
The Microhylidae, commonly known as narrow-mouthed frogs, are a geographically widespread family of frogs. The 683 species are in 63 genera and 11 subfamilies, which is the largest number of genera of any frog family.

Cophylinae is a subfamily of microhylid frogs endemic to Madagascar. It has over 100 species in eight genera. Members of this subfamily range from minute to fairly large, and they are highly ecologically diverse. DNA barcode research has revealed a significant taxonomic gap in this subfamily, and an estimated 70+ candidate species were identified. Many of these have subsequently been described, as well as numerous new discoveries.

Anodonthyla is a genus of microhylid frogs endemic to Madagascar. Molecular data suggest that it is the sister taxon to all other species in the subfamily Cophylinae.

Plethodontohyla is a genus of microhylid frogs endemic to Madagascar.

Mantella are a prominent genus of aposematic frogs in the family Mantellidae, endemic to the island of Madagascar. The members of the genus are diurnal and terrestrial in behaviour, exhibiting bright colouration or cryptic markings which are species specific.
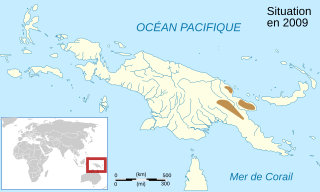
Cophixalus shellyi is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to Papua New Guinea and occurs in the New Guinea Highlands as well as in the Adelbert Range and on the Huon Peninsula. The specific name shellyi honors Father Otto Schellenberger ("Shelly"), an American missionary and former professor in mathematics who collected the type series.
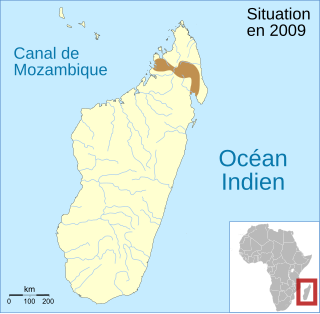
Rhombophryne minuta is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to northern Madagascar. It has been mixed with other species such as Rhombophryne mangabensis; it is known with certainty only from the Marojejy National Park.

Rhombophryne is a genus of microhylid frogs endemic to Madagascar. It is currently estimated to include more than 23 species, but only 20 of these are currently described. The common name 'diamond frog' has been proposed and used for members of this genus.
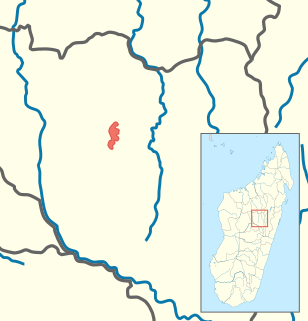
Anilany helenae is a species of frog in the microyhlid subfamily Cophylinae. It is the only species in the monotypic genus Anilany, and is endemic to central Madagascar.

Rhombophryne coudreaui is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to northeastern Madagascar. The specific name coudreaui honours Jean Coudreau, a colonial forestry administrator in Madagascar who collected the holotype. Common names Coudreau's frog and Betampona digging frog have been coined for it.

Plethodontohyla alluaudi is a frog belonging to the Madagascar-endemic subfamily Cophylinae of the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to southeastern Madagascar. It is a terrestrial and fossorial frog that occurs in rainforest, including littoral forest. Despite being locally abundant, it is a difficult frog to find.

Rhombophryne serratopalpebrosa is a species of frog of the Madagascar endemic microhylid subfamily Cophylinae. Genetic evidence revealed that it is a species complex, in need of resolution. This work has made significant progress, and five related species have been described from this complex between 2014 and 2017. It is threatened by habitat loss.
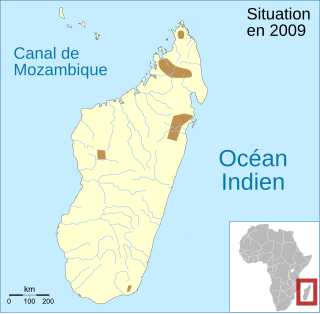
Rhombophryne laevipes is a frog of the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to Madagascar and known from localities in northern, eastern, southeastern, and mid-western parts of the island. It might be a species complex, with the "true" R. laevipes restricted to northern Madagascar.
Rhombophryne guentherpetersi is a frog of the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to northern Madagascar and known from the Tsaratanana Massif. It inhabits high-elevation forest and, perhaps, montane grassland, at elevations of 2,000–2,600 m (6,600–8,500 ft) above sea level. It is a rare species that suffers from habitat loss and degradation. It occurs in the Tsaratanana Reserve but the reserve borders are ambiguous, complicating management of the area.

Rhombophryne vaventy is a large species of frogs of the Madagascar endemic microhylid subfamily Cophylinae. It is one of the largest members of its genus.

Mini is a genus of tiny microhylid frogs that are endemic to southeastern Madagascar where they live among leaf litter in lowland forests. The three species and the genus itself were only scientifically described in 2019; although not yet rated by the IUCN, they have very small ranges and it has been recommended that two qualify as critically endangered and M. ature as data deficient.

Anodonthyla eximia is a species of frog from Ranomafana in Eastern Madagascar endemic microhylid subfamily Cophylinae. It is the smallest species of the genus Anodonthyla and is the only known terrestrial member of the genus.

Andolalao Rakotoarison is a Malagasy herpetologist.

Rhombophryne ellae is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to Montagne d'Ambre National Park in the northern Madagascar. The species was discovered soon after it was possibly forced out of its habitat by Cyclone Ava.

Mini scule is a species of microhylid frog endemic to Madagascar that was described in 2019. The scientific name of the species refers to its size, being a pun on the word miniscule. It is very small, measuring only 8.4–10.8 mm (0.33–0.43 in) in snout–vent length. It has bronze underparts with a brown groin and back of the thigh, cream upperparts with brown flecking, a dark brown side of the head, and a red iris. It is known only from the Sainte Luce Reserve, where it inhabits areas with deep leaf litter near semi-permanent water bodies. Specimens of frogs from Mandena, the Vohimena mountains, the southern Anosy Mountains, and Tsitongambarika may also be of this species. Like other species in its genus, it received a large amount of media attention when first described due to the wordplay in its scientific name.



















