Related Research Articles

The Mississippian is a subperiod in the geologic timescale or a subsystem of the geologic record. It is the earlier of two subperiods of the Carboniferous period lasting from roughly 358.9 to 323.2 million years ago. As with most other geochronologic units, the rock beds that define the Mississippian are well identified, but the exact start and end dates are uncertain by a few million years. The Mississippian is so named because rocks with this age are exposed in the Mississippi Valley.

The Mississippian culture were collections of Native American societies that flourished in what is now the Midwestern, Eastern, and Southeastern United States from approximately 800 to 1600, varying regionally. It was known for building large, earthen platform mounds, and often other shaped mounds as well. It was composed of a series of urban settlements and satellite villages linked together by loose trading networks. The largest city was Cahokia, believed to be a major religious center, located in what is present-day southern Illinois.
The Hickory Ridge Cemetery Archeological Site (8ES1280) is an archaeological site in Pensacola, Escambia County Florida. It is located north of Big Lagoon and west of Pensacola. During excavations in the 1980s carbon dating was done on burnt wood fragments associated with burials in the mound, with a determination that the site had been used c. 1450. Analysis of ceramics suggested it was a Mississippian culture site, probably from the Late Bottle Creek Phase or Early Bear Point Phases of the Pensacola culture. It was a cemetery associated with a village nearby, (8ES1052). On September 22, 2000, it was added to the U.S. National Register of Historic Places.

Sellars Farm site (40WI1), also known as the Sellars Farm state archaeological area and Sellars Indian mound, is a Mississippian culture archaeological site located in Wilson County, Tennessee, near Lebanon. The platform mound was the site of a settlement from about 1000 to 1300 CE. Today, the site is a satellite unit of Long Hunter State Park. The non-profit Friends of the Sellars Farm State Archaeological Area organization conducts tours and upkeep of the site. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places on December 11, 1972.
The Cloverdale archaeological site (23BN2) is an archaeological site located near present-day St. Joseph, Missouri. It is situated at the mouth of a small valley that opens into the Missouri River.

The Murphy Mound Archeological Site, is a prehistoric archaeological site in the Bootheel region of the U.S. state of Missouri. Located southwest of Caruthersville in Pemiscot County, Missouri the site was occupied by peoples of the Late Mississippian period, centuries before European colonization of the area.

Hovey Lake-Klein Archeological Site is an archaeological site of the Caborn-Welborn variant of the Mississippian culture. Hovey Lake-Klein Archeological Site is located on the west bank of Hovey Lake, a backwater lake near the Ohio River close to its confluence with the Wabash River. The site was an extensive village occupation dating between 1400 and 1650 CE.

Welborn Village Archeological Site, also known as the Murphy's Landings site, is an archaeological site of the prehistoric Caborn-Welborn culture variant of the Mississippian culture of indigenous peoples of North America.

The Battle Mound Site (3LA1) is an archaeological site in Lafayette County, Arkansas in the Great Bend region of the Red River basin. The majority of the mound was built from 1200 to 1400 CE. The site has the largest mound of the Caddoan Mississippian culture. It measures approximately 670 feet (200 m) in length, 320 feet (98 m) wide, and 34 feet (10 m) in height.
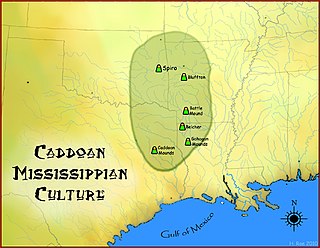
The Bluffton Mound Site is a Caddoan Mississippian culture archaeological site in Yell County, Arkansas on the Fourche La Fave River.

The Turk Site (15CE6) is a Mississippian culture archaeological site located near Bardwell in Carlisle County, Kentucky, on a bluff spur overlooking the Mississippi River floodplain.

The Ware Mounds and Village Site (11U31), also known as the Running Lake Site, located west of Ware, Illinois, is an archaeological site comprising three platform mounds and a 160-acre (65 ha) village site. The site was inhabited by the Late Woodland and Mississippian cultures from c. 800 to c. 1300. The village may be the only Mississippian village known to have existed in the Mississippi River valley in Southern Illinois. As the village was located near two major sources of chert, which Mississippian cultures used to make agricultural tools, it was likely a trading center for the mineral.

The Orr-Herl Mound and Village Site is an archaeological site located along the Ohio River in Hardin County, Illinois, United States. The site consists of a mound, which includes a sizable midden, and the remains of a village. The village was inhabited from roughly 900 to 1500 AD by Mississippian peoples. The site was an important source of fluorspar, which Mississippian peoples used for carvings and beads. The village was likely a manufacturing site for fluorspar items, which were then traded to other villages; this theory is supported by fluorspar artifacts recovered from the Kincaid Site, a Mississippian chiefdom center on the Ohio River in Illinois.

The Lunsford-Pulcher Archeological Site is a prehistoric archaeological site in rural Monroe and St. Clair counties in Illinois. The site was the location of a Middle Mississippian village which was probably a satellite community of Cahokia. Several pyramidal burial mounds are included in the site. Archaeological excavations at the site have also discovered the remains of houses and garden beds, making the site one of the few Mississippian villages at which garden beds have been found. The site has been known to European settlers since early settlement of the area in the late 18th century; despite being used for farmland, the site remains in good condition.

The Duck River cache is the archaeological collection of 46 Mississippian culture artifacts discovered by a worker on at the Link Farm site in Middle Tennessee in December 1894.

The Larson Site is a prehistoric archaeological site in Fulton County, Illinois, near the city of Lewistown. The site was the location of a Mississippian town and was occupied during the 13th and 14th centuries. The town was one of seven major town sites in the central Illinois River valley and served as a social and economic center for surrounding villages and farms. The artifacts uncovered at the site have been well-preserved and include both organic remains and intact homes, providing significant archaeological evidence regarding the Mississippian way of life.

The Link Farm State Archaeological Area, also known as the Duck River Temple Mounds or Duck River site, is a Mississippian culture archaeological site located at the confluence of the Duck and Buffalo Rivers south of Waverly in Humphreys County, Tennessee. The site is most widely known for the stone artifacts found during excavations in the late 19th century.
The Starr Village and Mound Group (11MP3), is a Mississippian culture archaeological site located on a bluff overlooking Macoupin Creek southwest of Carlinville in Macoupin County, Illinois.
The Bessemer Site, also known as the Talley Mounds and the Jonesboro Mounds, is a South Appalachian Mississippian culture archaeological site located near the confluence of Halls Mill Creek and Valley Creek, west of downtown Bessemer in Jefferson County, Alabama. The site was occupied in the early Mississippian period from about 1150 to 1250 CE.
References
- ↑ Frederick R. Schram & John Horner (1978). "Crustacea of the Mississippian Bear Gulch Limestone of Central Montana". Journal of Paleontology . 52 (2): 394–406. JSTOR 1303712.
- ↑ W. D. Ian Rolfe (1981). "Phyllocarida and the origin of the Malacostraca". Geobios . 14 (1): 17–26. doi:10.1016/S0016-6995(81)80164-7.