
Cepheus is a constellation in the deep northern sky, named after Cepheus, a king of Aethiopia in Greek mythology. It is one of the 48 constellations listed by the second century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 constellations in the modern times.

Rho Cassiopeiae is a yellow hypergiant star in the constellation Cassiopeia. It is about 8,150 light-years (2,500 pc) from Earth, yet can still be seen by the naked eye as it is over 300,000 times brighter than the Sun. On average it has an absolute magnitude of −9.5, making it visually one of the most luminous stars known. Recently imaged and measured by the CHARA array in 2024, its diameter measures between 564 and 700 times that of the Sun, approximately 879,000,000 kilometers, or 2.6 to 3.3 times the size of Earth's orbit.

Mu Cephei, also known as Herschel's Garnet Star, Erakis, or HD 206936, is a red supergiant or hypergiant star in the constellation Cepheus. It appears garnet red and is located at the edge of the IC 1396 nebula. It is a 4th magnitude star easily visible to the naked eye under good observing conditions. Since 1943, the spectrum of this star has served as a spectral standard by which other stars are classified.

VV Cephei, also known as HD 208816, is an eclipsing binary star system located in the constellation Cepheus. It is both a B[e] star and shell star.
KW Sagittarii is a red supergiant star, located approximately 2,420 parsecs away from the Sun in the direction of the constellation Sagittarius. It is one of the largest known stars, with a diameter about 1,000 times larger than the Sun. If placed at the center of the Solar System, the star's surface would engulf Mars, coming close to Jupiter's orbit.
V354 Cephei is a red supergiant star located within the Milky Way. It is an irregular variable located over 13,000 light-years away from the Sun. It has an estimated radius of 1,139 solar radii. If it were placed in the center of the Solar System, it would extend to between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter.

Zeta Cephei is a red supergiant star, located about 1000 light-years away in the constellation of Cepheus. Zeta Cephei marks the left shoulder of Cepheus, the King of Ethiopia. It is one of the fundamental stars of the MK spectral sequence, defined as type K1.5 Ib.

Nu Cephei is a class A2, fourth-magnitude blue supergiant star in the constellation Cepheus, visible to the naked eye. It is a white pulsating α Cygni variable star located about 4,700 light-years from Earth.

MY Cephei is a red supergiant located in open cluster NGC 7419 in the constellation of Cepheus. It is a semiregular variable star with a maximum brightness of magnitude 14.4 and a minimum of magnitude 15.5.

RW Cephei is a K-type hypergiant and a semirregular variable star in the constellation Cepheus, at the edge of the Sharpless 132 H II region and close to the small open cluster Berkeley 94. It is among the largest stars known with a radius of 1,100 times that of the Sun (R☉), nearly as large as the orbit of Jupiter.

Lambda Cephei is a fifth magnitude blue supergiant star in the constellation Cepheus, one of the hottest and most luminous visible to the naked eye.

9 Cephei, also known as V337 Cephei, is a variable star in the constellation Cepheus.

UY Scuti (BD-12°5055) is a red supergiant star, located 5,900 light-years away in the constellation Scutum. It is also a pulsating variable star, with a maximum brightness of magnitude 8.29 and a minimum of magnitude 10.56, which is too dim for naked-eye visibility. It is considered to be one of the largest known stars, with a radius estimated at 909 solar radii, thus a volume of 750 million times that of the Sun. This estimate implies if it were placed at the center of the Solar System, its photosphere would extend past the orbit of Mars or even the asteroid belt.
7 Cephei is a single star located approximately 820 light years away, in the northern circumpolar constellation of Cepheus. It is visible to the naked eye as a dim, blue-white hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.42.
IRC −10414 is a red supergiant and runaway star in the constellation Scutum, a rare case of a red supergiant with a bow shock.

RW Cygni is a semiregular variable star in the constellation Cygnus, about a degree east of 2nd magnitude γ Cygni. Its apparent magnitude varies between 8.05 and 9.70 and its spectral type between M3 and M4.

V419 Cephei is an irregular variable star in the constellation of Cepheus with an apparent magnitude that varies between 6.54 and 6.89.

BI Cygni(BI Cyg, IRC +40408, BD+36 4025) is a red supergiant in the constellation Cygnus. It is an irregular variable star with a maximum brightness of magnitude 8.4 and a minimum of magnitude 9.9. It is considered a member of the Cygnus OB1 stellar association, its distance is around 1,300 parsecs (4,200 ly) of the Solar System. It is less than a degree south of another variable red supergiant, BC Cygni.
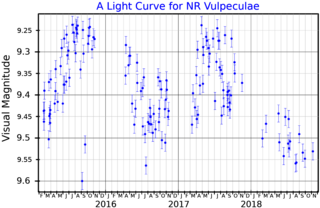
NR Vulpeculae is a red supergiant and irregular variable star in the constellation Vulpecula. It has an apparent magnitude varying between 9.13 and 9.61, which is too faint to be seen to the naked eye.

AR Cephei is a variable star in the constellation Cepheus. It is classified as a semiregular star, and has a maximum apparent magnitude of +7.32.













