
| Corazon - 2 (with Corrizozo) | December 3, 1970 15:07:00.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U3ha 37°00′07″N116°02′19″W / 37.00202°N 116.03865°W | 1,180 m (3,870 ft) – 241.12 m (791.1 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 100 t | [1] [5] [6] [7] | |||
| Artesia | December 16, 1970 16:00:00.09 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U7x 37°06′00″N116°00′32″W / 37.10012°N 116.00881°W | 1,302 m (4,272 ft) – 484.83 m (1,590.6 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 45 kt | [1] [6] [7] [10] | |||
| Avens-Alkermes - 2 | December 16, 1970 16:00:00.17 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U9itsu24 37°08′15″N116°02′21″W / 37.13737°N 116.03903°W | 1,262 m (4,140 ft) + | underground shaft, weapons development | 4 kt | Venting detected on site | [1] [3] [6] [7] | Simultaneous, separate holes. | |
| Avens-Andorre - 1 | December 16, 1970 16:00:00.17 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U9itst28 37°08′30″N116°02′26″W / 37.14173°N 116.04053°W | 1,264 m (4,147 ft) + | underground shaft, weapons development | 4 kt | Venting detected on site | [1] [3] [6] [7] | Simultaneous, separate holes. | |
| Avens-Asamite - 3 | December 16, 1970 16:00:00.17 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U9itsw21 37°08′03″N116°02′11″W / 37.13406°N 116.03632°W | 1,264 m (4,147 ft) + | underground shaft, weapons development | 4 kt | Venting detected on site | [1] [3] [6] [7] | Simultaneous, separate holes. | |
| Avens-Cream - 4 | December 16, 1970 16:00:00.17 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U9itsx29 37°08′34″N116°02′06″W / 37.1428°N 116.03502°W | 1,271 m (4,170 ft) – 292.91 m (961.0 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 20 kt | Venting detected on site, 66 Ci (2,400 GBq) | [1] [3] [4] [6] [7] [10] | Simultaneous, separate holes. | |
| Canjilon | December 16, 1970 16:00:00.05 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U3fq 37°04′21″N116°01′33″W / 37.07247°N 116.02586°W | 1,227 m (4,026 ft) – 302.19 m (991.4 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | less than 20 kt | [1] [6] [7] | |||
| Carpetbag | December 17, 1970 16:05:00.16 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U2dg 37°07′46″N116°05′01″W / 37.12931°N 116.08365°W | 1,284 m (4,213 ft) – 661.42 m (2,170.0 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 220 kt | Venting detected, 5 Ci (180 GBq) | [1] [3] [4] [6] [7] [10] | ||
| Baneberry | December 18, 1970 15:30:00.2 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U8d 37°10′23″N116°05′59″W / 37.17309°N 116.09973°W | 1,367 m (4,485 ft) – 277.98 m (912.0 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 10 kt | Venting detected off site, 6.7 MCi (250 PBq) | [1] [3] [4] [6] [7] [10] [11] | 6-month moratorium caused by 6.7 MCi (250 PBq) escaped radioactivity in this test. | |
| Embudo | June 16, 1971 14:50:00.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U3hd 37°01′59″N116°00′52″W / 37.03318°N 116.01435°W | 1,191 m (3,907 ft) – 303.06 m (994.3 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 18 kt | [1] [5] [6] [7] [10] | |||
| Dexter | June 23, 1971 14:00:00.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U3hs 37°00′47″N116°01′02″W / 37.01319°N 116.01716°W | 1,182 m (3,878 ft) – 119.94 m (393.5 ft) | underground shaft, safety experiment | less than 20 kt | [1] [6] [7] | |||
| Laguna | June 23, 1971 15:30:00.04 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U3fd 37°01′19″N116°01′24″W / 37.02195°N 116.02345°W | 1,186 m (3,891 ft) – 454.92 m (1,492.5 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 20 kt | [1] [6] [7] [9] [10] | |||
| Harebell | June 24, 1971 14:00:00.16 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U2br 37°08′48″N116°04′04″W / 37.14665°N 116.0677°W | 1,287 m (4,222 ft) – 518.77 m (1,702.0 ft) | underground shaft, weapons development | 38 kt | Venting detected, 840 Ci (31,000 GBq) | [1] [3] [4] [6] [7] [10] | ||
