
Usnea is a genus of mostly pale grayish-green fruticose lichens that grow like leafless mini-shrubs or tassels anchored on bark or twigs. The genus is in the family Parmeliaceae. It grows all over the world. Members of the genus are commonly called old man's beard, beard lichen, or beard moss.

The Parmeliaceae is a large and diverse family of Lecanoromycetes. With over 2700 species in 71 genera, it is the largest family of lichen-forming fungi. The most speciose genera in the family are the well-known groups: Xanthoparmelia, Usnea, Parmotrema, and Hypotrachyna.

Ramalina is a genus of greenish fruticose lichens that grow in the form of flattened, strap-like branches. Members of the genus are commonly called strap lichens or cartilage lichens. Apothecia are lecanorine.

Pannaria is a genus of lichen-forming fungi in the family Pannariaceae. The widespread genus contains an estimated 51 species, found primarily in tropical regions.

Lethariella is a genus of fruticose lichens in the family Parmeliaceae. The genus was originally proposed as a subgenus of Usnea by Polish lichenologist Józef Motyka in his 1936 monograph of that genus. Norwegian botanist Hildur Krog elevated the taxon to generic status in 1976.

Hypogymnia is a genus of foliose lichens in the family Parmeliaceae. They are commonly known as tube lichens, bone lichens, or pillow lichens. Most species lack rhizines that are otherwise common in members of the Parmeliaceae, and have swollen lobes that are usually hollow. Other common characteristics are relatively small spores and the presence of physodic acid and related lichen products. The lichens usually grow on the bark and wood of coniferous trees.

Myelochroa is a genus of foliose lichens in the family Parmeliaceae. They are commonly known as axil-bristle lichens. It was created in 1987 to contain species formerly placed in genus Parmelina that had a yellow-orange medulla due to the presence of secalonic acids. Characteristics of the genus include tightly attached thalli with narrow lobes, cilia on the axils, and a rhizinate black lower surface. Chemical characteristics are the production of zeorin and related triterpenoids in the medulla. Myelochroa contains about 30 species, most of which grow on bark. The genus has centres of distribution in Asia and North America.

Flavopunctelia is a genus of foliose lichens in the family Parmeliaceae. The genus contains species that are widespread in temperate and tropical areas. The genus is characterised by broad, yellow-green lobes, point-like (punctiform) pseudocyphellae on the thallus surface, and bifusiform conidia. All species contain usnic acid as a major secondary chemical in the cortex. Flavopunctelia was originally conceived as a subgenus of Punctelia by Hildur Krog in 1982; Mason Hale promoted it to generic status in 1984.

Flavoparmelia is a genus of foliose lichens in the family Parmeliaceae. Because of their appearance, they are commonly known as greenshield lichens. The widely distributed genus contains 32 species. It was circumscribed by American lichenologist Mason Hale in 1986 to contain 17 former Pseudoparmelia species with broad lobes, usnic acid in the cortex, and isolichenan in the cell walls.

Punctelia is a genus of foliose lichens belonging to the large family Parmeliaceae. The genus, which contains about 50 species, was segregated from genus Parmelia in 1982. Characteristics that define Punctelia include the presence of hook-like to thread-like conidia, simple rhizines, and point-like pseudocyphellae. It is this last feature that is alluded to in the vernacular names speckled shield lichens or speckleback lichens.
Menegazzia fumarprotocetrarica is a species of corticolous (bark-dwelling), foliose lichen found in South America. It was formally described as a new species in 1996 by Mónica Adler and Susana Calvelo. The type specimen was collected by the second author from Bariloche. The species epithet refers to the presence of protocetraric acid, a lichen product that is rare in the genus Menegazzia. The lichen grows on the hard bark of Nothofagus alpina, N. dombeyi, and Araucaria araucana.

Crespoa is a genus of five species of lichen in the family Parmeliaceae. Species in this genus are characterized by having an upper thallus surface that is wrinkled and reticulately ridged to coarsely foveolate.
Emodomelanelia is a lichen genus in the family Parmeliaceae. It is monotypic, containing the single foliose Himalayan species Emodomelanelia masonii.
Thomas Hawkes Nash III is an American lichenologist. His research is about the biology and ecology of lichens, and the effects of air pollution on plants and lichens. He is known as an authority on the family Parmeliaceae. During his long career at the Arizona State University, he helped develop the lichen herbarium into a world-class collection with over 100,000 specimens representing more than 5000 species. In 2010, the year of his retirement, he was awarded the Acharius Medal for lifetime achievements in lichenology, and the following year had a Festschrift published in his honor.
John Alan (Jack) Elix emeritus professor in chemistry at the Australian National University, is an organic chemist who has contributed in many fields: lichenology, lichen chemotaxonomy, plant physiology and biodiversity and natural product chemistry. He has authored 2282 species names, and 67 genera in the field of mycology.

Constipatic acid is a fatty acid found in several lichen species. It was isolated, identified, and named by Douglas Chester and John Alan Elix in a 1979 publication. The compound was extracted from the Australian leafy lichen called Xanthoparmelia constipata, which was collected on schist boulders west of Springton, South Australia. The related compounds protoconstipatic acid and dehydroconstipatic acid were also reported concurrently. Syo Kurokawa and Rex Filson had previously detected the compounds using thin-layer chromatography when they formally described the lichen as a new species in 1975, but had not characterised them chemically.

Punctelia punctilla is a species of foliose lichen in the family Parmeliaceae. It is found in Africa, South America, and North America, where it grows on bark and on rocks. The main characteristics that distinguish Punctelia punctilla from other species of Punctelia are the presence of isidia on the thallus surface, a pale brown thallus undersurface, and the presence of lecanoric acid in the medulla.
Flavopunctelia darrowii is a species of foliose lichen in the family Parmeliaceae. It was first formally described as a new species by John Walter Thomson in 1950 as Parmelia darrowi. It is named after American botanist Robert Arthur Darrow. In 1982, Hildur Krog transferred it to the subgenus Flavopunctelia of her newly circumscribed genus Punctelia, created to contain Parmelia species with punctate (point-like) pseudocyphellae. Mason Hale raised this subgenus to generic status a couple of years later.
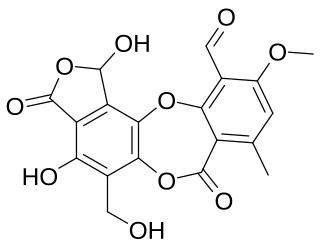
Constictic acid is a chemical compound of the depsidone class. It was first isolated in 1968 from lichen of the genus Usnea. It has since been found in many other lichen genera including Menegazzia, Crespoa, and Xanthoparmelia.













