This article needs additional citations for verification .(July 2008) |
The Russian Research Module (RM) was to be a Russian component of the International Space Station (ISS) that provided facilities for Russian science experiments and research.
This article needs additional citations for verification .(July 2008) |
The Russian Research Module (RM) was to be a Russian component of the International Space Station (ISS) that provided facilities for Russian science experiments and research.
The original designs of ISS featured two research modules shaped like a rounded Zarya Functional Cargo Block, but Russian budget problems caused one of them along with the Universal Docking Module to be cancelled early in the program, leaving only one Research Module. This Research Module was scheduled to be built and launched in 2010 or later. In 2007 it was decided that, due to the continuing budget problems, the last Research Module was to be cancelled as well.[ citation needed ]
According to the schedule[ when? ] the module with scientific designation for the Russian Orbital Segment became the FGB-2 based Multipurpose Laboratory Module Nauka approved after the cancellation of the original RM1 and RM2.
Additionally the Russian Orbital Segment contains two smaller modules, initially named Mini-Research Module (MRM) 1 and 2. The MRM1 Rassvet implements the Docking and Stowage Module of the original design and is based on the canceled Science Power Platform pressurised compartment. Rassvet was launched in 2010 by STS-132 on board the Space Shuttle Atlantis by NASA. MRM2 is one of the names for the original Docking Compartment 2 module Poisk, that was canceled, but later scheduled again for 2009 launch by Progress M-MIM2.
RKK Energia, the manufacturer of the ROS components, proposes to execute a similar plan to the original ISS proposal with the addition of the nodal module Prichal in 2021 and two additional science/energy modules to the segment around the mid-2020s, though it has decided as of April 2022 [update] to launch the modules as their own space station. [1] [2] [ needs update ]

The International Space Station (ISS) is a modular space station in low Earth orbit. It is a multinational collaborative project involving five participating space agencies: NASA, Roscosmos (Russia), JAXA (Japan), ESA (Europe), and CSA (Canada). The ownership and use of the space station is established by intergovernmental treaties and agreements. The station serves as a microgravity and space environment research laboratory in which scientific research is conducted in astrobiology, astronomy, meteorology, physics, and other fields. The ISS is suited for testing the spacecraft systems and equipment required for possible future long-duration missions to the Moon and Mars.

The State Space Corporation "Roscosmos", commonly known simply as Roscosmos, is a state corporation of the Russian Federation responsible for space flights, cosmonautics programs, and aerospace research.

Zvezda, Salyut DOS-8, also known as the Zvezda Service Module, is a module of the International Space Station (ISS). It was the third module launched to the station, and provided all of the station's life support systems, some of which are supplemented in the US Orbital Segment (USOS), as well as living quarters for two crew members. It is the structural and functional center of the Russian Orbital Segment (ROS), which is the Russian part of the ISS. Crew assemble here to deal with emergencies on the station.

Zarya, also known as the Functional Cargo Block or FGB, is the first module of the International Space Station to have been launched. The FGB provided electrical power, storage, propulsion, and guidance to the ISS during the initial stage of assembly. With the launch and assembly in orbit of other modules with more specialized functionality, it's as of August 2021 primarily used for storage, both inside the pressurized section and in the externally mounted fuel tanks. The Zarya is a descendant of the TKS spacecraft designed for the Russian Salyut program. The name Zarya ("Dawn") was given to the FGB because it signified the dawn of a new era of international cooperation in space. Although it was built by a Russian company, it is owned by the United States.
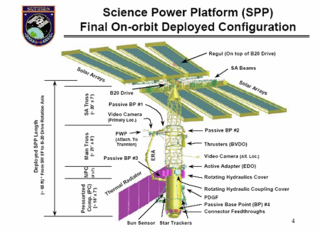
The Science Power Platform was a planned Russian element of the International Space Station (ISS) that was intended to be delivered to the ISS by a Russian Proton rocket or Zenit rocket but was shifted to launch by Space Shuttle as part as a tradeoff agreement on other parts of the ISS.

Nauka, also known as the Multipurpose Laboratory Module-Upgrade or simply Multipurpose Laboratory Module (MLM), is a module of the International Space Station (ISS). The MLM-U is funded by Roscosmos. In the original ISS plans, Nauka was to use the location of the Docking and Storage Module (DSM). Later, the DSM was replaced by the Rassvet module and Nauka was moved from Zarya's nadir port to Zvezda's nadir port.

The European Robotic Arm (ERA) is a robotic arm that is attached to the Russian Orbital Segment (ROS) of the International Space Station. Launched to the ISS in July 2021; it is the first robotic arm that is able to work on the Russian Segment of the station. The arm supplements the two Russian Strela cargo cranes that were originally installed on the Pirs module, but were later moved to the docking compartment Poisk and Zarya module.

STS-132 was a NASA Space Shuttle mission, during which Space Shuttle Atlantis docked with the International Space Station on 16 May 2010. STS-132 was launched from the Kennedy Space Center on 14 May 2010. The primary payload was the Russian Rassvet Mini-Research Module, along with an Integrated Cargo Carrier-Vertical Light Deployable (ICC-VLD). Atlantis landed at the Kennedy Space Center on 26 May 2010.

