
Rhodiola rosea is a perennial flowering plant in the family Crassulaceae. It grows naturally in wild Arctic regions of Europe, Asia, and North America, and can be propagated as a groundcover. Rhodiola rosea has been used in traditional medicine for several disorders, notably including treatment of anxiety and depression. As of 2019, there is no high-quality randomized or clinical controlled trails adequately assessing its effectiveness for treating "physical fatigue and mild to moderate depression and/or mental fatigue", for "enhancing physical endurance and performance" or "evaluating [its] adaptogenic properties". The United States Food and Drug Administration has issued several warnings to manufacturers of R. rosea dietary supplements for making false health claims about its safety and efficacy.

Sedum acre, commonly known as the goldmoss stonecrop, mossy stonecrop, goldmoss sedum, biting stonecrop and wallpepper, is a perennial flowering plant in the family Crassulaceae. It is native to Europe, but also naturalised in North America, Japan and New Zealand.

Rhodiola is a genus of perennial plants in the family Crassulaceae that resemble Sedum and other members of the family. Like sedums, Rhodiola species are often called stonecrops. Some authors merge Rhodiola into Sedum.

Spergularia rubra, the red sandspurry or red sand-spurrey, is a plant species in the family Caryophyllaceae. It is native to Europe, Asia and North Africa, and it is present on other continents, including North and South America and Australia, as an introduced species and in many areas a common weed. It grows in a wide variety of habitat types.

Crassula connata is a succulent plant in the family Crassulaceae. It is known by the common names sand pygmyweed and pygmy stonecrop. It is a very small plant which grows in patches on the ground, especially in rocky areas. It is also sometimes associated with vernal pool plant communities. The stems are a few centimeters in length and are covered with tiny fleshy pointed leaves. Each leaf is only millimeters long. The plant is green when new and it matures to shades of pink and red. It is found in western North America and in parts of Central and South America.

Galium grayanum is a species of flowering plant in the coffee family known by the common name Gray's bedstraw. It is native to the high mountains of northern California, western Nevada and southwestern Oregon.
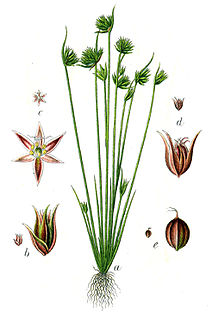
Juncus capitatus is a species of rush known by the common names dwarf rush and leafybract dwarf rush. It is native to Europe, Asia and North Africa. It is also an introduced species in parts of North America such as California and the Gulf Coast. It grows in moist areas, such as wet sand, vernal pools, and ditches.

Montia parvifolia is a species of flowering plant in the family Montiaceae known by the common names little-leaf miner's lettuce, small-leaved blinks and small-leaved montia. It is native to western North America from Alaska to California to Montana, where it grows in moist to wet areas in several types of mountain habitat.
Sagina maxima is a species of flowering plant in the family Caryophyllaceae known by the common names stickystem pearlwort and thick-stemmed pearlwort. It is native to the west coast of North America from Alaska to California, where it can be found in many types of sandy and rocky coastal habitat. It is a small, fleshy perennial herb growing in a clump of linear leaves and thick stems. The fleshy, pointed leaves are 1 or 2 centimeters long. The inflorescence is a solitary flower with five sepals and five small white petals. There are two subspecies which differ mainly in the arrangement of hairs on the stem.

Sedum lanceolatum is a species of flowering plant in the family Crassulaceae known by the common names spearleaf stonecrop and lanceleaf stonecrop.

Senecio hydrophiloides is a species of flowering plant in the aster family known by the common names tall groundsel and sweet marsh ragwort. It is native to western North America from British Columbia and Alberta to northern California to Utah, where it grows in wet meadows and similar habitat. It is a biennial or perennial herb producing a single erect stem or a cluster of a few stems which may exceed one meter in maximum height. The plants are green to red in color and usually without hairs, but new growth can be woolly. The leaves are lance-shaped to oval with toothed edges, the blades up to 25 centimeters long and borne on long winged petioles. The leaves are firm and sometimes a bit fleshy. The inflorescence is a loose or dense cluster of up to 30 or more flower heads lined with black-tipped phyllaries. They contain many yellowish disc florets at the center and often have some yellow ray florets, though these are sometimes absent. Senecio Hydrophiloides can cause Dermatitis.

Spergularia macrotheca is a species of flowering plant in the family Caryophyllaceae known by the common name sticky sandspurry. It is native to western North America from British Columbia to Baja California, where it grows in many types of moist coastal and inland habitat, often in alkaline and saline substrates. It may be found in marshes, alkali flats, beaches, meadows, seeps, and vernal pools. It is a perennial herb producing a narrow stem up to 40 centimeters long with a woody, thickened base and taproot. They may grow erect or prostrate across the ground. It is covered in sticky glandular hairs, especially in the inflorescence. The stems are lined with fleshy linear leaves, sometimes tipped with spines. The leaves are accompanied by triangular stipules up to a centimeter long each. Flowers occur in clusters at the end of the stem as well as in leaf axils. The small flowers have five pointed sepals and five oval white to lavender-pink petals. The fruit is a capsule containing tiny reddish brown, winged seeds.

