Transport in Panama covers a vast network of routes predominantly traversed by cargo trucks and buses. The country's railway system, known as the Panama Canal Railway, facilitates the transportation of both passengers and goods. With a total of 15,137 km of roads, its four expressways—Corredor Sur, Corredor Norte, Autopista La Chorrera, and Colón Panama—are the arteries that link various parts of the country. Tocumen International Airport (PTY) is the key hub for international travel, ranking among the largest and most important airports in Latin America. Additionally, the renowned Panama Canal links the mere 60 km that separate the Pacific Ocean and Atlantic Ocean, offering an alternative route for maritime cargo transportation, avoiding the need to sail around South America.

A transcontinental railroad or transcontinental railway is contiguous railroad trackage, that crosses a continental land mass and has terminals at different oceans or continental borders. Such networks can be via the tracks of either a single railroad or over those owned or controlled by multiple railway companies along a continuous route. Although Europe is crisscrossed by railways, the railroads within Europe are usually not considered transcontinental, with the possible exception of the historic Orient Express. Transcontinental railroads helped open up interior regions of continents not previously colonized to exploration and settlement that would not otherwise have been feasible. In many cases they also formed the backbones of cross-country passenger and freight transportation networks. Many of them continue to have an important role in freight transportation and some like the Trans-Siberian Railway even have passenger trains going from one end to the other.

Rail transport in Spain operates on four rail gauges and services are operated by a variety of private and public operators. Total railway length in 2020 was 15,489 km. The Spanish high-speed rail network is the longest HSR network in Europe with 3,966 km and the second longest in the world, after China's.

The Panama Canal Railway is a railway line linking the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean in Central America. The route stretches 47.6 miles (76.6 km) across the Isthmus of Panama from Colón (Atlantic) to Balboa. Because of the difficult physical conditions of the route and state of technology, the construction was renowned as an international engineering achievement, one that cost US$8 million and the lives of an estimated 5,000 to 10,000 workers. Opened in 1855, the railway preceded the Panama Canal by half a century; the railway was vital in assisting the construction of the canal in the early 1900s. With the opening of the canal, the railroad's route was changed as a result of the creation of Gatun Lake, which flooded part of the original route. Following World War II, the railroad's importance declined and much of it fell into a state of neglect until 1998, when a project to rebuild the railroad to haul intermodal traffic began; the new railroad opened in 2001.

David, known as David City in colonial times, is a city and corregimiento in the west of Panama. It is the capital of the province of Chiriquí and has an estimated population of 82,907 inhabitants as confirmed in 2013. It is a relatively affluent city with a firmly established, dominant middle class and a very low unemployment and poverty index. The Pan-American Highway is a popular route to David. It is named after the Biblical King David. David is the largest city in Panama that is not part of the Panama city metro area.
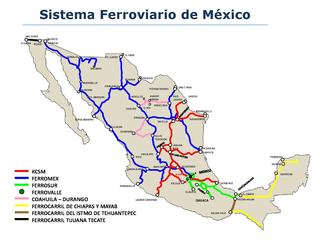
Mexico has a freight railway system owned by the national government and operated by various entities under concessions (charters) granted by the national government. The railway system provides freight and service throughout the country, connecting major industrial centers with ports and with rail connections at the United States border. Passenger rail services were limited to a number of tourist trains between 1997, when Ferrocarriles Nacionales de México suspended service, and 2008, when Ferrocarril Suburbano de la Zona Metropolitana de México inaugurated Mexico's first commuter rail service between Mexico City and the State of Mexico. This is not including the Mexico City Metro, which started service in 1969.
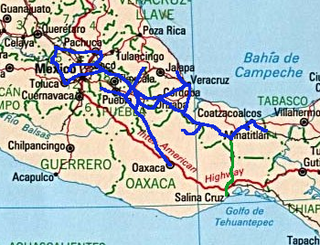
The Ferrocarril del Istmo de Tehuantepec, also known as Tren Interoceánico, Line Z, Ferrocarril Transístmico or simply Ferroistmo, is part of the Interoceanic Corridor of the Isthmus of Tehuantepec, owned by the Mexican government, that crosses the Isthmus of Tehuantepec between Puerto Mexico, Veracruz, and Salina Cruz, Oaxaca. It is leased to Ferrocarril del Sureste FERROSUR.

Rail transport in Peru has a varied history. Peruvian rail transport has never formed a true network, primarily comprising separate lines running inland from the coast and built according to freight need rather than passenger need.
Almirante is the head city of Almirante District of the Bocas del Toro Province in the Republic of Panama. Its name is Spanish for admiral.

Guatemala had a network of 914 mm narrow gauge railroads.

Railroads in Honduras were built in late 19th and early 20th centuries by two competing U.S. corporations, United Fruit and Standard Fruit. All were in the Caribbean coastal area and never reached the capital. In 1993, the combined network had 785 km (488 mi). As of 2006, only three separate segments remain in operation under the management of FNH - Ferrocarril Nacional de Honduras:

Rail transport in Costa Rica is primarily under the stewardship of Incofer, an autonomous institution of the state. Incofer owns the national railway infrastructure and operates virtually all freight and passenger services, which consist primarily of commuter trains through the highly populated Central Valley. The whole Incofer network is 1,067 mm narrow gauge, although there are small tourist railways of other gauges.

Rail transport in Central America consists of several isolated railroad lines with freight or passenger service. The most famous one is the Panama Canal Railway, the oldest transcontinental railroad in the world, connecting Panama City with Colón since 1855. Other railroads in Belize, Guatemala, Honduras, El Salvador, Nicaragua, Costa Rica and Panama were built by private and public investors mainly to facilitate the transport of local agricultural produce to export markets and harbors. Their market share and profitability went into decline in the second half of the twentieth century and most lines have been decommissioned by the end of the 1990s. As of 2018, railroads operate locally in Honduras, Costa Rica and Panama only; all rail transport has been suspended in Belize, El Salvador, Guatemala and Nicaragua. The railways still operating do not cross national borders.

The General Manuel Belgrano Railway (FCGMB), named after the Argentine politician and military leader Manuel Belgrano, is a 1,000 mmmetre gauge railway and the longest of the Argentine system. It was one of the six State-owned Argentine railway companies formed after President Juan Perón's nationalisation of the railway network in 1948.

Rail transport in the Dominican Republic is provided by one state-owned operator and several private ones, mainly for sugar mills. There are no connections with the neighbouring Haiti.

Trams in Panama began with an electric tramway in Panama City in 1893 and remained in service, with interruptions, until 1941. Passenger rail transport in Panama dates back to the 1850s, when the first transisthmian railroad line across Panama was beginning to be built to supply an alternate route to California in search of gold and wealth. The Panama Railroad was operating between Colón and Panama City by 1855. An attempt to build a battery operated tram network in Colón in 1910 was not successful.

The history of rail transport in Chile has gone through several periods of boom and bust. It began in 1840, with the construction by William Wheelwright of the first branch in the north. Further construction proceeded apace linking cities from Pisagua all the way to Puerto Montt.


















