This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations .(May 2019) |
| Redlichiina Temporal range: | |
|---|---|
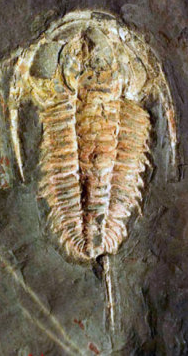 | |
| Redlichia takooensis , a member of the trilobite suborder Redlichiina. Lower Cambrian Emu Shale Kangaroo Island, South Australia | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Clade: | † Artiopoda |
| Class: | † Trilobita |
| Order: | † Redlichiida |
| Suborder: | † Redlichiina Richter, 1932 |
| Superfamilies | |
| |
Redlichiina is a suborder of the order Redlichiida of trilobites. The suborder contains three superfamilies: Emuelloidea, Redlichioidea and Paradoxidoidea. These trilobites are some of the oldest trilobites known. They originated at the beginning of the Cambrian Period and disappeared (possibly by evolving into members of the Ptychopariida order) at the end of the middle Cambrian.
