Related Research Articles
KOI (КОИ) is a family of several code pages for the Cyrillic script. The name stands for Kod obmena informatsiey which means "Code for Information Interchange".

Field marshal was, with the exception of Generalissimo, the highest military rank of the Russian Empire. It was a military rank of the 1st class in the Imperial Russian Army and equal to those of Chancellor and Active Privy Councillor, 1st class in civil service, and General Admiral in the Imperial Russian Navy. After the Russian Revolution of 1917 the rank was abolished, alongside the Table of Ranks. In 1935 however, the Red Army introduced the equivalent rank of "Marshal of the Soviet Union" as the highest military rank of the Soviet Union, when ranks were restored under Stalin's rule.

The Erivan Governorate was a province (guberniya) of the Caucasus Viceroyalty of the Russian Empire, with its centеr in Erivan. Its area was 27,830 sq. kilometеrs, roughly corresponding to what is now most of central Armenia, the Iğdır Province of Turkey, and the Nakhchivan exclave of Azerbaijan. At the end of the 19th century, it bordered the Tiflis Governorate to the north, the Elizavetpol Governorate to the east, the Kars Oblast to the west, and Persia and the Ottoman Empire to the south. Mount Ararat and the fertile Ararat Valley were included in the center of the province.

Grand Duchess Elizabeth Mikhailovna of Russia was the second child and daughter of Grand Duke Mikhail Pavlovich of Russia and Princess Charlotte of Württemberg who took the name Elena Pavlovna upon her conversion to the Orthodox faith. Through her father, Elizabeth was a granddaughter of Tsar Paul I of Russia, and a niece of both Russian emperors Alexander I and Nicholas I.
This is a summary of the use of Morse code to represent alphabets other than Latin.
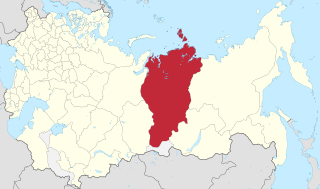
Yeniseysk Governorate was an administrative-territorial unit (guberniya) of the Russian Empire, the Russian Republic, and the Russian SFSR in 1822–1925. It was named after Yeniseysk.
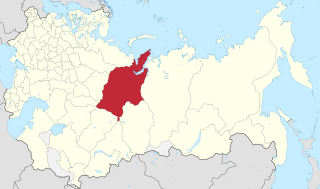
Tobolsk Governorate was an administrative-territorial unit (guberniya) of the Russian Empire, Russian Republic and Russian SFSR located in the Ural Mountains and Siberia. It existed from 1796 to 1920; its seat was in the city of Tobolsk, and from 1919 to 1920, in the city of Tyumen.
The Collegium of Commerce is the central government agency created by Peter I to protect the trade.

Vyatka Governorate was an administrative-territorial unit (guberniya) of the Russian Empire and the Russian SFSR from 1796 to 1929, with its capital in Vyatka. The area of the governorate roughly corresponds to modern-day Kirov Oblast and Udmurtia.

Vitebsk Governorate was an administrative-territorial unit (guberniya) of the Russian Empire, with the seat of governorship in Vitebsk. It was established in 1802 by splitting Belarusian Governorate and existed until 1924. Today most of the area belongs to Belarus, the northwestern part to Latvia and the northeastern part to Pskov and Smolensk Oblasts of Russia.Together with the Vilna, Kovno, Grodno, Minsk, and Mogilev Governorates, it formed the Northwestern Krai. The provincial city was Vitebsk, the largest city was Dvinsk.
Georgia-Imeretia Governorate was a short-lived governorate (guberniya) of the Caucasus Viceroyalty of the Russian Empire, administered from Tiflis (Tbilisi). Roughly corresponding to modern Georgia and parts of Armenia and Azerbaijan, it was created in 1840 from the territory of the Georgia Governorate and the oblasts of Imereti and Armenia.

Religion in Artsakh was characterized by a largely homogeneous Christian population (99%) who overwhelmingly belonged to the Armenian Apostolic Church (98%).

The flag of Irkutsk Oblast depicts three vertical stripes in the ratio 1:2:1: blue on the hoist and fly and white in the middle. Within the white strip, a stylized black tiger-beaver hybrid is seen holding a red sable in its mouth. These two are surrounded by branches of cedar. The blue represents the waters of Lake Baikal, while white represents purity, goodness, and honesty. The green of the cedar branches represents hope, joy, and abundance.

Tomsk Governorate was an administrative-territorial unit (guberniya) of the Russian Empire, the Russian Republic, and the Russian SFSR, which existed from 1804 to 1925 as part of Siberian Governorate-General (1804–1822) and West Siberian Governorate-General (1822–1882). Its capital was in Tomsk.
The Digest of Laws of the Russian Empire was the code of penal and civil law in the Russian Empire starting on January 1, 1835.

Saint-Petersburg Society of Mutual Credit was a Russian bank that operated between 1864 and 1918. The bank was the first commercial credit bank in Russia focused on providing credit to business and tangible assets deposits. The bank was founded in April 1863 by Evgeny Lamansky, then a vice-president of the State Bank of the Russian Empire.

National Guard Day is an official holiday that honors the National Guard of Russia, celebrated on 27 March.
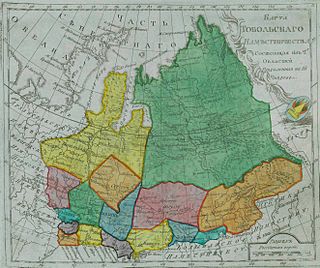
Tobolsk Viceroyalty was an administrative-territorial unit (namestnichestvo) of the Russian Empire, which existed in 1782–1796. It was located in Siberia with its capital in Tobolsk.
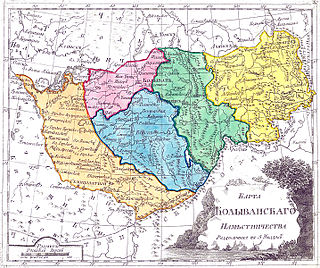
Kolyvan Viceroyalty, later Kolyvan Governorate, was an administrative-territorial unit of the Russian Empire, which existed in 1783–1796.

The Oblast of Siberian Kirghiz was an administrative-territorial unit of the Russian Empire, which existed from 1854 to 1868. The administrative centre was the city of Omsk.
References
- ↑ "Полное собрание законов Российской Империи. Собрание Второе. Том XXXI. Отделение 1". runivers.ru. Retrieved 2024-10-10.
- ↑ "Полное собрание законов Российской Империи. Собрание Второе. Том XXXI. Отделение 2". runivers.ru. Retrieved 2024-10-10.