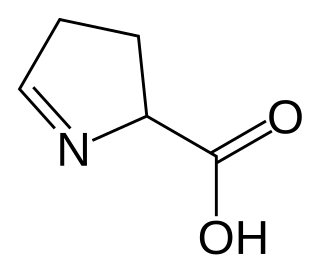
1-Pyrroline-5-carboxylic acid is a cyclic imino acid. Its conjugate base and anion is 1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate (P5C). In solution, P5C is in spontaneous equilibrium with glutamate-5-semialdhyde (GSA).
In enzymology, a glucuronate reductase (EC 1.1.1.19) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 4-oxoproline reductase (EC 1.1.1.104) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an oxaloglycolate reductase (decarboxylating) (EC 1.1.1.92) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 2-enoate reductase (EC 1.3.1.31) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glutamate-5-semialdehyde dehydrogenase (EC 1.2.1.41) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a L-aminoadipate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase (EC 1.2.1.31) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a rubredoxin—NAD(P)+ reductase (EC 1.18.1.4) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate dehydrogenase (EC 1.2.1.88) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, 6,7-dihydropteridine reductase (EC 1.5.1.34, also Dihydrobiopterin reductase) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a Delta1-piperideine-2-carboxylate reductase (EC 1.5.1.21) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, proline dehydrogenase (PRODH) (EC 1.5.5.2, formerly EC 1.5.99.8) is an enzyme of the oxidoreductase family, active in the oxidation of L-proline to (S)-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate during proline catabolism. The end product of this reaction is then further oxidized in a (S)-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate dehydrogenase (P5CDH)-dependent reaction of the proline metabolism, or spent to produce ornithine, a crucial metabolite of ornithine and arginine metabolism. The systematic name of this enzyme class is L-proline:quinone oxidoreductase. Other names in common use include L-proline dehydrogenase, L-proline oxidase,and L-proline:(acceptor) oxidoreductase. It employs one cofactor, FAD, which requires riboflavin (vitamin B2).

In enzymology, a pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase (EC 1.5.1.2) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a saccharopine dehydrogenase (NADP+, L-glutamate-forming) (EC 1.5.1.10) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a thiomorpholine-carboxylate dehydrogenase (EC 1.5.1.25) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase 1, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PYCR1 gene.

Delta-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate dehydrogenase, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ALDH4A1 gene.
Delta-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthetase (P5CS) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ALDH18A1 gene. This gene is a member of the aldehyde dehydrogenase family and encodes a bifunctional ATP- and NADPH-dependent mitochondrial enzyme with both gamma-glutamyl kinase and gamma-glutamyl phosphate reductase activities. The encoded protein catalyzes the reduction of glutamate to delta1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate, a critical step in the de novo biosynthesis of proline, ornithine and arginine. Mutations in this gene lead to hyperammonemia, hypoornithinemia, hypocitrullinemia, hypoargininemia and hypoprolinemia and may be associated with neurodegeneration, cataracts and connective tissue diseases. Alternatively spliced transcript variants, encoding different isoforms, have been described for this gene. As reported by Bruno Reversade and colleagues, ALDH18A1 deficiency or dominant-negative mutations in P5CS in humans causes a progeroid disease known as De Barsy Syndrome.

NADP Dependent Oxidoreductase Domain Containing 1 (NOXRED1) is a human protein encoded by the gene NADP-Dependent Oxidoreductase Domain Containing 1 (NOXRED1). An alias of this gene is Chromosome 14 Open Reading Frame 148 (c14orf148). This gene is located on chromosome 14, at 14q24.3. NOXRED1 is predicted to be involved in pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase activity as part of the L-proline biosynthetic pathway. It is expressed in a wide variety of tissues at a relatively low level, including the testes, thyroid, skin, small intestine, brain, kidney, colon, and more.










