
Caryophyllaceae, commonly called the pink family or carnation family, is a family of flowering plants. It is included in the dicotyledon order Caryophyllales in the APG III system, alongside 33 other families, including Amaranthaceae, Cactaceae, and Polygonaceae. It is a large family, with 81 genera and about 2,625 known species.

Pinus pumila, commonly known as the Siberian dwarf pine, dwarf Siberian pine, dwarf stone pine, Japanese stone pine, or creeping pine, is a tree in the family Pinaceae native to northeastern Asia and the Japanese isles. It shares the common name creeping pine with several other plants.
Saponins, also selectively referred to as triterpene glycosides, are bitter-tasting usually toxic plant-derived organic chemicals that have a foamy quality when agitated in water. They are widely distributed but found particularly in soapwort, a flowering plant, the soapbark tree and soybeans. They are used in soaps, medicines, fire extinguishers, speciously as dietary supplements, for synthesis of steroids, and in carbonated beverages. Saponins are both water and fat soluble, which gives them their useful soap properties. Some examples of these chemicals are glycyrrhizin and quillaia, a bark extract used in beverages.

Marshmallow creme is a marshmallow confectionery spread similar in flavor, but not texture, to regular solid marshmallow. One brand of marshmallow creme is Marshmallow Fluff, which is used to make the fluffernutter sandwich, a New England classic comfort food which debuted in 1918 in Massachusetts, just a year after marshmallow creme was invented.

Saponaria is a genus of flowering plants in the family Caryophyllaceae, native to Asia and Europe, and are commonly known as soapworts. They are herbaceous perennials and annuals, some with woody bases. The flowers are abundant, five-petalled and usually in shades of pink or white. The genus is closely related to the genus Silene, being distinguished from these by having only two styles in the flower. It is also related to Gypsophila, but its calyx is cylindrical rather than bell-shaped.

Quillaja saponaria, the soap bark tree or soapbark, is an evergreen tree in the family Quillajaceae, native to warm temperate central Chile. In Chile it occurs from 32 to 40° South Latitude approximately and at up to 2000 m (6500 ft) above sea level. It can grow to 15–20 m (50–65 ft) in height. The tree has thick, dark bark; smooth, leathery, shiny, oval evergreen leaves 3–5 cm long; white star-shaped flowers 15 mm diameter borne in dense corymbs; and a dry fruit with five follicles each containing 10–20 seeds. The tree has several practical and commercial uses.

Saponaria officinalis is a common perennial plant from the family Caryophyllaceae. This plant has many common names, including common soapwort, bouncing-bet, crow soap, wild sweet William, and soapweed. There are about 20 species of soapworts altogether.

Ulmus pumila, the Siberian elm, is a tree native to Asia. It is also known as the Asiatic elm and dwarf elm, but sometimes miscalled the 'Chinese elm'. U. pumila has been widely cultivated throughout Asia, North America, Argentina, and southern Europe, becoming naturalized in many places, notably across much of the United States.

Castanea pumila, commonly known as the Allegheny chinquapin, American chinquapin or dwarf chestnut, is a species of chestnut native to the southeastern United States. The native range is from Massachusetts and New York to Maryland and extreme southern New Jersey and southeast Pennsylvania south to central Florida, west to eastern Texas, and north to southern Missouri and Kentucky. The plant's habitat is dry sandy and rocky uplands and ridges mixed with oak and hickory to 1000 m elevation. It grows best on well-drained soils in full sun or partial shade.

The 'dwarf' elm cultivar Ulmus 'Jacqueline Hillier' ('JH') is an elm of uncertain origin. It was cloned from a specimen found in a private garden in Selly Park, Birmingham, England, in 1966. The garden's owner told Hillier that it might have been introduced from outside the country by a relative. Hillier at first conjectured U. minor, as did Heybroek (2009). Identical-looking elm cultivars in Russia are labelled forms of Siberian Elm, Ulmus pumila, which is known to produce 'JH'-type long shoots. Melville considered 'JH' a hybrid cultivar from the 'Elegantissima' group of Ulmus × hollandica. Uncertainty about its parentage has led most nurserymen to list the tree simply as Ulmus 'Jacqueline Hillier'. 'JH' is not known to produce flowers and samarae, or root suckers.

The dwarf cuckoo is a tropical American bird species of the cuckoo family (Cuculidae).
Saporin is a protein that is useful in biological research applications, especially studies of behavior. Saporins are so-called ribosome inactivating proteins (RIPs), due to its N-glycosidase activity, from the seeds of Saponaria officinalis. It was first described by Fiorenzo Stirpe and his colleagues in 1983 in an article that illustrated the unusual stability of the protein.
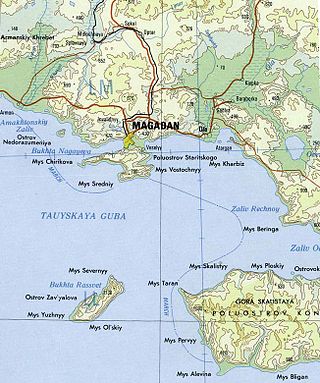
Zavyalov Island, formerly Ola Island, is a relatively large island in the Sea of Okhotsk, northwestern Pacific. It is located on the eastern side of Taui Bay, 20 km (12 mi) west of Cape Taran, Koni Peninsula, about 50 km (31 mi) south of the city of Magadan.

Iris pumila, sometimes known as pygmy iris or dwarf iris, probably originated as a natural hybrid between Iris pseudopumila Boissier & Heldreich and I. attica Tineo. It ranges from Austria through eastern Europe and the Balkans, in Eurasian steppe in Ukraine, southern Russia into southern Siberia and northern Kazakhstan, and the Caucasus into Turkey.

Saponaria ocymoides, the rock soapwort or tumbling Ted, is a species of semi-evergreen perennial flowering plant belonging to the family Caryophyllaceae, native to south western and southern central Europe.

Gentiana saponaria, the soapwort gentian or harvestbells, is a 1–2 ft (30–61 cm) tall flowering plant in the Gentianaceae family.

Kalanchoe pumila, the flower dust plant, is a species of flowering plant in the stonecrop family Crassulaceae, native to Madagascar. Growing to 20 cm (8 in) tall and 45 cm (18 in) wide, it is a spreading, dwarf succulent subshrub with arching stems of frosted leaves, and clusters of purple-veined pink flowers in spring. As the minimum temperature for cultivation is 12 °C (54 °F), in temperate regions it is grown under glass as a houseplant.

Spergularia marina, also called Spergularia salina, is a species of flowering plant in the family Caryophyllaceae. It is known as salt sandspurry or lesser sea-spurrey. S. marina is a sprawling annual or sometimes perennial, with stems up to 35 cm (14 in) long. Like other sea-spurrey species, its flowers have white to pink petals, with sepals usually longer than the petals, at 2.5–4 mm (0.1–0.2 in). Plants are salt-tolerant, being found by the sea and in saline areas inland.
Caladenia pumila, commonly known as the dwarf spider orchid is a plant in the orchid family Orchidaceae and is endemic to Victoria, Australia. It is a ground orchid with a single erect, hairy leaf and a single white flower with pale pink stripes. Its short flowering stem distinguishes it from other Victorian spider orchids. After 1933 it was presumed extinct until two plants were discovered in 2009.

Cerastium subtriflorum, the Slovenian mouse-ear chickweed, is a perennial plant species in the family Caryophyllaceae. It is mostly restricted to the Slovenian and Italian Alps.

















