
Saturniidae, members of which are commonly named the saturniids, is a family of Lepidoptera with an estimated 2,300 described species. The family contains some of the largest species of moths in the world. Notable members include the emperor moths, royal moths, and giant silk moths.

Samia cynthia, the ailanthus silkmoth, is a saturniid moth, used to produce silk fabric but not as domesticated as the silkworm, Bombyx mori. The moth has very large wings of 113–125 mm (4.4–4.9 in), with a quarter-moon shaped spot on both the upper and lower wings, whitish and yellow stripes and brown background. There are eyespots on the outer forewings. The species was first described by Dru Drury in 1773.

Anisota senatoria, the orangestriped oakworm, also known as the orange-tipped oakworm, is a Nearctic moth of the family Saturniidae and subfamily Ceratocampinae. It is one of the more common Saturniids, reaching pest status occasionally in the northern parts of its range. As they are late-season feeders, however, they do little lasting damage to their hosts. It is very similar to A. finlaysoni in southern Ontario and A. peigleri in the southern US. The species was first described by James Edward Smith in 1797.

The Saturniinae or saturniines are a subfamily of the family Saturniidae, also known as giant silkmoths. They are commonly known as emperor moths or wild silk moths. They are easily spotted by the eyespots on the upper surface of their wings. Some exhibit realistic eye-like markings, whilst others have adapted the eyespots to form crescent moon or angular shapes or have lost their wing scales to create transparent windows. They are medium to very large moths, with adult wingspans ranging from 7.5 to 15 cm, in some cases even more. They consist of some of the largest sized Lepidoptera, such as the luna moth, atlas moth, and many more. The Saturniinae is an important source of wild silk and human food in many different cultures.

James Anderson was a Scottish physician and botanist who worked in India as an employee of the East India Company. During his career in India, he was involved in establishing a botanical garden at Mambalam, Madras, originating from a nopalry or Opuntia garden where he made attempts to introduce the cultivation of cochineal insects. He then attempted to introduce various other economically valuable plants, and examined silk and lac production. He maintained a steady communication with his friend from youth, James Anderson LLD (1739–1808) who published some of his notes in The Bee, or Literary Weekly Intelligencer, which has led to the use of the distinguishing form James Anderson MD or James Anderson of Madras.

Wild silks have been known and used in many countries from early times, although the scale of production is far smaller than that from cultivated silkworms. Silk cocoons and nests often resemble paper or cloth, and their use has arisen independently in many societies.

Anisota stigma, the spiny oakworm moth, is a moth of the family Saturniidae. The species was first described by Johan Christian Fabricius in 1775. It is found in North America from Massachusetts and southern Ontario to Florida, west to Minnesota, Kansas and Texas.

Anisota virginiensis, the pink-striped oakworm moth, is a species of silk moth of the family Saturniidae.

Actias neidhoederi is a species of moth belonging to the family Saturniidae. It is endemic to Taiwan.

Automeris is a genus of moths in the family Saturniidae and the subfamily Hemileucinae. As of 1996 there were 124 species, and more have since been described. These moths are generally characterized by the eyelike patches on the hindwings and the leaflike pattern on the forewings, an example of crypsis. The genus was first described by Jacob Hübner in 1819 and it is distributed in the Neotropical realm.

Samia is a genus of moths in the family Saturniidae. The genus was erected by Jacob Hübner in 1819.

Antheraea paphia, known as the South India small tussore, the tasar silkworm and vanya silkworm is a species of moth of the family Saturniidae found in India and Sri Lanka. The bulk of the literature on this species uses a junior synonym, Antheraea mylitta, rather than the correct name, A. paphia. It is one of a number of tasar silkworms, species that produce Tussar silk, a kind of wild silk that is made from the products of saturniid silkworms instead of the domesticated silkworm.

Samia wangi, the lesser Atlas moth, is a species of moth in the family Saturniidae. It is found from Taiwan through northern Vietnam to easternmost Xizang, Sichuan, the far south of Shaanxi and southern Zhejiang.

Ahimsa silk is a method of nonviolent silk breeding and harvesting. Wild silk moths are bred rather than the domestic variety. It allows the completion of the metamorphosis of the silkworm to its moth stage, whereas most silk harvesting requires the silkworms to be killed in their cocoon stage. No animals suffer or die for the silk to be produced, making it a favorable alternative to normal silk for those who object to harming animals.

Rhodinia fugax, the squeaking silkmoth, is a moth in the family Saturniidae. It was described by Arthur Gardiner Butler in 1877. It is native to Korea, Japan, China, and the Russian Far East.
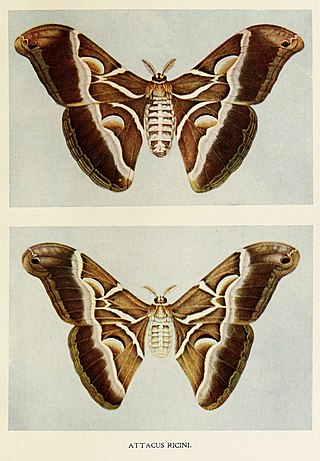
Samia ricini, the eri silkmoth, is a species of insect, a member of the family Saturniidae which includes the giant silk moths. This moth is a domestic polyhybrid that has been bred for centuries due to the silk it makes. The name is based on the host plant used for feeding the caterpillars, castor, Ricinus communis. This moth is derived from several different species within the genus including Samia cynthia and Samia canningi.
















