
Psilocybe semilanceata, commonly known as the liberty cap, is a species of fungus which produces the psychoactive compounds psilocybin, psilocin and baeocystin. It is both one of the most widely distributed psilocybin mushrooms in nature, and one of the most potent. The mushrooms have a distinctive conical to bell-shaped cap, up to 2.5 cm (1 in) in diameter, with a small nipple-like protrusion on the top. They are yellow to brown, covered with radial grooves when moist, and fade to a lighter color as they mature. Their stipes tend to be slender and long, and the same color or slightly lighter than the cap. The gill attachment to the stipe is adnexed, and they are initially cream-colored before tinting purple to black as the spores mature. The spores are dark purplish-brown in mass, ellipsoid in shape, and measure 10.5–15 by 6.5–8.5 micrometres.

Psilocybe tampanensis is a very rare psychedelic mushroom in the family Hymenogastraceae. Originally collected in the wild in a sandy meadow near Tampa, Florida, in 1977, the fungus would not be found in Florida again until 44 years later. The original Florida specimen was cloned, and descendants remain in wide circulation. The fruit bodies (mushrooms) produced by the fungus are yellowish-brown in color with convex to conic caps up to 2.4 cm (0.9 in) in diameter atop a thin stem up to 6 cm (2.4 in) long. Psilocybe tampanensis forms psychoactive truffle-like sclerotia that are known and sold under the nickname "philosopher's stones". The fruit bodies and sclerotia are consumed by some for recreational or entheogenic purposes. In nature, sclerotia are produced by the fungus as a rare form of protection from wildfires and other natural disasters.

Psilocybe quebecensis is a moderately active hallucinogenic mushroom in the section Aztecorum, having psilocybin and psilocin as main active compounds. Native to Quebec, it is the most northern known psilocybin mushroom after Psilocybe semilanceata in northern Scandinavia. Macroscopically this mushroom somewhat resembles Psilocybe baeocystis.

Psilocybe baeocystis is a psilocybin mushroom of the family Hymenogastraceae. It contains the hallucinogenic compounds psilocybin, psilocin and baeocystin. The species is commonly known by various names such as bottle caps, knobby tops, blue bells, olive caps.

Psilocybe ovoideocystidiata is a psilocybin mushroom, having psilocybin and/or psilocin as main active compounds. It is closely related to P. subaeruginascens from Java, P. septentrionalis from Japan, and P. wayanadensis from India. This mushroom was first documented by Richard V. Gaines in Montgomery County, Pennsylvania in June 2003. Although it is sometimes confused with Psilocybe caerulipes, it can be distinguished by its rhomboid spores, larger stature, earlier fruiting season and membranous annulus.

Psilocybe caerulipes, commonly known as blue-foot, is a rare psilocybin mushroom of the family Hymenogastraceae, having psilocybin and psilocin as main active compounds. An older synonym is Agaricus caerulipes.

Psilocybe aucklandiae is a species of agaric fungus in the family Hymenogastraceae. The species is known from the Auckland Region of New Zealand, where it grows from clay soils in exotic pine plantations and native forests. It is phylogenetically similar to or almost the same as Psilocybe zapotecorum from Mexico and South America. As a blueing member of the genus Psilocybe it contains the psychoactive compounds psilocin and psilocybin.
Psilocybe graveolens is an extremely rare psilocybin mushroom which has psilocybin and psilocin as main active compounds, discovered in the salt marshes or "meadows" of Hackensack, New Jersey. This mushroom is known for its strong and persistent odor.

Psilocybe caerulescens, also known as landslide mushroom, is a psilocybin mushroom having psilocybin and psilocin as main active compounds. Along with Psilocybe mexicana and Psilocybe aztecorum, it is one of the mushrooms likely to have been used by the Aztecs and is currently used by Mazatec shamans for its entheogenic properties.

Psilocybe aztecorum is a species of psilocybin mushroom in the family Hymenogastraceae. Known from Arizona, Colorado, central Mexico, India and Costa Rica, the fungus grows on decomposing woody debris and is found in mountainous areas at elevations of 2,000 to 4,000 m, typically in meadows or open, grassy conifer forests. The mushrooms have convex to bell-shaped caps 1.5–2 cm (0.6–0.8 in) in diameter, atop slender cylindrical stems that are up to 7.5 cm (3.0 in) long. The color of the caps changes with variations in hydration, ranging from dark chestnut brown to straw yellow or whitish when dry. The base of the stem is densely covered with conspicuous white rhizomorphs, a characteristic uncommon amongst Psilocybe species.
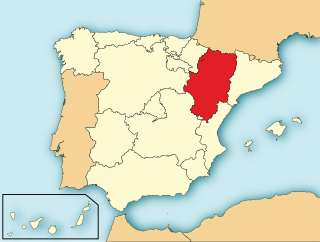
Psilocybe hispanica is a species of fungus in the family Hymenogastraceae. It produces small brown mushrooms with conical to convex caps up to 10 mm (0.4 in) in diameter and stems 16 to 25 mm long by 0.5 to 1 mm thick. Reported as new to science in 2000, it is only known from the Pyrenees mountain range in northern Spain and southwestern France, where it grows on horse dung in grass fields at elevations of 1,700 to 2,300 m. The mushroom contains the psychoactive compound psilocybin. The possible depiction of this species in the 6,000-year-old Selva Pascuala rock art suggests that it might have been used in ancient religious rituals—the oldest evidence of such usage in prehistoric Europe.

