Related Research Articles

A brothel, bordello, bawdy house, ranch, house of ill repute, house of ill fame, or whorehouse is a place where people engage in sexual activity with prostitutes. However, for legal or cultural reasons, establishments often describe themselves as massage parlors, bars, strip clubs, body rub parlours, studios, or by some other description. Sex work in a brothel is considered safer than street prostitution.

Street prostitution is a form of prostitution in which a prostitute solicits customers from a public place, most commonly a street, while waiting at street corners or walking alongside a street, but also other public places such as parks, benches, etc. The street prostitute is often dressed in a provocative manner. The sex act may be performed in the customer's car, in a nearby secluded street location, or at the prostitute's residence or in a rented motel room.

Prostitution in Germany is legal, as are other aspects of the sex industry, including brothels, advertisement, and job offers through HR companies. Full-service sex work is widespread and regulated by the German government, which levies taxes on it. In 2016, the government adopted a new law, the Prostitutes Protection Act, in an effort to improve the legal situation of sex workers, while also now enacting a legal requirement for registration of prostitution activity and banning prostitution which involves no use of condoms. The social stigmatization of sex work persists and many workers continue to lead a double life. Human rights organizations consider the resulting common exploitation of women from East Germany to be the main problem associated with the profession.

Prostitution in the Netherlands is legal and regulated. Operating a brothel is also legal. De Wallen, the largest and best-known Red-light district in Amsterdam, is a destination for international sex tourism.

Male prostitution is a form of sex work consisting of act or practice of men providing sexual services in return for payment. Although clients can be of any gender, the vast majority are older males looking to fulfill their sexual needs. Male prostitutes have been far less studied than female prostitutes by researchers. Even so, male prostitution has an extensive history including regulation through homosexuality, conceptual developments on sexuality, and the HIV/AIDS epidemic impact. In the last century, male sex work has seen various advancements such as popularizing new sexual acts, methods of exchange, and carving out a spot in cinema.

In Great Britain, the act of engaging in sex or exchanging various sexual services for money is legal, but a number of related activities, including soliciting in a public place, kerb crawling, owning or managing a brothel, and pimping, are illegal. In Northern Ireland, which previously had similar laws, paying for sex became illegal from 1 June 2015.
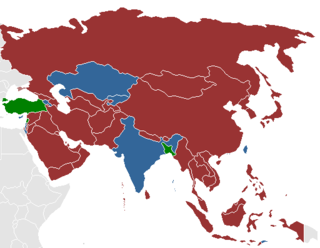
Prostitution is legal in India, but a number of related activities including soliciting, kerb crawling, owning or managing a brothel, prostitution in a hotel, child prostitution, pimping and pandering are illegal. There are, however, many brothels illegally operating in Indian cities including Mumbai, Delhi, Kolkata, Pune, and Nagpur, among others. UNAIDS estimate there were 657,829 prostitutes in the country as of 2016. Other unofficial estimates have calculated India has roughly 3 million prostitutes. India is widely regarded as having one of the world's largest commercial sex industry. It has emerged as a global hub of sex tourism, attracting sex tourists from wealthy countries. The sex industry in India is a multi-billion dollar one, and one of the fastest growing.
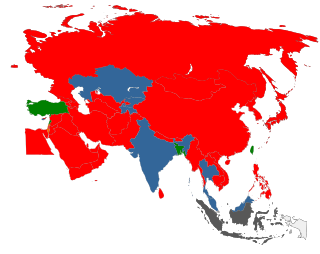
The legality of prostitution in Asia varies by country. There is often a significant difference in Asia between prostitution laws and the practice of prostitution. In 2011, the Asian Commission on AIDS estimated there were 10 million sex workers in Asia and 75 million male customers.

Prostitution is illegal in the vast majority of the United States as a result of state laws rather than federal laws. It is, however, legal in some rural counties within the state of Nevada. Additionally, it is decriminalized to sell sex in the state of Maine, but illegal to buy sex. Prostitution nevertheless occurs elsewhere in the country.
Prostitution in Myanmar is illegal, but widespread. Prostitution is a major social issue that particularly affects women and children. UNAIDS estimate there to be 66,000 prostitutes in the country.