The Stykovochnyy Otsek, GRAU index 316GK, otherwise known as the Mir docking module or SO, was the sixth module of the Russian space station Mir, launched in November 1995 aboard the Space ShuttleAtlantis. The module, built by RKK Energia, was designed to help simplify space shuttle dockings to Mir during the Shuttle-Mir programme, preventing the need for the periodic relocation of the Kristall module necessary for dockings prior to the compartment's arrival. The module was also used to transport two new photovoltaic arrays to the station, as a mounting point for external experiments, and as a storage module when not in use for dockings.

Rassvet, also known as the Mini-Research Module 1 and formerly known as the Docking Cargo Module (DCM), is a component of the International Space Station (ISS). The module's design is similar to the Mir Docking Module launched on STS-74 in 1995. Rassvet is primarily used for cargo storage and as a docking port for visiting spacecraft. It was flown to the ISS aboard Space ShuttleAtlantis on the STS-132 mission on 14 May 2010, and was connected to the ISS on 18 May 2010. The hatch connecting Rassvet with the ISS was first opened on 20 May 2010. On 28 June 2010, the Soyuz TMA-19 spacecraft performed the first docking with the module.

The process of assembling the International Space Station (ISS) has been under way since the 1990s. Zarya, the first ISS module, was launched by a Proton rocket on 20 November 1998. The STS-88 Space Shuttle mission followed two weeks after Zarya was launched, bringing Unity, the first of three node modules, and connecting it to Zarya. This bare 2-module core of the ISS remained uncrewed for the next one and a half years, until in July 2000 the Russian module Zvezda was launched by a Proton rocket, allowing a maximum crew of three astronauts or cosmonauts to be on the ISS permanently.

Poisk, also known as the Mini-Research Module 2, Малый исследовательский модуль 2, or МИМ 2, is a docking module of the International Space Station. Its original name was Docking Module 2, as it is almost identical to the Pirs Docking Compartment. Added in 2009, Poisk was the first major Russian addition to the International Space Station since 2001. Poisk is overall the same design as the docking module Pirs. Whereas Pirs had been attached to the nadir ("bottom") port of Zvezda, Poisk is attached to the zenith ("top"); Pirs was closer to the Earth with the ISS in its usual orientation, and Poisk is on the other side. Poisk is Russian for explore or search. Poisk combines various docking, EVA, and science capabilities. It has two egress hatches for EVAs in addition to the two spacecraft docking ports. Although Poisk is designated as Mini-Research Module 2, it arrived before Mini-Research Module 1 (Rassvet), which had a different design; Poisk looks more like the Pirs docking port, which is not designated as a mini-research module.

The Russian Orbital Segment (ROS) is the name given to the components of the International Space Station (ISS) constructed in Russia and operated by the Russian Roscosmos. The ROS handles Guidance, Navigation, and Control for the entire Station.

The Orbital Piloted Assembly and Experiment Complex was a 2009–2017 proposed third-generation Russian modular space station for low Earth orbit. The concept was to use OPSEK to assemble components of crewed interplanetary spacecraft destined for the Moon, Mars, and possibly Saturn. The returning crew could also recover on the station before landing on Earth. Thus, OPSEK could form part of a future network of stations supporting crewed exploration of the Solar System.

Soyuz TMA-03M was a spaceflight to the International Space Station (ISS). It launched on 21 December 2011 from Site One at the Baikonur Cosmodrome, Kazakhstan, carrying three members of Expedition 30 to the ISS. TMA-03M was the 112th flight of a Russian Soyuz spacecraft, since the first in 1967, and the third flight of the modernised Soyuz-TMA-M version. The docking with the International Space Station took place at 19:19 Moscow Time on 23 December, three minutes ahead of schedule.
The Universal Docking Module (UDM), was a planned Russian docking module for the International Space Station, to be jointly built by RKK Energia and Khrunichev. The Prichal nodal addition to the Nauka laboratory, the eventual form of the FGB-2 design upon which the UDM was based, grew out of this proposal.

Prichal nodal module also known as Uzlovoy Module or UM is a Russian spacecraft which is part of the International Space Station (ISS). It was approved in 2011 and was launched on 24 November 2021, at 13:06:35 UTC, atop Progress M-UM, with operations beginning in 2022. Originally, the nodal module was intended to serve as the only permanent element of the future Orbital Piloted Assembly and Experiment Complex (OPSEK), but those plans were scrapped in 2017.

The European contribution to the International Space Station comes from 10 members of the European Space Agency (ESA) and amounts to an 8% share in the programme. It consists of a number of modules in the US Orbital Segment, ATV supply ships, launchers, software and €8 billion.

The project to create the International Space Station required the utilization and/or construction of new and existing manufacturing facilities around the world, mostly in the United States and Europe. The agencies overseeing the manufacturing involved NASA, Roscosmos, the European Space Agency, JAXA, and the Canadian Space Agency. Hundreds of contractors working for the five space agencies were assigned the task of fabricating the modules, trusses, experiments and other hardware elements for the station.

Progress M-UM, was a specially modified Progress M 11F615A55, Russian production No.303, developed by Roscosmos to deliver the Prichal module to the Russian Orbital Segment (ROS) of the International Space Station (ISS). It was launched on 24 November 2021 at 13:06:35 UTC, along with a Progress M propulsion compartment and has the pressurised cargo module removed to accommodate Prichal. This was the 171st flight of a Progress spacecraft. It was the final flight of a Progress M and the first launch of a Progress spacecraft on a Soyuz 2.1b.