
Mountain Province is a landlocked province of the Philippines in the Cordillera Administrative Region in Luzon. Its capital is Bontoc. Mountain Province was formerly referred to as Mountain in some foreign references. The name is usually shortened by locals to Mt. Province.

Kalinga, officially the Province of Kalinga, is a landlocked province in the Philippines situated within the Cordillera Administrative Region in Luzon. Its capital is Tabuk and borders Mountain Province to the south, Abra to the west, Isabela to the east, Cagayan to the northeast, and Apayao to the north. Kalinga and Apayao are the result of the 1995 partitioning of the former province of Kalinga-Apayao which was seen to better service the respective needs of the various indigenous peoples in the area.

The Cordillera Administrative Region, also known as the Cordillera Region and Cordillera, is an administrative region in the Philippines, situated within the island of Luzon. It is the only landlocked region in the insular country, bordered by the Ilocos Region to the west and southwest, and by the Cagayan Valley Region to the north, east, and southeast. It is the least populous region in the Philippines, with a population less than that of the city of Manila.

Luna, officially the Municipality of Luna, is a 2nd class municipality in the province of Apayao, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 21,297 people. It currently serves as the de facto capital of Apayao where the provincial capitol and related offices is located the New Apayao Government Center. Kabugao remains as the de jure capital.

Bauko, officially the Municipality of Bauko is a 4th class municipality in the province of Mountain Province, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 32,021 people.

Sanchez Mira, officially the Municipality of Sanchez Mira, is a 3rd class municipality in the province of Cagayan, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 26,164 people.

Santa Marcela, officially the Municipality of Santa Marcela, is a 4th class municipality in the province of Apayao, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 13,317 people.

Tineg, officially the Municipality of Tineg, is a 2nd class municipality in the province of Abra, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 4,977 people.

Abulug, officially the Municipality of Abulug, is a 3rd class municipality in the province of Cagayan, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 34,579 people.
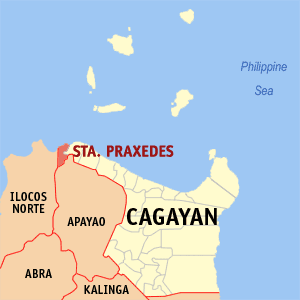
Santa Praxedes, officially the Municipality of Santa Praxedes, is a 5th class municipality in the province of Cagayan, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 4,434 people.

Barlig, officially the Municipality of Barlig is a 5th class municipality in the province of Mountain Province, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 4,796 people.

Bontoc, officially the Municipality of Bontoc, is a 2nd class municipality and capital of the province of Mountain Province, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 24,104 people.

Natonin, officially the Municipality of Natonin, is a 4th class municipality in the province of Mountain Province, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 10,339 people.

Sabangan, officially the Municipality of Sabangan is a 5th class municipality in the province of Mountain Province, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 9,621 people.

Sagada, officially the Municipality of Sagada is a 5th class municipality in the province of Mountain Province, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 11,510 people.

Calanasan, officially the Municipality of Calanasan,, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Apayao, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 12,550 people.

Flora, officially the Municipality of Flora, is a 3rd class municipality in the province of Apayao, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 17,944 people.

Pasil, officially the Municipality of Pasil, is a 5th class municipality in the southwestern part of the Kalinga. It is bounded on the north by the municipality of Balbalan, on the south by the municipality of Tinglayan, on the east by Tabuk city, and on the west by the province of Abra and south-western part of the municipality of Sadanga, Mountain Province. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 10,577 people.

Mankayan, officially the Municipality of Mankayan, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Benguet, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 37,233 people.

Hungduan, officially the Municipality of Hungduan is a 4th class municipality in the province of Ifugao, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 8,866 people.
























