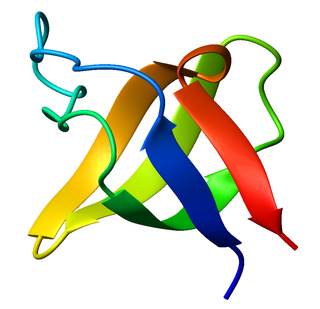
The SRC Homology 3 Domain is a small protein domain of about 60 amino acid residues. Initially, SH3 was described as a conserved sequence in the viral adaptor protein v-Crk. This domain is also present in the molecules of phospholipase and several cytoplasmic tyrosine kinases such as Abl and Src. It has also been identified in several other protein families such as: PI3 Kinase, Ras GTPase-activating protein, CDC24 and cdc25. SH3 domains are found in proteins of signaling pathways regulating the cytoskeleton, the Ras protein, and the Src kinase and many others. The SH3 proteins interact with adaptor proteins and tyrosine kinases. Interacting with tyrosine kinases, SH3 proteins usually bind far away from the active site. Approximately 300 SH3 domains are found in proteins encoded in the human genome. In addition to that, the SH3 domain was responsible for controlling protein-protein interactions in the signal transduction pathways and regulating the interactions of proteins involved in the cytoplasmic signaling.

Tyrosine-protein kinase ABL1 also known as ABL1 is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ABL1 gene located on chromosome 9. c-Abl is sometimes used to refer to the version of the gene found within the mammalian genome, while v-Abl refers to the viral gene, which was initially isolated from the Abelson murine leukemia virus.

Growth factor receptor-bound protein 2, also known as Grb2, is an adaptor protein involved in signal transduction/cell communication. In humans, the GRB2 protein is encoded by the GRB2 gene.
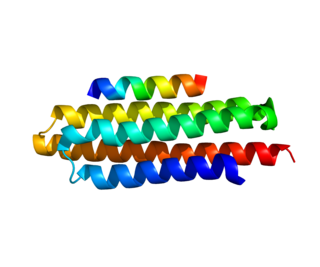
Paxillin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PXN gene. Paxillin is expressed at focal adhesions of non-striated cells and at costameres of striated muscle cells, and it functions to adhere cells to the extracellular matrix. Mutations in PXN as well as abnormal expression of paxillin protein has been implicated in the progression of various cancers.

Adapter molecule crk also known as proto-oncogene c-Crk is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CRK gene.

Cbl is a mammalian gene family. CBL gene, a part of the Cbl family, encodes the protein CBL which is an E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase involved in cell signalling and protein ubiquitination. Mutations to this gene have been implicated in a number of human cancers, particularly acute myeloid leukaemia.

Phospholipase C, gamma 1, also known as PLCG1 and PLCgamma1, is a protein that in humans involved in cell growth, migration, apoptosis, and proliferation. It is encoded by the PLCG1 gene and is part of the PLC superfamily.
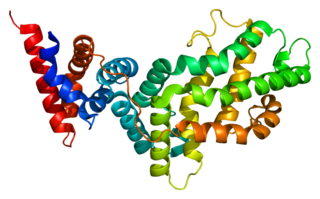
RAS p21 protein activator 1 or RasGAP, also known as RASA1, is a 120-kDa cytosolic human protein that provides two principal activities:

Crk-like protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CRKL gene.

SH3 domain-containing kinase-binding protein 1 is an adaptor protein that in humans is encoded by the SH3KBP1 gene.

Protein tyrosine kinase 2 beta is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PTK2B gene.
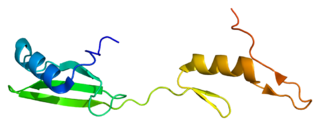
Cytoplasmic protein NCK1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NCK1 gene.

Breast cancer anti-estrogen resistance protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BCAR1 gene.

Tyrosine-protein kinase ABL2 also known as Abelson-related gene (Arg) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ABL2 gene.

Flotillin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FLOT1 gene.
CAP/Ponsin protein, also known as Sorbin and SH3 domain-containing protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SORBS1 gene. It is part of a small family of adaptor proteins that regulate cell adhesion, growth factor signaling and cytoskeletal formation. It is mainly expressed in heart, skeletal muscle, liver, adipose tissue, and macrophages; in striated muscle tissue, it is localized to costamere structures.

CD2-associated protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CD2AP gene.

Cytoplasmic protein NCK2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NCK2 gene.

Vinexin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SORBS3 gene.
A non-receptor tyrosine kinase (nRTK) is a cytosolic enzyme that is responsible for catalysing the transfer of a phosphate group from a nucleoside triphosphate donor, such as ATP, to tyrosine residues in proteins. Non-receptor tyrosine kinases are a subgroup of protein family tyrosine kinases, enzymes that can transfer the phosphate group from ATP to a tyrosine residue of a protein (phosphorylation). These enzymes regulate many cellular functions by switching on or switching off other enzymes in a cell.























