
In organic chemistry, an amide, also known as an organic amide or a carboxamide, is a compound with the general formula R−C(=O)−NR′R″, where R, R', and R″ represent any group, typically organyl groups or hydrogen atoms. The amide group is called a peptide bond when it is part of the main chain of a protein, and an isopeptide bond when it occurs in a side chain, such as in the amino acids asparagine and glutamine. It can be viewed as a derivative of a carboxylic acid with the hydroxyl group replaced by an amine group ; or, equivalently, an acyl (alkanoyl) group joined to an amine group.
Chromic acid is an inorganic acid composed of the elements chromium, oxygen, and hydrogen. It is a dark, purplish red, odorless, sand-like solid powder. When dissolved in water, it is a strong acid. There are 2 types of chromic acid, they are: molecular chromic acid with the formula H
2CrO
4 and dichromic acid with the formula H
2Cr
2O
7.

Phthalic anhydride is the organic compound with the formula C6H4(CO)2O. It is the anhydride of phthalic acid. Phthalic anhydride is a principal commercial form of phthalic acid. It was the first anhydride of a dicarboxylic acid to be used commercially. This white solid is an important industrial chemical, especially for the large-scale production of plasticizers for plastics. In 2000, the worldwide production volume was estimated to be about 3 million tonnes per year.
In organic chemistry, an acyl chloride is an organic compound with the functional group −C(=O)Cl. Their formula is usually written R−COCl, where R is a side chain. They are reactive derivatives of carboxylic acids. A specific example of an acyl chloride is acetyl chloride, CH3COCl. Acyl chlorides are the most important subset of acyl halides.

In organic chemistry, an acyl halide is a chemical compound derived from an oxoacid by replacing a hydroxyl group with a halide group.

In organic chemistry, an imide is a functional group consisting of two acyl groups bound to nitrogen. The compounds are structurally related to acid anhydrides, although imides are more resistant to hydrolysis. In terms of commercial applications, imides are best known as components of high-strength polymers, called polyimides. Inorganic imides are also known as solid state or gaseous compounds, and the imido group (=NH) can also act as a ligand.

Polyimide is a polymer containing imide groups belonging to the class of high-performance plastics. With their high heat-resistance, polyimides enjoy diverse applications in roles demanding rugged organic materials, e.g. high temperature fuel cells, displays, and various military roles. A classic polyimide is Kapton, which is produced by condensation of pyromellitic dianhydride and 4,4'-oxydianiline.

Acetic anhydride, or ethanoic anhydride, is the chemical compound with the formula (CH3CO)2O. Commonly abbreviated Ac2O, it is the simplest isolable anhydride of a carboxylic acid and is widely used as a reagent in organic synthesis. It is a colorless liquid that smells strongly of acetic acid, which is formed by its reaction with moisture in the air.

An organic acid anhydride is an acid anhydride that is an organic compound. An acid anhydride is a compound that has two acyl groups bonded to the same oxygen atom. A common type of organic acid anhydride is a carboxylic anhydride, where the parent acid is a carboxylic acid, the formula of the anhydride being (RC(O))2O. Symmetrical acid anhydrides of this type are named by replacing the word acid in the name of the parent carboxylic acid by the word anhydride. Thus, (CH3CO)2O is called acetic anhydride.Mixed (or unsymmetrical) acid anhydrides, such as acetic formic anhydride (see below), are known, whereby reaction occurs between two different carboxylic acids. Nomenclature of unsymmetrical acid anhydrides list the names of both of the reacted carboxylic acids before the word "anhydride" (for example, the dehydration reaction between benzoic acid and propanoic acid would yield "benzoic propanoic anhydride").

Maleic anhydride is an organic compound with the formula C2H2(CO)2O. It is the acid anhydride of maleic acid. It is a colorless or white solid with an acrid odor. It is produced industrially on a large scale for applications in coatings and polymers.

Mellitic acid, also called graphitic acid or benzenehexacarboxylic acid, is an acid first discovered in 1799 by Martin Heinrich Klaproth in the mineral mellite (honeystone), which is the aluminium salt of the acid. It crystallizes in fine silky needles and is soluble in water and alcohol.

Polyester is a category of polymers that contain the ester functional group in every repeat unit of their main chain. As a specific material, it most commonly refers to a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET). Polyesters include naturally occurring chemicals, such as in plants and insects, as well as synthetics such as polybutyrate. Natural polyesters and a few synthetic ones are biodegradable, but most synthetic polyesters are not. Synthetic polyesters are used extensively in clothing.
Pivalic acid, also known as neovaleric acid, is a carboxylic acid with a molecular formula of (CH3)3CCO2H. This colourless, odiferous organic compound is solid at room temperature. A common abbreviation for the pivalyl or pivaloyl group (t-BuC(O)) is Piv and for pivalic acid (t-BuC(O)OH) is PivOH. It is an isomer of valeric acid, the other two isomers of it are 2-Methylbutanoic acid and 3-Methylbutanoic acid.

Durene, or 1,2,4,5-tetramethylbenzene, is an organic compound with the formula C6H2(CH3)4. It is a colourless solid with a sweet odor. The compound is classified as an alkylbenzene. It is one of three isomers of tetramethylbenzene, the other two being prehnitene (1,2,3,4-tetramethylbenzene) and isodurene (1,2,3,5-tetramethylbenzene). Durene has an unusually high melting point (79.2 °C), reflecting its high molecular symmetry.

In organic chemistry, ethenone is the formal name for ketene, an organic compound with formula C2H2O or H2C=C=O. It is the simplest member of the ketene class. It is an important reagent for acetylations.

4,4′-Oxydianiline (ODA) is an organic compound with the formula O(C6H4NH2)2. It is an ether derivative of aniline. This colourless solid is a useful monomer and cross-linking agent for polymers, especially the polyimides, such as Kapton.
A thermoset polymer matrix is a synthetic polymer reinforcement where polymers act as binder or matrix to secure in place incorporated particulates, fibres or other reinforcements. They were first developed for structural applications, such as glass-reinforced plastic radar domes on aircraft and graphite-epoxy payload bay doors on the Space Shuttle.
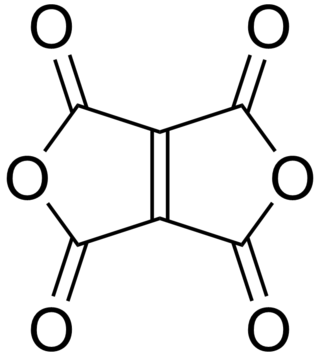
Ethylenetetracarboxylic dianhydride is a chemical compound with formula C
6O
6, that can be seen as the twofold anhydride of ethylenetetracarboxylic acid C
6H
4O
8. It has a bicyclic molecular structure consisting of two maleic anhydride rings fused by their respective alkene units. It is a pale yellow oily liquid, soluble in dichloromethane and chloroform.

4,4′-(Hexafluoroisopropylidene)diphthalic anhydride (6FDA) is an aromatic organofluorine compound and the dianhydride of 4,4′-(hexafluoroisopropylidene)bisphthalic acid.

Transition metal carboxylate complexes are coordination complexes with carboxylate (RCO2−) ligands. Reflecting the diversity of carboxylic acids, the inventory of metal carboxylates is large. Many are useful commercially, and many have attracted intense scholarly scrutiny. Carboxylates exhibit a variety of coordination modes, most common are κ1- (O-monodentate), κ2 (O,O-bidentate), and bridging.




















