Ambrosia beetles are beetles of the weevil subfamilies Scolytinae and Platypodinae, which live in nutritional symbiosis with ambrosia fungi. The beetles excavate tunnels in dead or stressed trees in which they cultivate fungal gardens, their sole source of nutrition. After landing on a suitable tree, an ambrosia beetle excavates a tunnel in which it releases its fungal symbiont. The fungus penetrates the plant's xylem tissue, extracts nutrients from it, and concentrates the nutrients on and near the surface of the beetle gallery. Ambrosia fungi are typically poor wood degraders, and instead utilize less demanding nutrients. Symbiotic fungi produce and detoxify ethanol, which is an attractant for ambrosia beetles and likely prevents growth of antagonistic pathogens and selects for other beneficial symbionts. The majority of ambrosia beetles colonize xylem of recently dead trees, but some attack stressed trees that are still alive, and a few species attack healthy trees. Species differ in their preference for different parts of trees, different stages of deterioration, and in the shape of their tunnels ("galleries"). However, the majority of ambrosia beetles are not specialized to any taxonomic group of hosts, unlike most phytophagous organisms including the closely related bark beetles. One species of ambrosia beetle, Austroplatypus incompertus exhibits eusociality, one of the few organisms outside of Hymenoptera and Isoptera to do so.

A bark beetle is the common name for the subfamily of beetles Scolytinae. Previously, this was considered a distinct family (Scolytidae), but is now understood to be a specialized clade of the "true weevil" family (Curculionidae). Although the term "bark beetle" refers to the fact that many species feed in the inner bark (phloem) layer of trees, the subfamily also has many species with other lifestyles, including some that bore into wood, feed in fruit and seeds, or tunnel into herbaceous plants. Well-known species are members of the type genus Scolytus, namely the European elm bark beetle S. multistriatus and the large elm bark beetle S. scolytus, which like the American elm bark beetle Hylurgopinus rufipes, transmit Dutch elm disease fungi (Ophiostoma). The mountain pine beetle Dendroctonus ponderosae, southern pine beetle Dendroctonus frontalis, and their near relatives are major pests of conifer forests in North America. A similarly aggressive species in Europe is the spruce ips Ips typographus. A tiny bark beetle, the coffee berry borer, Hypothenemus hampei is a major pest on coffee plantations around the world.
Coprinopsis psychromorbida or Cottony Snow Mold is a cause of snow mold. It is a basidiomycete, a psychrophile, and a plant pathogen.
Typhula ishikariensis is, along with Typhula incarnata, the causal agent of grey snow mould, an obligately parasitic plant pathogen that can destroy turfgrass when covered for a long period with snow. It is a particular problem on golf courses established in unsuitable areas. More importantly, it can also damage crops of winter wheat. The species was described as new to science in 1930 by Japanese mycologist Sanshi Imai. The varieties canadensis and ishikariensis were described in 1978. There is a wide variety within the species and not all authorities agree as to subspecies, or even whether it should be monophyletic.
Achlya klebsiana is a plant pathogen. Studies say that this fungi potentially poses threats against fish in the Nile.

Bursaphelenchus xylophilus, commonly known as pine wood nematode or pine wilt nematode (PWN), is a species of nematode that infects trees in the Pinus genus of coniferous trees and causes the disease pine wilt. While native to North America, it spread in the early 20th century to Japan and in the latter half of the century to other areas of Asia, including China, Taiwan, and Korea, as well as to Europe, including Portugal and Spain.

Persea palustris, also known as swamp bay or swampbay, is a small tree or shrub found throughout the Southeastern United States and the Bahamas, with much of its range overlapping with that of its relative Persea borbonia. It is generally not more than 40 feet tall, with bark separated into scales by fissures across its surface. Mature leaves are green, paler on their undersides, which have prominent brownish or reddish-brown hairs. The species prefers swamps and coastal areas, particularly locations with moist, peat-rich soil. It is sensitive to the fungal disease known as laurel wilt, even more so than related species.

Laurel wilt, also called laurel wilt disease, is a vascular disease that is caused by the fungus Raffaelea lauricola, which is transmitted by the invasive redbay ambrosia beetle, Xyleborus glabratus. The disease affects and kills members of the laurel family. The avocado is perhaps the most commercially valuable plant affected by laurel wilt.
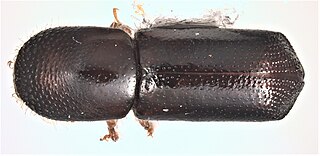
Xyleborus glabratus, the redbay ambrosia beetle, is a type of ambrosia beetle invasive in the United States. It has been documented as the primary vector of Raffaelea lauricola, the fungus that causes laurel wilt, a disease that can kill several North American tree species in the family Lauraceae, including redbay, sassafras, and avocado.
Ambrosiella is a genus of ambrosia fungi within the family Ceratocystidaceae. It was circumscribed by mycologists Josef Adolph von Arx and Grégoire L. Hennebert in 1965 with Ambrosiella xylebori designated as the type species. All Ambrosiella species are obligate symbionts of ambrosia beetles. Several former species were moved to genera Raffaelea, Hyalorhinocladiella, or Phialophoropsis, and there were nine species recognized 2017. Twelve species in as of 2023. One species, Ambrosiella cleistominuta, has been observed to produce a fertile sexual state with cleistothecious ascomata.
Japanese oak wilt is a fungal disease caused by Raffaelea quercivora fungus affecting by oak trees. In 1998, Japanese plant pathologists group was isolation, inoculation and reisolation the dead tree. It is the first disease known that Raffaela fungus cause plant disease.
Raffaelea subfusca is a mycangial fungus, first isolated from female adults of the redbay ambrosia beetle, Xyleborus glabratus.
Raffaelea fusca is a mycangial fungus, first isolated from female adults of the redbay ambrosia beetle, Xyleborus glabratus.
Raffaelea ellipticospora is a mycangial fungus, first isolated from female adults of the redbay ambrosia beetle, Xyleborus glabratus.
Raffaelea subalba is a mycangial fungus, first isolated from female adults of the redbay ambrosia beetle, Xyleborus glabratus.

Raffaelea is a genus of ambrosia fungi in the family Ophiostomataceae. It was circumscribed by mycologists Josef Adolph von Arx and Grégoire L. Hennebert in 1965 with Raffaelea ambrosiae as the type species. The genus is named in honor of Italian botanist Raffaele Ciferri.
Platypus quercivorus, the oak ambrosia beetle, is a species of weevil and pest of broad-leaved trees. This species is most commonly known for vectoring the fungus responsible for excessive oak dieback in Japan since the 1980s. It is found in Japan, India, Indonesia, New Guinea, and Taiwan.
Euplatypus parallelus, previously known as Platypus parallelus, is a species of ambrosia beetle in the weevil family Curculionidae. The adults and larvae form galleries in various species of tree and logs. It is native to Central and South America but has spread globally, is present in Africa and is well established in tropical Asia.
Euwallacea interjectus, is a species of weevil native to Asia but introduced to Westerns parts of the world.

Cantharellus anzutake, also known as Japanese golden chanterelle, is a fungus native to Japan and Korea. It is a member of the genus Cantharellus along with other popular edible chanterelles. It is named after the Japanese common name of chanterelle, anzutake (杏茸).





