A dehydrogenase is an enzyme belonging to the group of oxidoreductases that oxidizes a substrate by reducing an electron acceptor, usually NAD+/NADP+ or a flavin coenzyme such as FAD or FMN. Like all catalysts, they catalyze reverse as well as forward reactions, and in some cases this has physiological significance: for example, alcohol dehydrogenase catalyzes the oxidation of ethanol to acetaldehyde in animals, but in yeast it catalyzes the production of ethanol from acetaldehyde.
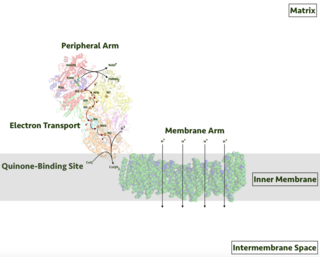
Respiratory complex I, EC 7.1.1.2 is the first large protein complex of the respiratory chains of many organisms from bacteria to humans. It catalyzes the transfer of electrons from NADH to coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) and translocates protons across the inner mitochondrial membrane in eukaryotes or the plasma membrane of bacteria.

Ribonucleotide reductase (RNR), also known as ribonucleoside diphosphate reductase (rNDP), is an enzyme that catalyzes the formation of deoxyribonucleotides from ribonucleotides. It catalyzes this formation by removing the 2'-hydroxyl group of the ribose ring of nucleoside diphosphates. This reduction produces deoxyribonucleotides. Deoxyribonucleotides in turn are used in the synthesis of DNA. The reaction catalyzed by RNR is strictly conserved in all living organisms. Furthermore, RNR plays a critical role in regulating the total rate of DNA synthesis so that DNA to cell mass is maintained at a constant ratio during cell division and DNA repair. A somewhat unusual feature of the RNR enzyme is that it catalyzes a reaction that proceeds via a free radical mechanism of action. The substrates for RNR are ADP, GDP, CDP and UDP. dTDP is synthesized by another enzyme from dTMP.
Thioredoxin reductases are enzymes that reduce thioredoxin (Trx). Two classes of thioredoxin reductase have been identified: one class in bacteria and some eukaryotes and one in animals. In bacteria TrxR also catalyzes the reduction of glutaredoxin like proteins known as NrdH. Both classes are flavoproteins which function as homodimers. Each monomer contains a FAD prosthetic group, a NADPH binding domain, and an active site containing a redox-active disulfide bond.

In biochemistry, flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) is a redox-active coenzyme associated with various proteins, which is involved with several enzymatic reactions in metabolism. A flavoprotein is a protein that contains a flavin group, which may be in the form of FAD or flavin mononucleotide (FMN). Many flavoproteins are known: components of the succinate dehydrogenase complex, α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, and a component of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex.

Flavoproteins are proteins that contain a nucleic acid derivative of riboflavin. These proteins are involved in a wide array of biological processes, including removal of radicals contributing to oxidative stress, photosynthesis, and DNA repair. The flavoproteins are some of the most-studied families of enzymes.

