
Schoenus quartziticus is a species of sedge endemic to the Agulhas Plain region of the Western Cape Province in southern South Africa.

Schoenus compar is a species of sedge endemic to southern South Africa.

Schoenus arenicola is a species of sedge endemic to the south-west coast of South Africa.

Schoenus pseudoloreus is a species of sedge endemic to the Western Cape and Northern Cape provinces of South Africa. Its range also reaches the western border of Eastern Cape Province.
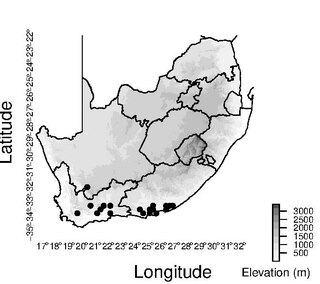
Schoenus megacarpus is a species of sedge endemic to the south-central region of South Africa.

Schoenus filiculmis is a species of sedge endemic to the western mountains of the Western Cape and Northern Cape Provinces of South Africa.

Schoenus graminifolius is a species of sedge endemic to the Cape Peninsula of South Africa.

Schoenus ligulatus is a species of sedge endemic to the western regions of the Western Cape Province of South Africa.

Schoenus exilis is a species of sedge endemic to the western areas of the Western Cape Province of South Africa.

Schoenus bolusii is a species of sedge endemic to the mountains of the Western Cape Province of South Africa. However, S. bolusii is not found on the Cape Peninsula.

Schoenus submarginalis is a species of sedge endemic to the mountains of the Western and Eastern Cape provinces of South Africa.

Schoenus crassiculmis is a species of sedge endemic to the mountains of the Western Cape Province of South Africa. Few collections of this species have also been made from western areas of the Eastern Cape Province.

Schoenus limosus is a species of sedge endemic to the KwaZulu-Natal and Eastern Cape provinces of South Africa. It is predominantly a species of wet grasslands, which explains its common name.
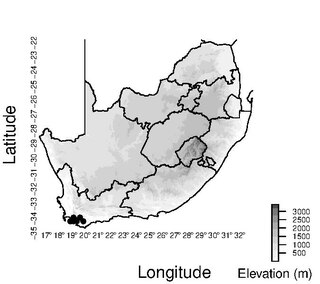
Schoenus purpurascens is a species of sedge endemic to the mountains of the southwestern part of the Western Cape Province of South Africa, with its distribution centered around the Caledon area.

Schoenus albovaginatus is a species of sedge endemic to the mountains of south-western South Africa.

Schoenus bracteosus is a species of sedge endemic to the mountains of southern South Africa.

Schoenus compactus is a species of sedge endemic to south-western South Africa.

Schoenus galpinii is a species of sedge endemic to eastern southern Africa.

Schoenus gracillimus is a species of sedge endemic to the Western Cape Province of South Africa.

Schoenus graciliculmis is a species of sedge endemic to regions of the southern Eastern Cape Province and nearby regions of the Western Cape Province of South Africa.






























