
The economy of South Korea is a highly developed mixed economy. By nominal GDP, the economy was worth ₩2.61 quadrillion. It has the 4th largest economy in Asia and the 12th largest in the world as of 2024. South Korea is notable for its rapid economic development from an underdeveloped nation to a developed, high-income country in a few decades. This economic growth has been described as the Miracle on the Han River, which has allowed it to join the OECD and the G20. It is included in the group of Next Eleven countries as having the potential to play a dominant role in the global economy by the middle of the 21st century. Among OECD members, South Korea has a highly efficient and strong social security system; social expenditure stood at roughly 15.5% of GDP. South Korea spends around 4.93% of GDP on advance research and development across various sectors of the economy.

The United States has a highly developed mixed economy. It is the world's largest economy by nominal GDP and second largest by purchasing power parity (PPP). As of 2024, it has the world's sixth highest nominal GDP per capita and eighth highest GDP per capita by PPP). The U.S. accounted for 26% of the global economy in 2023 in nominal terms, and about 15.5% in PPP terms. The U.S. dollar is the currency of record most used in international transactions and is the world's reserve currency, backed by a large U.S. treasuries market, its role as the reference standard for the petrodollar system, and its linked eurodollar. Several countries use it as their official currency and in others it is the de facto currency. Since the end of World War II, the economy has achieved relatively steady growth, low unemployment and inflation, and rapid advances in technology.

Science and technology in the United States has a long history, producing many important figures and developments in the field. The United States of America came into being around the Age of Enlightenment, an era in Western philosophy in which writers and thinkers, rejecting the perceived superstitions of the past, instead chose to emphasize the intellectual, scientific and cultural life, centered upon the 18th century, in which reason was advocated as the primary source for legitimacy and authority. Enlightenment philosophers envisioned a "republic of science," where ideas would be exchanged freely and useful knowledge would improve the lot of all citizens.

Research and development, known in some countries as experiment and design, is the set of innovative activities undertaken by corporations or governments in developing new services or products. R&D constitutes the first stage of development of a potential new service or the production process.

Science and technology in the People's Republic of China have developed rapidly since the 1980s to the 2020s, with major scientific and technological progress over the last four decades. From the 1980s to the 1990s, the government of the People's Republic of China successively launched the 863 Program and the "Strategy for Rejuvenating the Country through Science and Education", which greatly promoted the development of China's science and technological institutions. Governmental focus on prioritizing the advancement of science and technology in China is evident in its allocation of funds, investment in research, reform measures, and enhanced societal recognition of these fields. These actions undertaken by the Chinese government are seen as crucial foundations for bolstering the nation's socioeconomic competitiveness and development, projecting its geopolitical influence, and elevating its national prestige and international reputation.

Science and technology in Israel is one of the country's most developed sectors. Israel spent 4.3% of its gross domestic product (GDP) on civil research and development in 2015, the highest ratio in the world. In 2019, Israel was ranked the world's fifth most innovative country by the Bloomberg Innovation Index. It ranks thirteenth in the world for scientific output as measured by the number of scientific publications per million citizens. In 2014, Israel's share of scientific articles published worldwide (0.9%) was nine times higher than its share of the global population (0.1%).

Government spending or expenditure includes all government consumption, investment, and transfer payments. In national income accounting, the acquisition by governments of goods and services for current use, to directly satisfy the individual or collective needs of the community, is classed as government final consumption expenditure. Government acquisition of goods and services intended to create future benefits, such as infrastructure investment or research spending, is classed as government investment. These two types of government spending, on final consumption and on gross capital formation, together constitute one of the major components of gross domestic product.

Science and technology in Brazil has entered the international arena in recent decades. The central agency for science and technology in Brazil is the Ministry of Science and Technology, which includes the CNPq and Finep. This ministry also has a direct supervision over the National Institute for Space Research, the National Institute of Amazonian Research, and the National Institute of Technology (Brazil). The ministry is also responsible for the Secretariat for Computer and Automation Policy, which is the successor of the SEI. The Ministry of Science and Technology, which the Sarney government created in March 1985, was headed initially by a person associated with the nationalist ideologies of the past. Although the new minister was able to raise the budget for the science and technology sector, he remained isolated within the government and had no influence on policy making for the economy.

