
The River Severn, at 220 miles (354 km) long, is the longest river in Great Britain. It is also the river with the most voluminous flow of water by far in all of England and Wales, with an average flow rate of 107 m3/s (3,800 cu ft/s) at Apperley, Gloucestershire. It rises in the Cambrian Mountains in mid Wales, at an altitude of 2,001 feet (610 m), on the Plynlimon massif, which lies close to the Ceredigion/Powys border near Llanidloes. The river then flows through Shropshire, Worcestershire and Gloucestershire. The county towns of Shrewsbury, Worcester and Gloucester lie on its course.

Shropshire is a ceremonial county in the West Midlands of England, on the border with Wales. It is bordered by Cheshire to the north, the Welsh county of Wrexham to the north and northwest, Staffordshire to the east, Worcestershire to the southeast, Herefordshire to the south, and the Welsh county of Powys to the west. The largest settlement is Telford, while Shrewsbury is the county town.

Powys is a county and preserved county in Wales. It borders Gwynedd, Denbighshire, and Wrexham to the north; the English ceremonial counties of Shropshire and Herefordshire to the east; Monmouthshire, Blaenau Gwent, Merthyr Tydfil, Caerphilly, Rhondda Cynon Taf, and Neath Port Talbot to the south; and Carmarthenshire and Ceredigion to the west. The largest settlement is Newtown, and the administrative centre is Llandrindod Wells.

Montgomeryshire was one of the thirteen historic counties of Wales. It was named after its county town, Montgomery, which in turn was named after one of William the Conqueror's main counsellors, Roger de Montgomerie, who was the 1st Earl of Shrewsbury.

The River Teme rises in Mid Wales, south of Newtown, and flows southeast roughly forming the border between England and Wales for several miles through Knighton before entering England in the vicinity of Bucknell and continuing east to Ludlow in Shropshire. From there, it flows to the north of Tenbury Wells on the Shropshire/Worcestershire border on its way to join the River Severn south of Worcester. The whole of the River Teme was designated as an SSSI by English Nature in 1996.

The Stour(, rhymes with "flour") is a river flowing through the counties of Worcestershire, the West Midlands and Staffordshire in the West Midlands region of England. The Stour is a major tributary of the River Severn, and is about 25 miles (40 km) in length. It has played a considerable part in the economic history of the region.

The name Rea Brook can refer to either of two brooks in Shropshire, England.

The Shropshire Hills National Landscape is a designated Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONB) in Shropshire, England. It is located in the south of the county, extending to its border with Wales. Designated in 1958, the area encompasses 802 square kilometres (310 sq mi) of land primarily in south-west Shropshire, taking its name from the upland region of the Shropshire Hills. The A49 road and Welsh Marches Railway Line bisect the area north–south, passing through or near Shrewsbury, Church Stretton, Craven Arms and Ludlow.

The River Vyrnwy flows through northern Powys, Wales, and Shropshire, England. The name derives from Severn, the river of which it is a tributary.
The geology of the county of Shropshire, England is very diverse with a large number of periods being represented at outcrop. The bedrock consists principally of sedimentary rocks of Palaeozoic and Mesozoic age, surrounding restricted areas of Precambrian metasedimentary and metavolcanic rocks. The county hosts in its Quaternary deposits and landforms, a significant record of recent glaciation. The exploitation of the Coal Measures and other Carboniferous age strata in the Ironbridge area made it one of the birthplaces of the Industrial Revolution. There is also a large amount of mineral wealth in the county, including lead and baryte. Quarrying is still active, with limestone for cement manufacture and concrete aggregate, sandstone, greywacke and dolerite for road aggregate, and sand and gravel for aggregate and drainage filters. Groundwater is an equally important economic resource.

Corndon Hill is a hill in Powys, Mid Wales, whose summit rises to 513.6 metres (1,685 ft) above sea level. It has a topographic prominence of 203.1 metres (666 ft), so is listed as a Marilyn.

The River Rea is a small river that flows through south east Shropshire, England.

Bettws-y-Crwyn is a small, remote village and civil parish in south-west Shropshire, England. It is close to the England–Wales border and is one of a number of English villages to have a Welsh language placename.

Chirbury is a village and former civil parish, now in the parish of Chirbury with Brompton, in the Shropshire district, in west Shropshire, England. It is situated in the Vale of Montgomery, close to the Wales–England border, which is to its north, west and south. The A490 and B4386 routes cross at Chirbury.

The River Onny is a river in Shropshire, England. It is a major tributary of the River Teme.
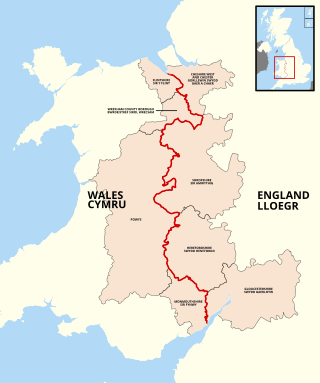
The England–Wales border, sometimes referred to as the Wales–England border or the Anglo-Welsh border, runs for 160 miles (260 km) from the Dee estuary, in the north, to the Severn estuary in the south, separating England and Wales.

The River Worfe is a river in Shropshire, England. The name Worfe is said to derive from the Old English meaning to wander which the river is notable for in its middle section. Mapping indicates that the river begins at Cosford Bridge where the Cosford Brook and Albrighton Brook meet.
The Tripartite Indenture was an agreement made in February 1405 among Owain Glyndŵr, Edmund Mortimer, and Henry Percy, 1st Earl of Northumberland, agreeing to divide England and Wales up among them at the expense of Henry IV. Glyndŵr was to be given Wales, and a substantial part of the west of England, including the English portions of the Welsh Marches. Northumberland was to have received the north, as well as Northamptonshire, Norfolk, Warwickshire, and Leicestershire. The Mortimers were to have received the rest of southern England.

Ledwyche Brook is a minor river in south Shropshire, England. It is sometimes referred to as the River Ledwyche and spelled variously, including "Ledwich" or "Ledwych". The brook is a tributary of the River Teme.
The Vale of Montgomery is an area of low land straddling the border between Shropshire, England and the former county of Montgomeryshire, Wales. The three principal settlements within it are the former county town of Montgomery and the village of Churchstoke, both in Wales, and Chirbury in England. The earthworks of Offa's Dyke run NNW-ESE through the middle of the vale and are followed by the Offa's Dyke Path. The national boundary also follows this monument for 3 km within the vale. The River Camlad rises to the southeast of the vale whilst its tributary the Caebitra rises to its southwest. They combine at Churchstoke and flow north within a gorge along the eastern margin of the vale, before turning west across the north end of the vale to join the River Severn.


















