
Lesser Poland, often known by its Polish name Małopolska, is a historical region situated in southern and south-eastern Poland. Its capital and largest city is Kraków. Throughout centuries, Lesser Poland developed a separate culture featuring diverse architecture, folk costumes, dances, cuisine, traditions and a rare Lesser Polish dialect. The region is rich in historical landmarks, monuments, castles, natural scenery and UNESCO World Heritage Sites.

Masovian Voivodeship or Mazovia Province is the largest and most populous of the 16 Polish provinces, or voivodeships. It occupies 35,579 square kilometres (13,737 sq mi) of east-central Poland, and has 5,411,446 inhabitants. Its principal cities are Warsaw in the centre of the Warsaw metropolitan area, Radom (212,230) in the south, Płock (119,709) in the west, Siedlce (77,990) in the east, and Ostrołęka (52,071) in the north. The capital of the voivodeship is the national capital, Warsaw.

Kielce Voivodeship is a former unit of administrative division and the local government in Poland. It was originally formed during Poland's return to independence in the aftermath of World War One, and recreated within the new Polish borders after the defeat of Nazi Germany in World War Two.

Pionki is a town in Radom County, Masovian Voivodeship, central Poland with 18 846 inhabitants (2016). Previously it was in Radom Voivodeship (1975-1998) and in Kielce Voivodeship. Surrounded by the Kozienice Wilderness, Pionki is located in northern part of historic province of Lesser Poland, 20 kilometres from Radom, and 105 kilometres from Warsaw.

Sandomierz Voivodeship was a unit of administration and local government in Poland from the 14th century to the partitions of Poland in 1772–1795. It was part of the Lesser Poland region. Originally Sandomierz Voivodeship also covered the area around Lublin, but in 1474 its three eastern counties were organized into Lublin Voivodeship. In the 16th century, it had 374 parishes, 100 towns and 2586 villages. The voivodeship was based on the Sandomerz ziemia, which earlier was the Duchy of Sandomierz. The Duchy of Sandomierz was created in 1138 by King Bolesław III Wrymouth, who in his testament divided Poland into five principalities. One of them, with the capital at Sandomierz, was assigned to Krzywousty's son, Henry of Sandomierz. Later on, with southern part of the Seniorate Province, the Duchy of Sandomierz created Lesser Poland, divided into Kraków and Sandomierz Voivodeships.
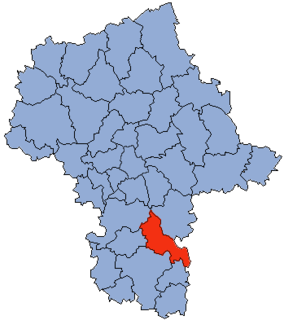
Kozienice County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Masovian Voivodeship, east-central Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and only town is Kozienice, which lies 81 kilometres (50 mi) south-east of Warsaw.

Szydłowiec is a town in Szydłowiec County, Mazovian Voivodeship, south-central Poland, with 15,243 inhabitants. It is the seat of Gmina Szydłowiec (commune). Szydłowiec is part of the historic region of Lesser Poland.
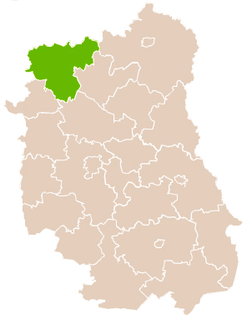
Łuków County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Lublin Voivodeship, eastern Poland. It was established on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Łuków, which lies 76 kilometres (47 mi) north of the regional capital Lublin. The only other town in the county is Stoczek Łukowski, lying 30 km (19 mi) west of Łuków.
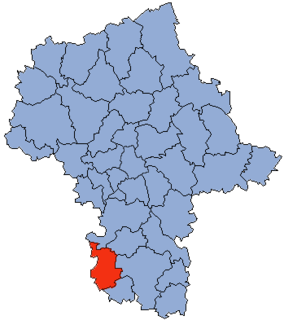
Przysucha County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Masovian Voivodeship, east-central Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and only town is Przysucha, which lies 98 kilometres (61 mi) south of Warsaw.

