
Schoenus quartziticus is a species of sedge endemic to the Agulhas Plain region of the Western Cape Province in southern South Africa.

Schoenus compar is a species of sedge endemic to southern South Africa.

Schoenus arenicola is a species of sedge endemic to the south-west coast of South Africa.

Schoenus graminifolius is a species of sedge endemic to the Cape Peninsula of South Africa.

Schoenus exilis is a species of sedge endemic to the western areas of the Western Cape Province of South Africa.

Schoenus bolusii is a species of sedge endemic to the mountains of the Western Cape Province of South Africa. However, S. bolusii is not found on the Cape Peninsula.

Schoenus submarginalis is a species of sedge endemic to the mountains of the Western and Eastern Cape provinces of South Africa.

Schoenus crassiculmis is a species of sedge endemic to the mountains of the Western Cape Province of South Africa. Few collections of this species have also been made from western areas of the Eastern Cape Province.

Schoenus limosus is a species of sedge endemic to the KwaZulu-Natal and Eastern Cape provinces of South Africa. It is predominantly a species of wet grasslands, which explains its common name.

Schoenus compactus is a species of sedge endemic to south-western South Africa.
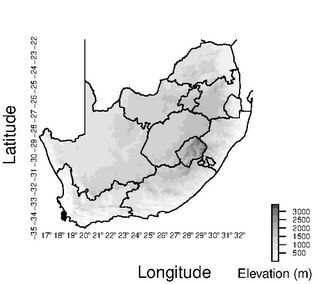
Schoenus riparius is a species of sedge endemic to the Cape Peninsula of South Africa.

Schoenus galpinii is a species of sedge endemic to eastern southern Africa.

Schoenus cuspidatus is a species of sedge endemic to the Cape region of South Africa where it is found in the provinces of Western Cape and Eastern Cape.

Schoenus dregeanus is a species of sedge endemic to mountainous locations in south-western South Africa.
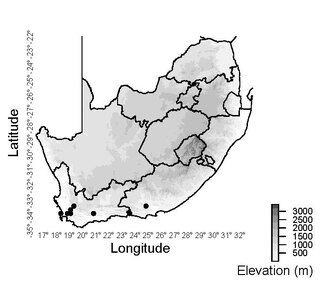
Schoenus adnatus is a species of sedge endemic to mountainous locations in southern regions of South Africa.

Schoenus gracillimus is a species of sedge endemic to the Western Cape Province of South Africa.

Schoenus neovillosus is a species of sedge endemic to the south-western mountains of the Western Cape Province of South Africa.

Schoenus australis is a species of sedge endemic to locations near the southern coast of South Africa.
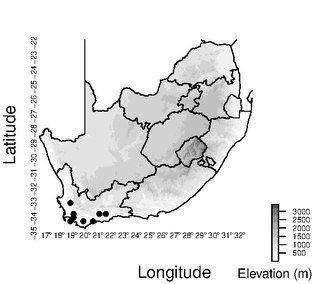
Schoenus brunnescens is a species of sedge endemic to the Western Cape Province of South Africa.

Schoenus inconspicuus is a species of sedge endemic to south-western areas of the Western Cape Province of South Africa.


