Psilocybe hoogshagenii is a species of psilocybin mushroom in the family Hymenogastraceae. The mushroom has a brownish conical or bell-shaped cap up to 3 cm (1.2 in) wide that has an extended papilla up to 4 mm long. The stem is slender and 5 to 9 cm long. The variety P. hoogshagenii var. convexa lacks the long papilla.

Psilocybe makarorae is a species of psilocybin mushroom in the family Hymenogastraceae. Officially described as new to science in 1995, it is known only from New Zealand, where it grows on rotting wood and twigs of southern beeches. The fruit body (mushroom) has a brownish cap with lighter coloured margins, measuring up to 3.5 cm (1.4 in) wide. The cap shape is either conical, bell-shaped, or flat depending on the age of the mushroom, and it features a prominent umbo. Although the whitish stem does not form a true ring, it retains remnants of the partial veil that covers and protects the gills of young fruit bodies. P. makarorae mushrooms can be distinguished from the similar North American species Psilocybe caerulipes by microscopic characteristics such as the presence of cystidia on the gill faces (pleurocystidia), and cheilocystidia with more elongated necks. Based on the bluing reaction to injury, P. makarorae is presumed to contain the psychedelic compounds psilocybin and psilocin.
Psilocybe subcaerulipes is a species of fungus in the family Hymenogastraceae. It is in the section Zapotecorum of the genus Psilocybe, other members of this section include Psilocybe muliercula, Psilocybe angustipleurocystidiata, Psilocybe aucklandii, Psilocybe collybioides, Psilocybe kumaenorum, Psilocybe zapotecorum, Psilocybe pintonii, Psilocybe graveolens, Psilocybe moseri, Psilocybe zapotecoantillarum, Psilocybe zapotecocaribaea, and Psilocybe antioquiensis. It is endemic to Japan. Fruit bodies grow on the ground in woody debris, and typically stand 6 to 8 cm tall with caps that are 2.5 to 5 cm in diameter. They are chestnut brown, and stain blue if bruised or handled. The species is a psychoactive mushroom, and contains the hallucinogenic compounds psilocybin and psilocin. There have been reports of poisoning caused by the accidental consumption of this mushroom. It has been used in research, specifically, to test the effects of its consumption of marble-burying in mice, an animal model of obsessive-compulsive disorder.
Psilocybe tasmaniana is a species of coprophilous agaric fungus in the family Hymenogastraceae. It was described by Gastón Guzmán and Roy Watling in 1978 as a small tawny orange mushroom that grows on dung, with a slight blueing reaction to damage, known only from Tasmania and southeastern Australia. It was likened to Psilocybe subaeruginosa although characteristics, appearance, and the association with dung were not typical for that species. As a blueing member of the genus Psilocybe it contains the psychoactive compounds psilocin and psilocybin.

Psilocybe pelliculosa is a species of fungus in the family Hymenogastraceae. The fruit bodies, or mushrooms, have a conical brownish cap up to 2 cm in diameter atop a slender stem up to 8 cm long. It has a white partial veil that does not leave a ring on the stem. American mycologist Alexander H. Smith first described the species in 1937 as a member of the genus known today as Psathyrella; it was transferred to Psilocybe by Rolf Singer in 1958.

Psilocybe neoxalapensis is a species of psilocybin mushroom in the family Hymenogastraceae. Found in Veracruz, Mexico, it was originally described in 2005 under the name Psilocybe novoxalapensis, but this naming was later determined to be invalid, and it was renamed P. neoxalapensis in 2009. It is in the Psilocybe fagicola complex with Psilocybe fagicola, Psilocybe oaxacana, Psilocybe banderillensis, Psilocybe columbiana, Psilocybe keralensis, Psilocybe herrerae, and Psilocybe teofiloi.
Psilocybe washingtonensis is a species of psilocybin mushroom in the family Hymenogastraceae. It is similar in appearance to Psilocybe pelliculosa and P. silvatica, and a microscope is needed to reliably distinguish between them.

Psilocybe allenii is a species of agaric fungus in the family Hymenogastraceae. Described as new to science in 2012, it is named after John W. Allen, who provided the type collection. It is found in the northwestern North America from British Columbia, Canada to Los Angeles, California, most commonly within 10 miles (16 km) of the Pacific coast.

Psilocybe angulospora is a species of agaric fungus in the family Hymenogastraceae. The species was described from Taiwan in 2015 and is also present in New Zealand, where it is considered introduced. As a blueing member of the genus Psilocybe it contains the psychoactive compounds psilocin and psilocybin.















