Related Research Articles
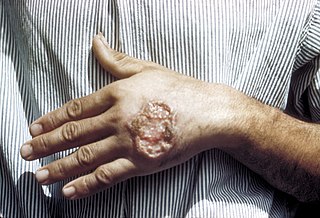
Leishmaniasis is a disease caused by parasites of the Leishmania type. It is spread by the bite of certain types of sandflies. The disease can present in three main ways: cutaneous, mucocutaneous, or visceral. The cutaneous form presents with skin ulcers, while the mucocutaneous form presents with ulcers of the skin, mouth, and nose, and the visceral form starts with skin ulcers and then later presents with fever, low red blood cells, and enlarged spleen and liver.

Bleomycin is a medication used to treat cancer. This includes Hodgkin's lymphoma, non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, testicular cancer, ovarian cancer, and cervical cancer among others. Typically used with other cancer medications, it can be given intravenously, by injection into a muscle or under the skin. It may also be administered inside the chest to help prevent the recurrence of a fluid around the lung due to cancer; however talc is better for this.

Hyperpigmentation is the darkening of an area of skin or nails caused by increased melanin.

Tuberculosis verrucosa cutis is a rash of small, red papular nodules in the skin that may appear 2–4 weeks after inoculation by Mycobacterium tuberculosis in a previously infected and immunocompetent individual.

Cutaneous leishmaniasis is the most common form of leishmaniasis affecting humans. It is a skin infection caused by a single-celled parasite that is transmitted by the bite of a phlebotomine sandfly. There are about twenty species of Leishmania that may cause cutaneous leishmaniasis.

The iliohypogastric nerve is a nerve that originates from the lumbar plexus that supplies sensation to skin over the lateral gluteal and hypogastric regions and motor to the internal oblique and transverse abdominal muscles.

The lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh is a cutaneous nerve that innervates the skin on the lateral part of the thigh.

Bleomycin hydrolase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the BLMH gene.
Electrochemotherapy is a type of chemotherapy that allows delivery of non-permeant drugs to the cell interior. It is based on the local application of short and intense electric pulses that transiently permeabilize the cell membrane, thus allowing transport of molecules otherwise not permitted by the membrane. Applications for treatment of cutaneous and subcutaneous tumors have reached clinical use by utilizing drugs such as bleomycin or cisplatin). Electrochemotherapy with bleomycin was used to treat a patient for the first time in 1991 at the Institute Gustave Roussy in France, while electrochemotherapy with cisplatin was used to treat for the first time in 1995 at the Institute of Oncology, Ljubljana, Slovenia. Since then, more than 4000 patients were treated with electrochemotherapy all over the world. Recently, new electrochemotherapy modalities have been developed for treatment of internal tumors using surgical procedures, endoscopic routes, or percutaneous approaches to gain access to the treatment area.

Polypeptide antibiotics are a chemically diverse class of anti-infective and antitumor antibiotics containing non-protein polypeptide chains. Examples of this class include actinomycin, bacitracin, colistin, and polymyxin B. Actinomycin-D has found use in cancer chemotherapy. Most other polypeptide antibiotics are too toxic for systemic administration, but can safely be administered topically to the skin as an antiseptic for shallow cuts and abrasions.
Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis (NEH) usually is a cutaneous complication of chemotherapy, but it can also occur for other reasons. It consists of fever and non specific skin lesions. It is rare, and self-limited.

Cutaneous small-vessel vasculitis (CSVV), also known as hypersensitivity vasculitis, cutaneous leukocytoclastic vasculitis, hypersensitivity angiitis, cutaneous leukocytoclastic angiitis, cutaneous necrotizing vasculitis and cutaneous necrotizing venulitis, is inflammation of small blood vessels, characterized by palpable purpura. It is the most common vasculitis seen in clinical practice.
Plummer's nail is a clinical sign in which there is onycholysis, or separation of the nail from the nail bed, particularly affecting the ring and little fingers. It occurs in patients with thyrotoxicosis. About 5% of hyperthyroid patients display abnormal nail changes. Plummer's nail is also associated with psoriasis, traumatic injury, and allergic contact dermatitis.
Paraneoplastic acrokeratosis, or Bazex syndrome is a cutaneous condition characterized by psoriasiform changes of hands, feet, ears, and nose, with involvement of the nails and periungual tissues being characteristic and indistinguishable from psoriatic nails. The condition is associated with carcinomas of the upper aerodigestive tract.

Cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia refers to a groups of benign cutaneous disorders characterized by collections of lymphocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells in the skin. Conditions included in this groups are:

A Myxoid cyst is a cutaneous condition often characterized by nail plate depression and grooves.
Brentuximab vedotin is an antibody-drug conjugate medication used to treat relapsed or refractory Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) and systemic anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL). It selectively targets tumor cells expressing the CD30 antigen, a defining marker of Hodgkin lymphoma and ALCL. The drug is being jointly marketed by Millennium: The Takeda Oncology Company outside the US, and Seattle Genetics in the US.
Laryngo-onycho-cutaneous syndrome is a rare epithelial disorder inherited in an autosomal recessive fashion. It is characterized by abnormalities in the larynx, nails ("onycho-"), and skin ("cutaneous"). The disorder is only found in Punjabi Muslims and only a few cases have been reported.

Shiitake mushroom dermatitis is an intensely pruritic dermatitis characterized by disseminated 1mm erythematous micropapules seen in a linear grouped arrangement secondary to Koebnerization due to patient scratching. It is caused by the ingestion of shiitake mushrooms and was first described in 1977 by Nakamura. Although it is rarely seen outside of China and Japan due to a lower incidence of shiitake consumption outside these regions, there is a well-established association between flagellate dermatitis and shiitake mushroom ingestion. Bleomycin ingestion may also cause similar findings. On physical exam, one key difference between the two is that post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation changes are usually seen with bleomycin-induced flagellate dermatitis and are not typically present with shiitake mushroom induced flagellate dermatitis. The median time of onset from ingestion of shiitake mushrooms is typically 24 hours, ranging from 12 hours to 5 days. Most patients completely recover by 3 weeks, with or without treatment. Although the pathogenesis of shiitake induced flagellate dermatitis is not clear, the theory most argued for is a toxic reaction to lentinan, a polysaccharide isolated from shiitake mushrooms. However, Type I and Type IV allergic hypersensitivities have also been supported by the 24-hour median time of onset, clearance in 3–21 days, severe pruritus, benefit of steroids and antihistamines, and lack of grouped outbreaks in people exposed to shared meals containing shiitake mushrooms. Most cases reported shortly after its discovery were due to consumption of raw shiitake mushrooms, but several cases have since been reported after consumption of fully cooked mushrooms.
Pseudoapoptosis can be defined from multiple viewpoints, with an underlying premise of the differences in cellular processes and states relating to apoptosis. Pseudoapoptosis can be referred to as an apoptotic-like cellular state that can be readily reversed, or as a process that induces rapid apoptosis through the introduction of drugs such as bleomycin.
References
- ↑ Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. pp. 950–1. ISBN 978-1-4160-2999-1.