| Camphor | June 29, 1971 18:30:00.16 | PST (–8 hrs) | NTS Area U12g.10 37°10′36″N116°12′45″W / 37.17673°N 116.21237°W | 2,289 m (7,510 ft) – 423.67 m (1,390.0 ft) | tunnel, weapon effect | 20 kt | Venting detected on site, 220 Ci (8,100 GBq) | [1] [3] [4] [6] [7] |
- ↑ A bomb test may be a salvo test, defined as two or more explosions "where a period of time between successive individual explosions does not exceed 5 seconds and where the burial points of all explosive devices can be connected by segments of straight lines, each of them connecting two burial points and does not exceed 40 kilometers in length". Mikhailov, V. N., Editor in Chief. "Catalog of World Wide Nuclear Testing". Begell-Atom, LLC. Archived from the original on April 26, 2014.
{{cite journal}}:|first=has generic name (help); Cite journal requires|journal=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ The US, France and Great Britain have code-named their test events, while the USSR and China did not, and therefore have only test numbers (with some exceptions – Soviet peaceful explosions were named). Word translations into English in parentheses unless the name is a proper noun. A dash followed by a number indicates a member of a salvo event. The US also sometimes named the individual explosions in such a salvo test, which results in "name1 – 1(with name2)". If test is canceled or aborted, then the row data like date and location discloses the intended plans, where known.
- ↑ To convert the UT time into standard local, add the number of hours in parentheses to the UT time; for local daylight saving time, add one additional hour. If the result is earlier than 00:00, add 24 hours and subtract 1 from the day; if it is 24:00 or later, subtract 24 hours and add 1 to the day. Historical time zone data obtained from the IANA time zone database.
- ↑ Rough place name and a latitude/longitude reference; for rocket-carried tests, the launch location is specified before the detonation location, if known. Some locations are extremely accurate; others (like airdrops and space blasts) may be quite inaccurate. "~" indicates a likely pro-forma rough location, shared with other tests in that same area.
- ↑ Elevation is the ground level at the point directly below the explosion relative to sea level; height is the additional distance added or subtracted by tower, balloon, shaft, tunnel, air drop or other contrivance. For rocket bursts the ground level is "N/A". In some cases it is not clear if the height is absolute or relative to ground, for example, Plumbbob/John. No number or units indicates the value is unknown, while "0" means zero. Sorting on this column is by elevation and height added together.
- ↑ Atmospheric, airdrop, balloon, gun, cruise missile, rocket, surface, tower, and barge are all disallowed by the Partial Nuclear Test Ban Treaty. Sealed shaft and tunnel are underground, and remained useful under the PTBT. Intentional cratering tests are borderline; they occurred under the treaty, were sometimes protested, and generally overlooked if the test was declared to be a peaceful use.
- ↑ Include weapons development, weapon effects, safety test, transport safety test, war, science, joint verification and industrial/peaceful, which may be further broken down.
- ↑ Designations for test items where known, "?" indicates some uncertainty about the preceding value, nicknames for particular devices in quotes. This category of information is often not officially disclosed.
- ↑ Estimated energy yield in tons, kilotons, or megatons. A ton of TNT equivalent is defined as 4.184 gigajoules (1 gigacalorie).
- ↑ Radioactive emission to the atmosphere aside from prompt neutrons, where known. The measured species is only iodine-131 if mentioned, otherwise it is all species. No entry means unknown, probably none if underground and "all" if not; otherwise notation for whether measured on the site only or off the site, where known, and the measured amount of radioactivity released.