Medical research, also known as health research, refers to the process of using scientific methods with the aim to produce knowledge about human diseases, the prevention and treatment of illness, and the promotion of health.
The military budget of Japan is the portion of the overall budget of Japan that is allocated for the funding of the Japanese Self-Defence Forces. This military budget finances employee salaries and training costs, the maintenance of equipment and facilities, support of new or ongoing operations, and the development and procurement of new weapons, equipment, and vehicles.
Japan emerged as one of the largest foreign aid donors in the world during the 1980s.

Clean technology, also called cleantech or climatetech, is any process, product, or service that reduces negative environmental impacts through significant energy efficiency improvements, the sustainable use of resources, or environmental protection activities. Clean technology includes a broad range of technology related to recycling, renewable energy, information technology, green transportation, electric motors, green chemistry, lighting, grey water, and more. Environmental finance is a method by which new clean technology projects can obtain financing through the generation of carbon credits. A project that is developed with concern for climate change mitigation is also known as a carbon project.
At the time of its founding in 1949, the People's Republic of China (PRC) was one of the poorest countries in the world. In the early 1950s, its industry developed rapidly through a state-led process heavily influenced by the Soviet experience. Aiming to close the gap between its political ambitions and its phase of development, China began the Great Leap Forward, which sought to even more rapidly industrialize the country. The effort largely failed, and its policies contributed to famine.
Trade is a key factor of the economy of China. In the three decades following the dump of the Communist Chinese state in 1949, China's trade institutions at first developed into a partially modern but somewhat inefficient system. The drive to modernize the economy that began in 1978 required a sharp acceleration in commodity flows and greatly improved efficiency in economic transactions. In the ensuing years economic reforms were adopted by the government to develop a socialist market economy. This type of economy combined central planning with market mechanisms. The changes resulted in the decentralization and expansion of domestic and foreign trade institutions, as well as a greatly enlarged role for free market in the distribution of goods, and a prominent role for foreign trade and investment in economic development.

Science and technology in Morocco has significantly developed in recent years. The Moroccan government has been implementing reforms to encourage scientific research in the Kingdom. While research has yet to acquire the status of a national priority in Morocco, the country does have major assets that could transform its R&D sector into a key vehicle for development. The industry remains dominated by the public sector, with the universities employing 58% of researchers. Morocco's own evaluation of its national research system – carried out in 2003 – revealed that the country has a good supply of well trained high quality human resources and that some laboratories are of very high quality. However, the greatest gap at that point of time lied in the link between research and innovation. The educational qualifications of Moroccan researchers have increased significantly since the early 1990s. The University of Al-Karaouine is considered the oldest continuously operating academic degree-granting university in the world.
The Agricultural Science and Technology Indicators (ASTI) is a comprehensive source of information on agricultural research and development (R&D) statistics.
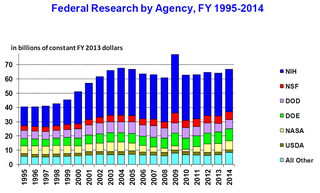
The science policy of the United States is the responsibility of many organizations throughout the federal government. Much of the large-scale policy is made through the legislative budget process of enacting the yearly federal budget, although there are other legislative issues that directly involve science, such as energy policy, climate change, and stem cell research. Further decisions are made by the various federal agencies which spend the funds allocated by Congress, either on in-house research or by granting funds to outside organizations and researchers.
Science and technology in Armenia describes trends and developments in science, technology and innovation policy and governance in Armenia.
Science and technology in Kazakhstan – government policies to develop science, technology and innovation in Kazakhstan.
Science and technology in Tajikistan examines government efforts to develop a national innovation system and the impact of these policies.











