The Cretaceous is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of the entire Phanerozoic. The name is derived from the Latin creta, "chalk", which is abundant in the latter half of the period. It is usually abbreviated K, for its German translation Kreide.

Ammonoids are a group of extinct marine mollusc animals in the subclass Ammonoidea of the class Cephalopoda. These molluscs, commonly referred to as ammonites, are more closely related to living coleoids than they are to shelled nautiloids such as the living Nautilus species. The earliest ammonites appeared during the Devonian, and the last species either vanished in the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, or shortly after during the Danian epoch of the Paleocene.

The Barremian is an age in the geologic timescale between 129.4 ± 1.5 Ma and 125.0 ± 1.0 Ma). It is a subdivision of the Early Cretaceous Epoch. It is preceded by the Hauterivian and followed by the Aptian Stage.

Baculites is an extinct genus of cephalopods with a nearly straight shell, included in the heteromorph ammonites. The genus, which lived worldwide throughout most of the Late Cretaceous, and which briefly survived the K-Pg mass extinction event, was named by Lamarck in 1799.
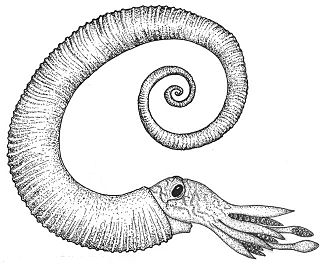
The Ancyloceratina were a diverse suborder of ammonite most closely related to the ammonites of order Lytoceratina. They evolved during the Late Jurassic but were not very common until the Cretaceous period, when they rapidly diversified and became one of the most distinctive components of Cretaceous marine faunas. They have been recorded from every continent and many are used as zonal or index fossils. The most distinctive feature of the majority of the Ancyloceratina is the tendency for most of them to have shells that are not regular spirals like most other ammonites. These irregularly-coiled ammonites are called heteromorph ammonites, in contrast to regularly coiled ammonites, which are called homomorph ammonites.
The Aptian is an age in the geologic timescale or a stage in the stratigraphic column. It is a subdivision of the Early or Lower Cretaceous Epoch or Series and encompasses the time from 125.0 ± 1.0 Ma to 113.0 ± 1.0 Ma, approximately. The Aptian succeeds the Barremian and precedes the Albian, all part of the Lower/Early Cretaceous.
In the geologic timescale, the Valanginian is an age or stage of the Early or Lower Cretaceous. It spans between 139.8 ± 3.0 Ma and 132.9 ± 2.0 Ma. The Valanginian Stage succeeds the Berriasian Stage of the Lower Cretaceous and precedes the Hauterivian Stage of the Lower Cretaceous.
The Campanian is the fifth of six ages of the Late Cretaceous Epoch on the geologic timescale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). In chronostratigraphy, it is the fifth of six stages in the Upper Cretaceous Series. Campanian spans the time from 83.6 to 72.1 million years ago. It is preceded by the Santonian and it is followed by the Maastrichtian.
The Hauterivian is, in the geologic timescale, an age in the Early Cretaceous Epoch or a stage in the Lower Cretaceous Series. It spans the time between 132.9 ± 2 Ma and 129.4 ± 1.5 Ma. The Hauterivian is preceded by the Valanginian and succeeded by the Barremian.

Ammonitina comprises a diverse suborder of ammonite cephalopods that lived during the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods of the Mesozoic Era. They are excellent index fossils, and it is often possible to link the rock layer in which they are found to specific geological time periods.

Nipponites is an extinct genus of heteromorph ammonites. The shells of Nipponites form "ox-bow" bends, resulting in some of the most bizarre shapes seen among ammonites.

Polyptychoceras is an extinct genus of ammonites from the Late Cretaceous of Asia, Europe, and North and South America. It was first named by Hisakatsu Yabe in 1927.

Albalophosaurus is a genus of ceratopsian ornithischian dinosaur. It was described in 2009 from remains found in 1997 by Yoshinori Kobayashi from the Kuwajima Formation of central Japan, outcropping in Hakusan in the Ishikawa Prefecture. The holotype, SBEI 176, consists of cranial bones from an incomplete, disarticulated skull and left lower jaw thought to belong to a single individual. The type species is named A. yamaguchiorum. The generic name is derived from Latin albus, "white", and Greek λόϕος (lophos), "crest", a reference to the snow-covered crest of Mount Hakusan. The specific name honours Ichio Yamaguchi and Mikiko Yamaguchi, who discovered and prepared many fossils from the site.

Eubostrychoceras is a genus of helically wound, corkscrew form, heteromorph ammonite which lived during the Upper Cretaceous. The genus is included in the ancycleratid family Nostoceratidae.

Menuites is a genus of extinct ammonites, forming a rather small offshoot of Anapachydiscus with a fairly widespread distribution from the Upper Cretaceous Santonian and Campanian stages.

Pachydesmoceras is a genus of ammonites belonging to the family Desmoceratidae.

Calycoceras is an extinct genus of cephalopods belonging to the subclass Ammonoidea and family Acanthoceratidae that lived during the Cenomanian stage of the Late Cretaceous, 100-94 Mya. Their shells had ornate ribs.

Puzosia is a genus of desmoceratid ammonites, and the type genus for the Puzosiinae, which lived during the middle part of the Cretaceous, from early Aptian to Maastrichtian. Sepkoski defines the range from Albian to Santonian. The generic name comes from the Serbian words "Puž" (snail) and "oce/ose" (axis), gaining its name from the shell's snail-like appearance.

Diplomoceratidae is a family of ammonites included in the order Ammonitida. Fossils of species within this genus have been found in the Cretaceous sediments. Studies of Diplomoceras suggest that members of this family could reach lifespans of over 200 years.
Clioscaphites is an extinct genus of ammonite belonging to the family Scaphitidae. Species in this genus are important index fossils of the Western Interior Seaway of the Coniacian to Santonian Ages of the Cretaceous.















