Louse is the common name for any member of the clade Phthiraptera, which contains nearly 5,000 species of wingless parasitic insects. Phthiraptera has variously been recognized as an order, infraorder, or a parvorder, as a result of developments in phylogenetic research.

The genus Haematomyzus includes three species of lice that differ so markedly from all other lice that the genus is placed in its own family Haematomyzidae, itself monotypic within the superfamily Rhynchophthirina. These unusual lice are ectoparasites of elephants and warthogs. Their mouthparts are elongated to form a drill-like structure that allows them to penetrate the thick skin of their host.

The calandra lark or European calandra-lark breeds in warm temperate countries around the Mediterranean and eastwards through Turkey into northern Iran and southern Russia. It is replaced further east by its relative, the bimaculated lark.

Menoponidae is a monophyletic family of lice in the superfamily of chewing lice, Amblycera, often referred to as the chicken body louse family. They are ectoparasites of a wide range of birds including chickens, which makes them important to understand for veterinary science and for human health. However, Menoponidae are not exclusive to poultry and are common parasites for migratory birds, with more and more species being discovered every year.

Heterogeomys is a genus of rodent in the family Geomyidae, found in Mexico, Central America and Colombia. Heterogeomys are a small genus of rodents commonly known as pocket gophers, though the term applies to all genera within the family Geomyidae. The name pocket gopher was earned for this family because of their fur lined cheek pouches that can be used for carrying food. These pouches can also be turned inside out. Species of Heterogeomys are regarded as pests, one of less than 5% of rodent species classified as pests, and the history of man's attempts to control their populations reaches back into Mayan times. Despite some efforts to the contrary, populations of Heterogeomys seem to be on a general upwards trend. Furthermore, all of the species of Heterogeomys are considered to be of Least Concern in the World Status Key.

Menacanthus is a genus of chewing lice which parasitise birds. The taxonomy of this genus is highly uncertain. Most taxonomies have given this genus as having over a hundred species, but recent studies have synonymised dozens of species and found other names to be invalid. Some Menacanthus species remain to be discovered, or are synonymised in error. Menacanthus lice feed on the blood of a wide variety of birds, including chickens, by piercing the quills of feathers and gnawing the epidermis. In doing so, they can spread disease and lower egg production. In Menacanthus stramineus, eggs are incubated for four or five days, each of the three nymphal stages lasts for about three days, and adult life for about twelve days. Females produce as many as four eggs in a day, averaging 1.6 eggs a day, with egg production peaking 5–6 days after reaching adulthood. On sparrows, Menacanthus lice are particularly common, and are found in many different niches, consuming blood and feathers.

Rhinonyssidae is a family of mites in the order Mesostigmata. There are about 16 genera and at least 460 described species in Rhinonyssidae.
Brueelia is a genus of bird lice in the family Philopteridae that infest Passerine (perching) birds. Lice in Brueelia are usually host specific, with more than 85% of described species each found on a single host bird species. Over 300 species of Brueelia have been described, and many more specimens that are presumed to belong to Brueelia are awaiting description and naming.

Polyplacidae is a family of lice in the suborder Anoplura, the sucking lice. Lice in this family are known commonly as the spiny rat lice. The family has a cosmopolitan distribution. As of 2010 there were 193 species.

The Ricinidae are a family of a larger group Amblycera of the chewing lice. All species are relatively large bodied avian ectoparasites. They typically exhibit low prevalence and low intensity. They feed on host blood which is atypical in chewing lice. Two or three genera are recognized.
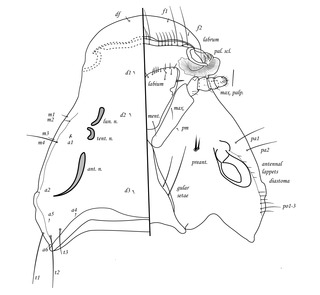
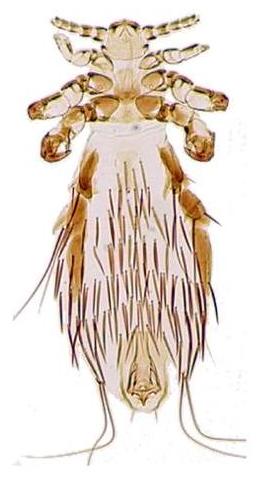
Ricinus vaderi is a species of chewing lice which parasitises the calandra lark in Azerbaijan. It is a member of Ricinus, the largest genus of chewing lice found parasitizing Passeriformes.
Campanulotes is a genus of lice in the disputed, probably paraphyletic, family Philopteridae, the chewing lice, or in the family Goniodidae.

Meromenopon is a genus of chewing lice which parasitise birds. The species Meromenopon meropsis is a parasite of bee-eaters.

Cospeciation is a form of coevolution in which the speciation of one species dictates speciation of another species and is most commonly studied in host-parasite relationships. In the case of a host-parasite relationship, if two hosts of the same species get within close proximity of each other, parasites of the same species from each host are able to move between individuals and mate with the parasites on the other host. However, if a speciation event occurs in the host species, the parasites will no longer be able to "cross over" because the two new host species no longer mate and, if the speciation event is due to a geographic separation, it is very unlikely the two hosts will interact at all with each other. The lack of proximity between the hosts ultimately prevents the populations of parasites from interacting and mating. This can ultimately lead to speciation within the parasite.

Colpocephalum is a genus of chewing louse. Christian Ludwig Nitzsch named the genus in 1818. The Plenary Powers of the International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature selected Colpocephalum zebraBurmeister, 1838 as its type species in the 1950s. There are approximately 135 species in this genus, and they are ectoparasites of birds in at least a dozen different orders.
Colpocephalum californici, the California condor louse, is an extinct species of chewing louse which parasitized the California condor. In an example of coextinction, it became extinct when the remaining, Critically Endangered California condors were deloused and treated with pesticides during a captive breeding program.

Rallicola is a genus of chewing louse. It is an ectoparasite of rails and other birds. It was named by Thomas Harvey Johnston and Launcelot Harrison in 1911. There are two subgenera aside from the nominotypical subgenus: Aptericola, whose species are found on kiwi birds, and Huiacola, a monospecific subgenus consisting of Rallicola extinctus, once found on the huia.

Trichodectidae is a family of louse in the suborder Ischnocera. Its species are parasites of mammals. The following 19 genera are recognized:

Harrison's rule is an observation in evolutionary biology by Launcelot Harrison which states that in comparisons across closely related species, host and parasite body sizes tend to covary positively.














