
In organic chemistry, an aldehyde is an organic compound containing a functional group with the structure R−CH=O. The functional group itself can be referred to as an aldehyde but can also be classified as a formyl group. Aldehydes are common and play important roles in the technology and biological spheres.
In organic chemistry, the Swern oxidation, named after Daniel Swern, is a chemical reaction whereby a primary or secondary alcohol is oxidized to an aldehyde or ketone using oxalyl chloride, dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and an organic base, such as triethylamine. It is one of the many oxidation reactions commonly referred to as 'activated DMSO' oxidations. The reaction is known for its mild character and wide tolerance of functional groups.
The term chromic acid is usually used for a mixture made by adding concentrated sulfuric acid to a dichromate, which may contain a variety of compounds, including solid chromium trioxide. This kind of chromic acid may be used as a cleaning mixture for glass. Chromic acid may also refer to the molecular species, H2CrO4 of which the trioxide is the anhydride. Chromic acid features chromium in an oxidation state of +6 (or VI). It is a strong and corrosive oxidising agent.

Pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC) is a yellow-orange salt with the formula [C5H5NH]+[CrO3Cl]−. It is a reagent in organic synthesis used primarily for oxidation of alcohols to form carbonyls. A variety of related compounds are known with similar reactivity. PCC offers the advantage of the selective oxidation of alcohols to aldehydes or ketones, whereas many other reagents are less selective.

In organic chemistry, a carbonate ester is an ester of carbonic acid. This functional group consists of a carbonyl group flanked by two alkoxy groups. The general structure of these carbonates is R−O−C(=O)−O−R' and they are related to esters, ethers and also to the inorganic carbonates.

p-Toluenesulfonic acid (PTSA or pTsOH) or tosylic acid (TsOH) is an organic compound with the formula CH3C6H4SO3H. It is a white extremely hygroscopic solid that is soluble in water, alcohols, and other polar organic solvents. The CH3C6H4SO2 group is known as the tosyl group and is often abbreviated as Ts or Tos. Most often, TsOH refers to the monohydrate, TsOH.H2O.

The Sarett oxidation is an organic reaction that oxidizes primary and secondary alcohols to aldehydes and ketones, respectively, using chromium trioxide and pyridine. Unlike the similar Jones oxidation, the Sarett oxidation will not further oxidize primary alcohols to their carboxylic acid form, neither will it affect carbon-carbon double bonds. Use of the original Sarett oxidation has become largely antiquated however, in favor of other modified oxidation techniques. The unadulterated reaction is still occasionally used in teaching settings and in small scale laboratory research.
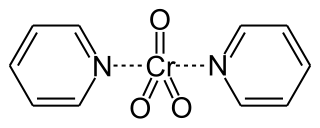
Collins reagent is the complex of chromium(VI) oxide with pyridine in dichloromethane. This metal-pyridine complex, a red solid, is used to oxidize primary alcohols to the corresponding aldehydes and secondary alcohols to the corresponding ketones. This complex is a hygroscopic orange solid.

The pyridinium dichromate(PDC) or Cornforth reagent is a pyridinium salt of dichromate with the chemical formula [C5H5NH]2[Cr2O7]. This compound is named after the Australian-British chemist Sir John Warcup Cornforth (b. 1917) who introduced it in 1962. The Cornforth reagent is a strong oxidizing agent which can convert primary and secondary alcohols to aldehydes and ketones respectively. In its chemical structure and functions it is closely related to other compounds made from hexavalent chromium oxide, such as pyridinium chlorochromate and Collins reagent. Because of their toxicity, these reagents are rarely used nowadays.

The oxidation of primary alcohols to carboxylic acids is an important oxidation reaction in organic chemistry.
In chemistry, carbonylation refers to reactions that introduce carbon monoxide (CO) into organic and inorganic substrates. Carbon monoxide is abundantly available and conveniently reactive, so it is widely used as a reactant in industrial chemistry. The term carbonylation also refers to oxidation of protein side chains.
The Parikh–Doering oxidation is an oxidation reaction that transforms primary and secondary alcohols into aldehydes and ketones, respectively. The procedure uses dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) as the oxidant and the solvent, activated by the sulfur trioxide pyridine complex (SO3•C5H5N) in the presence of triethylamine or diisopropylethylamine as base. Dichloromethane is frequently used as a cosolvent for the reaction.
Alcohol oxidation is a class of organic reactions in which the alcohol functional group is converted into another functional group in which carbon carries a higher oxidation state.
Oxidation with chromium(VI) complexes involves the conversion of alcohols to carbonyl compounds or more highly oxidized products through the action of molecular chromium(VI) oxides and salts. The principal reagents are Collins reagent, PDC, and PCC. These reagents represent improvements over inorganic chromium(VI) reagents such as Jones reagent.
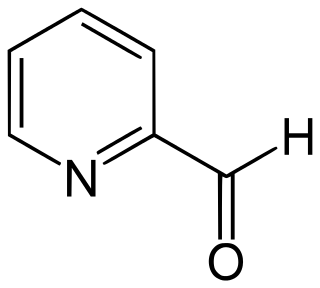
Pyridine-2-carbaldehyde, also called 2-formylpyridine, is an organic compound with the formula NC5H4CHO. It is one of three isomeric pyridinaldehydes. The other isomers are pyridine-3-carboxaldehyde and pyridine-4-carboxaldehyde.

The Collins oxidation is an organic reaction for the oxidation of primary alcohols to aldehydes. It is distinguished from other chromium oxide-based oxidations by the use of Collins reagent, a complex of chromium(VI) oxide with pyridine in dichloromethane.
The Roskamp reaction was first discovered by Eric J. Roskamp and co-workers in 1989. This reaction is very useful in synthesizing β-keto esters from aldehydes and diazoacetate, using various Lewis acids as catalysts (such as BF3, SnCl2, GeCl2).
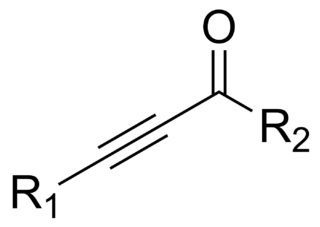
In organic chemistry, an ynone is an organic compound containing a ketone functional group and a C≡C triple bond. Many ynones are α,β-ynones, where the carbonyl and alkyne groups are conjugated. Capillin is a naturally occurring example. Some ynones are not conjugated.
The Stahl oxidation is a copper-catalyzed aerobic oxidation of primary and secondary alcohols to aldehydes and ketones. Known for its high selectivity and mild reaction conditions, the Stahl oxidation offers several advantages over classical alcohol oxidations.

Pyridine-4-carbaldehyde is an organic compound with the formula C5H4NCHO. It is one of three isomeric pyridinaldehydes. The other isomers are pyridine-2-carboxaldehyde and pyridine-3-carboxaldehyde. Pyridine-4-carboxaldehyde is a colorless liquid, although aged samples can appear yellow or even brown. It undergoes many reactions expected for aromatic aldehydes such as reductive amination and Schiff base formation. It condenses with pyrrole to give tetrapyridylporphyrin. The pKa has been experimentally determined by NMR spectroscopy to be 4.72.
















