Related Research Articles

Character encoding is the process of assigning numbers to graphical characters, especially the written characters of human language, allowing them to be stored, transmitted, and transformed using digital computers. The numerical values that make up a character encoding are known as "code points" and collectively comprise a "code space", a "code page", or a "character map".
While Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) has been in use since 1991, HTML 4.0 from December 1997 was the first standardized version where international characters were given reasonably complete treatment. When an HTML document includes special characters outside the range of seven-bit ASCII, two goals are worth considering: the information's integrity, and universal browser display.

Mojibake is the garbled or gibberish text that is the result of text being decoded using an unintended character encoding. The result is a systematic replacement of symbols with completely unrelated ones, often from a different writing system.
In computing, a code page is a character encoding and as such it is a specific association of a set of printable characters and control characters with unique numbers. Typically each number represents the binary value in a single byte.
ISO/IEC 8859-5:1999, Information technology — 8-bit single-byte coded graphic character sets — Part 5: Latin/Cyrillic alphabet, is part of the ISO/IEC 8859 series of ASCII-based standard character encodings, first edition published in 1988. It is informally referred to as Latin/Cyrillic.
KOI8-R is an 8-bit character encoding, derived from the KOI-8 encoding by the programmer Andrei Chernov in 1993 and designed to cover Russian, which uses a Cyrillic alphabet. KOI8-R was based on Russian Morse code, which was created from a phonetic version of Latin Morse code. As a result, Russian Cyrillic letters are in pseudo-Roman order rather than the normal Cyrillic alphabetical order. Although this may seem unnatural, if the 8th bit is stripped, the text is partially readable in ASCII and may convert to syntactically correct KOI-7. For example, "Код Обмена Информацией" in KOI8-R becomes kOD oBMENA iNFORMACIEJ.
KOI8-U is an 8-bit character encoding, designed to cover Ukrainian, which uses a Cyrillic alphabet. It is based on KOI8-R, which covers Russian and Bulgarian, but replaces eight box drawing characters with four Ukrainian letters Ґ, Є, І, and Ї in both upper case and lower case.
KOI (КОИ) is a family of several code pages for the Cyrillic script. The name stands for Kod obmena informatsiey which means "Code for Information Interchange".
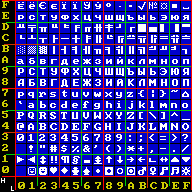
Code page 866 is a code page used under DOS and OS/2 in Russia to write Cyrillic script. It is based on the "alternative code page" developed in 1984 in IHNA AS USSR and published in 1986 by a research group at the Academy of Science of the USSR. The code page was widely used during the DOS era because it preserves all of the pseudographic symbols of code page 437 and maintains alphabetic order of Cyrillic letters. Initially this encoding was only available in the Russian version of MS-DOS 4.01 (1990), but with MS-DOS 6.22 it became available in any language version.
Code page 852 is a code page used under DOS to write Central European languages that use Latin script.
Mazovia encoding is a character set used under DOS to represent Polish text. The character set derives from code page 437, with specific positions modified to accommodate Polish letters. Notably, the Mazovia encoding maintains the block graphic characters from code page 437, distinguishing it from IBM's later official Central European code page 852, which failed to preserve all block graphics, leading to incorrect display in programs such as Norton Commander.
KOI-7 (КОИ-7) is a 7-bit character encoding, designed to cover Russian, which uses the Cyrillic alphabet.
In computing, a hardware code page (HWCP) refers to a code page supported natively by a hardware device such as a display adapter or printer. The glyphs to present the characters are stored in the alphanumeric character generator's resident read-only memory and are thus not user-changeable. They are available for use by the system without having to load any font definitions into the device first. Startup messages issued by a PC's System BIOS or displayed by an operating system before initializing its own code page switching logic and font management and before switching to graphics mode are displayed in a computer's default hardware code page.
CWI-2 is a Hungarian code page frequently used in the 1980s and early 1990s. If this code page is erroneously interpreted as code page 437, it will still be fairly readable.
KOI8-RU is an 8-bit character encoding, designed to cover Russian, Ukrainian, and Belarusian which use a Cyrillic alphabet. It is closely related to KOI8-R, which covers Russian and Bulgarian, but replaces ten box drawing characters with five Ukrainian and Belarusian letters Ґ, Є, І, Ї, and Ў in both upper case and lower case. It is even more closely related to KOI8-U, which does not include Ў but otherwise makes the same letter replacements. The additional letter allocations are matched by KOI8-E, except for Ґ which is added to KOI8-F.
KOI8-T is an 8-bit single-byte extended ASCII character encoding adapting KOI8 to cover the Tajik Cyrillic alphabet. It was introduced by Michael Davis as an interim solution for representing Tajiki Cyrillic text in an interchangeable manner appropriate for use on the web, in an attempt to bridge the gap between existing non-interoperable font-specific encodings and the eventual wide adoption of Unicode. It is used by the GNU C Library as its default encoding for Tajik. FreeDOS calls it code page 62318.
KOI8-F or KOI8 Unified is an 8-bit character set. It was designed by Peter Cassetta of Fingertip Software as an attempt to support all the encoded letters from both KOI8-E (ISO-IR-111) and KOI8-RU, along with some of the pseudographics from KOI8-R, with some additional punctuation in the remaining space, sourced partly from Windows-1251. This encoding was only used in the software of that company. FreeDOS calls it code page 60270.
ISO-IR-111 or KOI8-E is an 8-bit character set. It is a multinational extension of KOI-8 for Belarusian, Macedonian, Serbian, and Ukrainian. The name "ISO-IR-111" refers to its registration number in the ISO-IR registry, and denotes it as a set usable with ISO/IEC 2022.
DKOI is an EBCDIC encoding for Russian Cyrillic. It is a Telegraphy-based encoding used in ES EVM mainframes. It has been defined by several standards: GOST 19768-74 / ST SEV 358-76, ST SEV 358-88 / GOST 19768-93, CSN 36 9103.

Andrei Aleksandrovich Chernov, also known as Andrew Chernov and Ache, was a Soviet and Russian programmer who was one of the founders of the Russian Internet and the creator of the character encoding KOI8-R.
References
- ↑ "Cyrillic X11 fonts in koi8-o encoding".
- ↑ Winitzki, Serge (2002-01-29). KOI8-C (Report). Internet Engineering Task Force.
- ↑ "KOI8-C encoding".
- ↑ "FreeDOS KOI code page numbers". GitHub .