
The fish family Psychrolutidae contains over 35 recognized species in 8 genera. This family consists of bottom-dwelling marine sculpins shaped like tadpoles, with large heads and bodies that taper back into small, flat tails. The skin is loosely attached and movable, and the layer underneath it is gelatinous. The eyes are placed high on the head, focused forward closer to the tip of the snout. Members of the family generally have large, leaf-like pectoral fins and lack scales, although some species are covered with soft spines. This is important to the species as the depths in which they live are highly pressurized and they are ambush/opportunistic/foraging predators that do not expend energy unless they are forced to.

Pelagic fish live in the pelagic zone of ocean or lake waters—being neither close to the bottom nor near the shore—in contrast with demersal fish that live on or near the bottom, and reef fish that are associated with coral reefs.

Demersal fish, also known as groundfish, live and feed on or near the bottom of seas or lakes. They occupy the sea floors and lake beds, which usually consist of mud, sand, gravel or rocks. In coastal waters, they are found on or near the continental shelf, and in deep waters, they are found on or near the continental slope or along the continental rise. They are not generally found in the deepest waters, such as abyssal depths or on the abyssal plain, but they can be found around seamounts and islands. The word demersal comes from the Latin demergere, which means to sink.
The spiny-back eel, Notacanthus sexspinis, is a deep-sea spiny eel of the genus Notacanthus, found in all the Southern Hemisphere oceans at depths between 500 and 1,000 m. The length of this fish is up to 60 cm (24 in).

The Draconettidae, slope dragonets, are a small family of fish in the order Perciformes. They are found in temperate to tropical waters of the Atlantic, Indian and western Pacific Oceans. They are closely related to, and appear similar to, the fish of the Callionymidae. They are small fish, the largest species reaching 12 cm (4.7 in) long. Like the callionymids, they are bottom-dwelling fish, and usually sexually dimorphic.

Ogcocephalidae is a family of anglerfish specifically adapted for a benthic lifestyle of crawling about on the seafloor. Ogcocephalid anglerfish are sometimes referred to as batfishes, deep-sea batfishes, handfishes, and seabats. They are found in tropical and subtropical oceans worldwide. They are mostly found at depths between 200 and 3,000 m, but have been recorded as deep as 4,000 m (13,000 ft). A few species live in much shallower coastal waters and, exceptionally, may enter river estuaries.

Psychrolutes marcidus, the smooth-head blobfish, also known simply as blobfish, is a deep-sea fish of the family Psychrolutidae. It inhabits the deep waters off the coasts of mainland Australia and Tasmania, as well as the waters of New Zealand.

The comet grouper, also known as the comet cod or dot-dash grouper, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a grouper from the subfamily Epinephelinae which is part of the family Serranidae, which also includes the anthias and sea basses. It is a species of deep coral reefs in the Indo-Pacific region.

Helicolenus percoides, the reef ocean perch, coral cod, coral perch, Jock Stewart, kuriarki, ocean perch, red gurnard perch, red gurnard scorpionfish, red ocean perch, red perch, red rock perch, scarpee or sea perch, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the subfamily Sebastinae, part of the family Scorpaenidae. It is found in the southwestern Pacific Ocean.
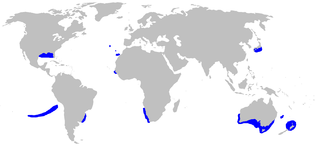
The roughskin dogfish is a sleeper shark of the family Somniosidae, found around the world on continental shelves in tropical, subtropical and temperate seas, at depths of between 100 and 1,500 m. It reaches a length of 121 cm.
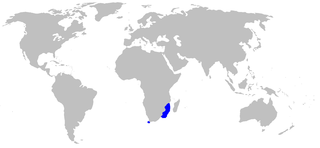
The white-spotted Izak or African spotted catshark is a species of shark belonging to the family Pentanchidae, the deepwater catsharks. It is found in the western Indian Ocean off the coasts of Natal, South Africa, southern Mozambique, Madagascar, Kenya, and Tanzania between latitudes 4° S and 37° S, at depths of between 220 and 440 m. It can grow up to 35 cm in length.

The whitesaddled catshark is a species of catshark, and part of the family Scyliorhinidae. It is found on the upper continental slope of the western central Atlantic Ocean, off the coasts of Honduras, Panama and Colombia, between latitudes 22° N and 9° N, at depths between 274 and 457 m. It can grow to a length of 47 cm (19 in). The reproduction of this catshark is oviparous but otherwise, little is known about its biology.

Ogilby's ghostshark, also known as the whitefish, is a species of chimaera, native to the waters of Australia and southern Indonesia. It lives near the ocean floor on the continental shelf and continental slope 120–350 m (390–1,150 ft) deep. It reaches a maximum size of 85.0 cm (33.5 in). Reproduction is oviparous and eggs are encased in horny shells. It reaches maturity between 64–70 cm (25–28 in) in length. It is listed as a near-threatened species by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) due to steep declines in population in areas affected by trawling.

The greenback stingaree is a little-known species of stingray in the family Urolophidae, endemic to the outer continental shelf and upper continental slope off southeastern Australia. Growing to a length of 51 cm (20 in), this species has a diamond-shaped pectoral fin disc wider than long and uniformly light green in color above. Between its nostrils is a skirt-shaped curtain of skin. Its tail bears skin folds on either side and a deep, lanceolate caudal fin, but lacks a dorsal fin.

Psychrolutes is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Psychrolutidae, the fatheads and toadfishes. Though found predominantly in the deep sea, a handful of species are present in the intertidal regions of the North Pacific rim. In June 2003, During the NORFANZ Expedition north-west of New Zealand, scientists trawled a specimen of P. microporos at a depth between 1,013 metres (3,323 ft) and 1,340 metres (4,400 ft) on the Norfolk Ridge.

The blob fish is a species of deep-sea fish of the family Psychrolutidae. It feeds mainly on crustaceans, molluscs, and sea pens.

The Integrated Marine and Coastal Regionalisation of Australia (IMCRA), formerly the Interim Marine and Coastal Regionalisation for Australia, is a biogeographic regionalisation of the oceanic waters of Australia's exclusive economic zone (EEZ). As of 2008, the most recent version is IMCRA Version 4.0.
Psychrolutes microporos is a species of deepwater marine fish in the family Psychrolutidae, commonly known as a blobfish or fathead. It is found in the abyssal zone in waters around Australia and New Zealand. A photograph of an individual taken in 2003 has become famous on the internet.

Macrurocyttus is a monotypic genus of tinselfish, family Grammicolepididae. The only species is Macrurocyttus acanthopodus, the dwarf dory. It is native to the western Pacific Ocean where it has been found in the deep waters around the Philippines and Australia on the continental slope at depths at around 878 to 1,190 metres. It is dark brown species with a relatively shallow body and large eyes. Pelvic fins have a single, large serrated spine. It is scaleless. It can grow to 4.5 cm (1.8 in) standard length.