Methane monooxygenase (MMO) is an enzyme capable of oxidizing the C-H bond in methane as well as other alkanes. Methane monooxygenase belongs to the class of oxidoreductase enzymes.
Nitrate reductase (NAD(P)H) (EC 1.7.1.2, assimilatory nitrate reductase, assimilatory NAD(P)H-nitrate reductase, NAD(P)H bispecific nitrate reductase, nitrate reductase (reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (phosphate)), nitrate reductase NAD(P)H, NAD(P)H-nitrate reductase, nitrate reductase [NAD(P)H2], NAD(P)H2:nitrate oxidoreductase) is an enzyme with systematic name nitrite:NAD(P)+ oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalises the following chemical reaction
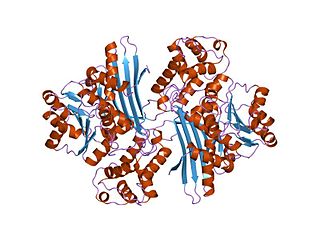
In molecular biology, the protein domain Saccharopine dehydrogenase (SDH), also named Saccharopine reductase, is an enzyme involved in the metabolism of the amino acid lysine, via an intermediate substance called saccharopine. The Saccharopine dehydrogenase enzyme can be classified under EC 1.5.1.7, EC 1.5.1.8, EC 1.5.1.9, and EC 1.5.1.10. It has an important function in lysine metabolism and catalyses a reaction in the alpha-Aminoadipic acid pathway. This pathway is unique to fungal organisms therefore, this molecule could be useful in the search for new antibiotics. This protein family also includes saccharopine dehydrogenase and homospermidine synthase. It is found in prokaryotes, eukaryotes and archaea.
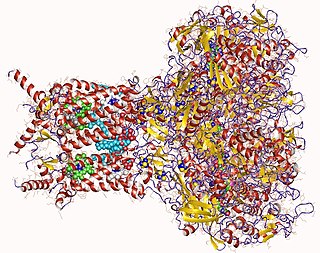
Formate dehydrogenases are a set of enzymes that catalyse the oxidation of formate to carbon dioxide, donating the electrons to a second substrate, such as NAD+ in formate:NAD+ oxidoreductase (EC 1.17.1.9) or to a cytochrome in formate:ferricytochrome-b1 oxidoreductase (EC 1.2.2.1). This family of enzymes has attracted attention as inspiration or guidance on methods for the carbon dioxide fixation, relevant to global warming.

4-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-monooxygenase (EC 1.14.14.9) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Flavin reductase a class of enzymes. There are a variety of flavin reductases, which bind free flavins and through hydrogen bonding, catalyze the reduction of these molecules to a reduced flavin. Riboflavin, or vitamin B, and flavin mononucleotide are two of the most well known flavins in the body and are used in a variety of processes which include metabolism of fat and ketones and the reduction of methemoglobin in erythrocytes. Flavin reductases are similar and often confused for ferric reductases because of their similar catalytic mechanism and structures.
In enzymology, an FMN reductase (EC 1.5.1.29) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a NAD(P)H dehydrogenase (quinone) (EC 1.6.5.2) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a nitrite reductase [NAD(P)H] (EC 1.7.1.4) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

The prokaryotic riboflavin biosynthesis protein is a bifunctional enzyme found in bacteria that catalyzes the phosphorylation of riboflavin into flavin mononucleotide (FMN) and the adenylylation of FMN into flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD). It consists of a C-terminal riboflavin kinase and an N-terminal FMN-adenylyltransferase. This bacterial protein is functionally similar to the monofunctional riboflavin kinases and FMN-adenylyltransferases of eukaryotic organisms, but only the riboflavin kinases are structurally homologous.

Fumarate reductase (quinol) (EC 1.3.5.4, QFR,FRD, menaquinol-fumarate oxidoreductase, quinol:fumarate reductase) is an enzyme with systematic name succinate:quinone oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyzes the following chemical reaction:
Flavin reductase (NADH) (EC 1.5.1.36, NADH-dependent flavin reductase, flavin:NADH oxidoreductase) is an enzyme with systematic name flavin:NAD+ oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
FMN reductase (NADPH) (EC 1.5.1.38, FRP, flavin reductase P, SsuE) is an enzyme with systematic name FMNH2:NADP+ oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction:
Morphinone reductase is an enzyme which catalyzes the NADH-dependent saturation of the carbon-carbon double bond of morphinone and codeinone, yielding hydromorphone and hydrocodone respectively. This saturation reaction is assisted by a FMN cofactor and the enzyme is a member of the α/β-barrel flavoprotein family. The sequence of the enzyme has been obtained from bacteria Pseudomonas putida M10 and has been successfully expressed in yeast and other bacterial species. The enzyme is reported to harbor high sequence and structural similarity to the Old Yellow Enzyme, a large group of flavin-dependent redox biocatalysts of yeast species, and an oestrogen-binding protein of Candida albicans. The enzyme has demonstrated value in biosynthesis of semi-opiate drugs in microorganisms, expanding the chemical diversity of BIA biosynthesis.