Prostitution is the business or practice of engaging in sexual activity in exchange for payment. The definition of "sexual activity" varies, and is often defined as an activity requiring physical contact with the customer. The requirement of physical contact also creates the risk of transferring infections. Prostitution is sometimes described as sexual services, commercial sex or, colloquially, hooking. It is sometimes referred to euphemistically as "the world's oldest profession" in the English-speaking world. A person who works in the field is usually called a prostitute or sex worker, but other words, such as hooker and whore, are sometimes used pejoratively to refer to those who work as prostitutes.
Prostitution in Trinidad and Tobago is legal but related activities such as brothel keeping, soliciting and pimping are illegal.
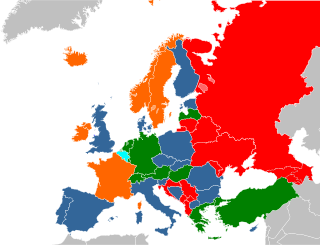
The legality of prostitution in Europe varies by country.
Prostitution in Croatia is illegal but common. Forcible prostitution, any kind of brothels, or procuring are treated as a felony, while voluntary prostitution is considered to be infraction against public order. Like in many other Southeast European countries, the problem of human trafficking for the purposes of sex is big in Croatia.

The sex industry consists of businesses that either directly or indirectly provide sex-related products and services or adult entertainment. The industry includes activities involving direct provision of sex-related services, such as prostitution, strip clubs, host and hostess clubs and sex-related pastimes, such as pornography, sex-oriented men's magazines, women's magazines, sex movies, sex toys and fetish or BDSM paraphernalia. Sex channels for television and pre-paid sex movies for video on demand, are part of the sex industry, as are adult movie theaters, sex shops, peep shows, and strip clubs. The sex industry employs millions of people worldwide, mainly women. These range from the sex worker, also called adult service provider (ASP), who provides sexual services, to a multitude of support personnel.
Prostitution in Namibia is legal and a highly prevalent common practice. Related activities such as solicitation, procuring and being involved in the running of a brothel are illegal. A World Bank study estimated there were about 11,000 prostitutes in Namibia.
Prostitution in Algeria is legal but most related activities such as brothel-keeping and solicitation are criminalised. Coastal resorts, particularly Tichy, are destinations for sex tourism. As of 2017 there were only two brothels in Algeria.
Prostitution in Hawaii is illegal but common. There are about 150 brothels in Oahu alone.
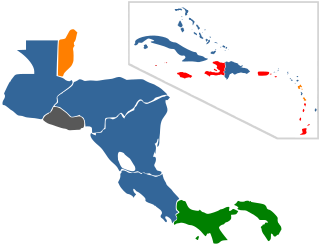
Legality of prostitution in the Americas varies by country. Most countries only legalized prostitution, with the act of exchanging money for sexual services legal. The level of enforcement varies by country. One country, the United States, is unique as legality of prostitution is not the responsibility of the federal government, but rather state, territorial, and federal district's responsibility.
Prostitution in Oceania varies greatly across the region. In American Samoa, for instance, prostitution is illegal, whereas in New Zealand most aspects of the trade are decriminalised.
References
- ↑ Huggins, Nathan Irvin. ''Harlem Renaissance''. New York: Oxford UP, 1971. Print. Pg. 87
- ↑ "Divorce Raids". October 5, 2009.
- ↑ Robertson, S. "Harlem Undercover: Vice Investigators, Race, and Prostitution, 1910--1930." ''Journal of Urban History'' 35.4 (2009): 486-504. Web.
- ↑ Gilfoyle, Timothy J. ''City of Eros: New York City, Prostitution, and the Commercialization of Sex, 1790-1920''. New York, NY: W.W. Norton, 1992. Print.