Stellaria calycantha is a species of flowering plant in the family Caryophyllaceae known by the common name northern starwort. It is native to western North America from Alaska and northwestern Canada to California and New Mexico, as well as eastern Russia. It occurs in subalpine and alpine climates, in many types of moist, shady habitat. It is a rhizomatous perennial herb producing a prostrate to erect stem up to 25 centimeters long, taking a clumpy form. The thin oval leaves have smooth edges and pointed tips, and measure up to 2.5 centimeters in length. The inflorescence bears one or more flowers, each on a long pedicel. Each flower has five pointed green sepals, and some flowers have up to five deeply lobed white petals.
Streptanthus drepanoides is an uncommon species of flowering plant in the mustard family known by the common name sicklefruit jewelflower. It is endemic to California, where it is known from a scattered distribution throughout several mountain ranges in the northern part of the state, including the Klamath Mountains. It is a resident of chaparral and woodlands, generally on serpentine soils. It is an annual herb producing a mostly hairless, waxy stem up to 40 or 45 centimeters tall. The ephemeral basal leaves have round or oval blades, sometimes edged with teeth. Leaves higher on the stem have fleshy oval blades that clasp the stem, the lower ones each measuring up to 9 centimeters long by 7.5 wide. Flowers occur at intervals along the upper stem. Each has an urn-shaped calyx of greenish or yellowish sepals under a centimeter long with whitish or purplish, purple-veined petals emerging from the tip. The fruit is a straight or sickle-shaped curving silique up to 9 centimeters long.
Streptanthus morrisonii is an uncommon species of flowering plant in the mustard family known by the common name Morrison's jewelflower. It is endemic to California, where it is known from the North and Central Coast Ranges. It is limited to serpentine soils in chaparral and forest habitat. It is considered a species complex which includes Streptanthus brachiatus. S. morrisonii is divided into four subspecies and is variable. In general, it is a biennial herb producing a hairless, waxy stem up to 1.2 to 1.5 meters in maximum height, often branching at the tip. The basal leaves have fleshy, lance-shaped blades 3 to 5 centimeters long borne on petioles. The blades are gray-green on the upper surface and purple or purple-mottled underneath. Leaves higher on the stem are variable in shape and become smaller toward the top of the plant. Flowers occur at intervals along the upper stem. Each has an urn-shaped calyx of keeled sepals in shades of yellow-green to purple. The petals emerging from the tip are whitish with purple-brown veining. The fruit is a flattened straight or slightly curved silique up to 8 centimeters long.

Swertia perennis is a species of flowering plant in the gentian family known by the common names felwort and star swertia. It is native to several regions of the northern hemisphere, including much of Eurasia and western North America. It is a plant of wetlands, particularly calcareous fens. It is common to abundant in many areas, but it is known to be negatively impacted by habitat fragmentation and other habitat destruction, and human activity has led to its extirpation from some areas where it was once common. It is a perennial herb producing usually one erect stem growing 10 to 50 centimeters tall. The basal leaves are spoon-shaped with rounded tips, and leaves higher on the plant are widely lance-shaped or somewhat oval, with pointed tips. The inflorescence is an open panicle of flowers atop the stem. Each flower has a calyx of four or five pointed sepals and a corolla of four or five pointed lobes each up to 1.3 centimeters long. The corolla is dull blue to violet in color with darker purplish veining or stippling. There are two rounded nectary pits at the base of each lobe of the corolla. Stamens tipped with large anthers surround a central ovary.

Trianthema portulacastrum is a species of flowering plant in the ice plant family known by the common names desert horsepurslane, black pigweed, and giant pigweed. It is native to areas of several continents, including Africa and North and South America, and present as an introduced species in many other areas. It grows in a wide variety of habitat types and it can easily take hold in disturbed areas and cultivated land as a weed. It is an annual herb forming a prostrate mat or clump with stems up to a meter long. It is green to red in color, hairless except for small lines of hairs near the leaves, and fleshy. The leaves have small round or oval blades up to 4 centimeters long borne on short petioles. Solitary flowers occur in leaf axils. The flower lacks petals but has purple, petallike sepals. The fruit is a curved, cylindrical capsule emerging from the stem. It is up to half a centimeter long and has two erect, pointed wings on top, where the capsule opens.
Mimulus hymenophyllus is a species of flowering plant in the lopseed family known by the common names thinsepal monkeyflower and membrane-leaf monkeyflower. It is native to Hells Canyon on the border between Oregon and Idaho in the United States. It has also been reported from Montana.
Sedum moraniii is a rare species of flowering plant in the family Crassulaceae known by the common name Rogue River stonecrop. It is endemic to Oregon in the United States, where it only grows in Josephine County next to the Rogue River.

Erythranthe gemmipara is a rare species of flowering plant in the family Phrymaceae, known by the common name Rocky Mountain monkeyflower. It is endemic to Colorado in the United States, where there are eight known occurrences. It was formerly known as Mimulus gemmiparus.

