Szydłowiec County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Masovian Voivodeship, east-central Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and only town is Szydłowiec, which lies 110 kilometres (68 mi) south of Warsaw.
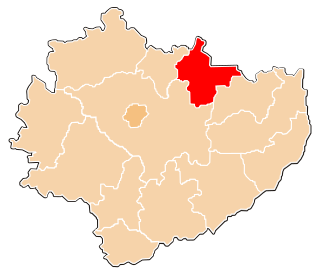
Starachowice County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship, south-central Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Starachowice, which lies 37 kilometres (23 mi) north-east of the regional capital Kielce. The only other town in the county is Wąchock, lying 5 km (3 mi) north-west of Starachowice.
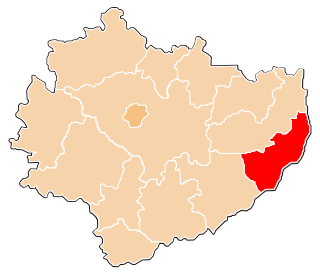
Sandomierz County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship, south-central Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Sandomierz, which lies 83 kilometres (52 mi) east of the regional capital Kielce. The county also contains the towns of Koprzywnica, lying 16 km (10 mi) south-west of Sandomierz, and Zawichost, 16 km (10 mi) north-east of Sandomierz.
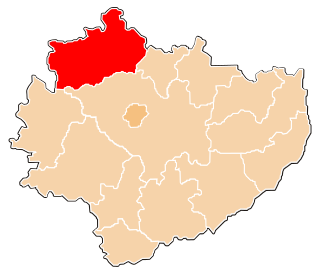
Końskie County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship, central Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Końskie, which lies 38 kilometres (24 mi) north of the regional capital Kielce. The only other town in the county is Stąporków, lying 11 km (7 mi) south-east of Końskie.

Opoczno County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Łódź Voivodeship, south-east Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Opoczno, which lies 72 kilometres (45 mi) south-east of the regional capital Łódź. The only other town in the county is Drzewica, lying 15 km (9 mi) north-east of Opoczno.

Kielce Voivodeship - a unit of administrative division and local government in Poland in years 1921–1939. At that time, it covered northern counties of the historic province of Lesser Poland, including such cities as Radom, Częstochowa and Sosnowiec. On 1 April 1938, its borders changed, see: Territorial changes of Polish Voivodeships on 1 April 1938. Capital city: Kielce.
Gmina Gózd is a rural gmina in Radom County, Masovian Voivodeship, in east-central Poland. Its seat is the village of Gózd, which lies approximately 15 kilometres (9 mi) east of Radom and 98 km (61 mi) south of Warsaw.

Gmina Iłża is an urban-rural gmina in Radom County, Masovian Voivodeship, in east-central Poland. Its seat is the town of Iłża, which lies approximately 27 kilometres (17 mi) south of Radom and 118 km (73 mi) south of Warsaw.

Gmina Skaryszew is an urban-rural gmina in Radom County, Masovian Voivodeship, in east-central Poland. Its seat is the town of Skaryszew, which lies approximately 12 kilometres (7 mi) south-east of Radom and 103 km (64 mi) south of Warsaw.

Wierzbica is a village in Radom County, Masovian Voivodeship, in east-central Poland. It is the seat of the gmina called Gmina Wierzbica. It lies approximately 18 kilometres (11 mi) south of Radom and 108 km (67 mi) south of Warsaw. The village has a population of 1,900, and belongs to historic Polish province of Lesser Poland. Wierzbica was a town from 1469 to 1870. For most of its history, it belonged to Lesser Poland’s Sandomierz Voivodeship.
Jastrząb is a village in Szydłowiec County, Masovian Voivodeship, in east-central Poland. It is the seat of the gmina called Gmina Jastrząb. It lies approximately 8 kilometres (5 mi) east of Szydłowiec and 108 km (67 mi) south of Warsaw. It lies approximately 8 kilometres (5 mi) east of SzydΠowiec and 108 km (67 mi) south of Warsaw. Jastrzab belongs to Lesser Poland, and used to be a town from 1427 to 1869.























