
Ammonoids are a group of extinct marine mollusc animals in the subclass Ammonoidea of the class Cephalopoda. These molluscs, commonly referred to as ammonites, are more closely related to living coleoids than they are to shelled nautiloids such as the living Nautilus species. The earliest ammonites appeared during the Devonian, and the last species either vanished in the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, or shortly after during the Danian epoch of the Paleocene.

Subclass Coleoidea, or Dibranchiata, is the grouping of cephalopods containing all the various taxa popularly thought of as "soft-bodied" or "shell-less". Unlike its extant sister group, Nautiloidea, whose members have a rigid outer shell for protection, the coleoids have at most an internal cuttlebone, gladius, or shell that is used for buoyancy or support. Some species have lost their cuttlebone altogether, while in some it has been replaced by a chitinous support structure.

Belemnoids are an extinct group of marine cephalopod, very similar in many ways to the modern squid and closely related to the modern cuttlefish. Like them, the belemnoids possessed an ink sac, but, unlike the squid, they possessed ten arms of roughly equal length, and no tentacles. The name "belemnoid" comes from the Greek word βέλεμνον, belemnon meaning "a dart or arrow" and the Greek word είδος, eidos meaning "form".

Ammonitida is an order of more highly evolved ammonoid cephalopods that lived from the Jurassic through Cretaceous time periods, commonly with intricate ammonitic sutures.
The Phyllocertina comprise a suborder of ammonoid cephalopods, belonging to the Ammonitida, whose range extends from the Lower Triassic to the Upper Cretaceous. Shells of the Phylloceratina are generally smooth with small to large umbilici and complex sutures with leaf-like phylloid saddle endings and lobes with thorn-like projections.

Aulacostephanus is an extinct ammonoid cephalopod genus from the Upper Jurassic Tithonian belonging to the perisphinctacean family Aulacostephanidae.

Ammonitina comprises a diverse suborder of ammonite cephalopods that lived during the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods of the Mesozoic Era. They are excellent index fossils, and it is often possible to link the rock layer in which they are found to specific geological time periods.

Oxycerites is an extinct ammonoid cephalopod belonging to the haploceratoid family, Oppeliidae, that lived during the Middle Jurassic.

Stephanoceratoidea, formerly Stephanocerataceae, is a superfamily of middle- upper Jurassic ammonoid cephalopods within the order Ammonitida containing diverse forms, generally with sharp ribbing and complex suture lines. Aptychi are believed to be mostly granular (Granulaptycus) or concentrically ribbed on the surface (Praestriaptychus)
Pseudonautilidae is a family of Jurassic and Lower Cretaceous nautilid cephalopods belonging to the same superfamily as modern Nautilus, Nautilaceae, but forming a different branch from the family Nautilidae. Pseudonautilids, together with other nautilids, were contemporary with the ammonoids, which comprise an entirely different set of shelled cephalopod stocks more closely related to octopus and squid.

Belemnitida is an extinct order of squid-like cephalopods that existed from the Late Triassic to Late Cretaceous. Unlike squid, belemnites had an internal skeleton that made up the cone. The parts are, from the arms-most to the tip: the tongue-shaped pro-ostracum, the conical phragmocone, and the pointy guard. The calcitic guard is the most common belemnite remain. Belemnites, in life, are thought to have had 10 hooked arms and a pair of fins on the guard. The chitinous hooks were usually no bigger than 5 mm (0.20 in), though a belemnite could have had between 100 and 800 hooks in total, using them to stab and hold onto prey.
The gladius, or pen, is a hard internal bodypart found in many cephalopods of the superorder Decapodiformes and in a single extant member of the Octopodiformes, the vampire squid. It is so named for its superficial resemblance to the Roman short sword of the same name, and is a vestige of the ancestral mollusc shell, which was external. The gladius is located dorsally within the mantle and usually extends for its entire length. Composed primarily of chitin, it lies within the shell sac, which is responsible for its secretion.

Cymatoceras is a wide-ranging extinct genus from the nautilitacean cephalopod family, Cymatoceratidae. They lived from the Late Jurassic to Late Oligocene, roughly from 155 to 23 Ma.
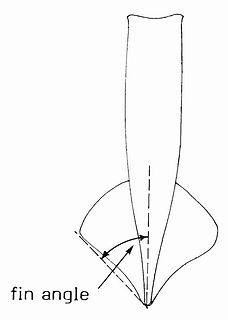
Cephalopod fins, sometimes known as wings, are paired flap-like locomotory appendages. They are found in ten-limbed cephalopods as well as in the eight-limbed cirrate octopuses and vampire squid. Many extinct cephalopod groups also possessed fins. Nautiluses and the more familiar incirrate octopuses lack swimming fins. An extreme development of the cephalopod fin is seen in the bigfin squid of the family Magnapinnidae.

Lytoceras is an ammonite genus that was extant during most of the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods, and is the type genus for the family Lytoceratidae. These cephalopods were fast-moving nektonic carnivores.

Schlotheimia is a genus of extinct cephalopods belonging to the subclass Ammonoidea that lived during the Hettangian stage at the beginning of the Early Jurassic.

Lytoceras cornucopia is an ammonite species belonging to the family Lytoceratidae. These cephalopods were fast-moving nektonic carnivores. They lived in the Jurassic period.

Lytoceras fimbriatum is an ammonite species belonging to the family Lytoceratidae. These cephalopods were fast-moving nektonic carnivores. They lived in the Jurassic period.

Ataxioceratidae is an extinct Ammonite cephalopod family included in the superfamily Perisphinctoidea. These fast-moving nektonic carnivores lived during the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods.

Pictonia is an extinct ammonoid cephalopod genus belonging to the family Aulacostephanidae. These fast-moving nektonic carnivores lived during the Jurassic period, Kimmeridgian age.


















