
The British Isles are a group of islands in the North Atlantic off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Hebrides and over six thousand smaller islands. They have a total area of 315,159 km2 (121,684 sq mi) and a combined population of almost 72 million, and include two sovereign states, the Republic of Ireland, and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. The Channel Islands, off the north coast of France, are sometimes taken to be part of the British Isles, even though they do not form part of the archipelago.

Belfast is the capital and largest city of Northern Ireland, standing on the banks of the River Lagan on the east coast. It is the 12th-largest city in the United Kingdom and the second-largest on the island of Ireland. It had a population of 343,542 as of 2019. Belfast suffered greatly during the violence that accompanied the partition of Ireland, and especially during the more recent conflict known as the Troubles: in the 1970s and 1980s it was one of the world's most dangerous cities, with a homicide rate around 31 per 100,000.

Dublin is the capital and largest city of Ireland. Situated on a bay on the east coast, at the mouth of the River Liffey, it lies within the province of Leinster. It is bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, a part of the Wicklow Mountains range. It has an urban area population of 1,173,179, while the population of the Dublin Region as of 2016 was 1,347,359. The population of the Greater Dublin Area was 1,904,806 per the 2016 census.

Derry, officially Londonderry, is the second-largest city in Northern Ireland and the fourth-largest city on the island of Ireland. The name Derry is an anglicisation of the Old Irish name Daire meaning "oak grove". In 1613, the city was granted a royal charter by King James I and gained the "London" prefix to reflect the funding of its construction by the London guilds. While the city is more usually known colloquially as Derry, Londonderry is also commonly used and remains the legal name.

Ireland, also known as the Republic of Ireland, is a country in north-western Europe occupying 26 of 32 counties of the island of Ireland. The capital and largest city is Dublin, which is located on the eastern side of the island. Around 40% of the country's population of 4.9 million people resides in the Greater Dublin Area. The sovereign state shares its only land border with Northern Ireland which is part of the United Kingdom. It is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, with the Celtic Sea to the south, St George's Channel to the south-east, and the Irish Sea to the east. It is a unitary, parliamentary republic. The legislature, the Oireachtas, consists of a lower house, Dáil Éireann, an upper house, Seanad Éireann, and an elected President who serves as the largely ceremonial head of state, but with some important powers and duties. The head of government is the Taoiseach, who is elected by the Dáil and appointed by the President; the Taoiseach in turn appoints other government ministers.

The counties of Ireland are historic administrative divisions of the island, now used in various contexts. They began as Norman structures, and as the powers exercised by the Cambro-Norman barons and the Old English nobility waned over time, new offices of political control came to be established at a county level.

Northern Ireland is variously described as a country, province, or region which is part of the United Kingdom. Located in the northeast of the island of Ireland, Northern Ireland shares a border to the south and west with the Republic of Ireland. In 2011, its population was 1,810,863, constituting about 30% of the island's population and about 3% of the UK's population. The Northern Ireland Assembly, established by the Northern Ireland Act 1998, holds responsibility for a range of devolved policy matters, while other areas are reserved for the British government. Northern Ireland co-operates with the Republic of Ireland in several areas.

The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK), or Britain, is a sovereign country in north-western Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland. The United Kingdom includes the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland, and many smaller islands within the British Isles. Northern Ireland shares a land border with the Republic of Ireland. Otherwise, the United Kingdom is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, with the North Sea to the east, the English Channel to the south and the Celtic Sea to the south-west, giving it the 12th-longest coastline in the world. The Irish Sea separates Great Britain and Ireland. The total area of the United Kingdom is 94,000 square miles (240,000 km2).

Ulster is one of the four traditional Irish provinces, in the north of Ireland. It is made up of nine counties: six of these constitute Northern Ireland ; the remaining three are in the Republic of Ireland.

Ireland is an island in the North Atlantic. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel, the Irish Sea, and St George's Channel. Ireland is the second-largest island of the British Isles, the third-largest in Europe, and the twentieth-largest on Earth.

Saint Patrick's Day, or the Feast of Saint Patrick, is a cultural and religious celebration held on 17 March, the traditional death date of Saint Patrick, the foremost patron saint of Ireland.

The House of Windsor is the reigning royal house of the United Kingdom and the other Commonwealth realms. In 1901, the House of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha succeeded the House of Hanover to the British monarchy with the accession of King Edward VII, son of Queen Victoria and Prince Albert of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha. In 1917, the name of the royal house was changed from the anglicised German Saxe-Coburg and Gotha to the English Windsor because of anti-German sentiment in the United Kingdom during World War I. There have been four British monarchs of the House of Windsor since then: George V, Edward VIII, George VI, and Elizabeth II.

The Irish are an ethnic group and nation native to the island of Ireland, who share a common identity and culture. Ireland has been inhabited for about 12,500 years according to archaeological studies. For most of Ireland's recorded history, the Irish have been primarily a Gaelic people. From the 9th century, small numbers of Vikings settled in Ireland, becoming the Norse-Gaels. Anglo-Normans conquered parts of Ireland in the 12th century, while England's 16th/17th-century conquest and colonisation of Ireland brought many English and Lowland Scots people to parts of the island, especially the north. Today, Ireland is made up of the Republic of Ireland and the smaller Northern Ireland. The people of Northern Ireland hold various national identities including British, Irish, Northern Irish or some combination thereof.
A formal Irish-language personal name consists of a given name and a surname. Surnames in Irish are generally patronymic in etymology, although they are no longer literal patronyms, as most Icelandic names are. The form of a surname varies according to whether its bearer is male or female and in the case of a married woman, whether she chooses to adopt her husband's surname.

The Irish Republican Army (IRA) is a name used by various paramilitary organisations in Ireland throughout the 20th and the 21st centuries. Organisations going by this name have been dedicated to irredentism through Irish republicanism, the belief that all of Ireland should be an independent republic free from British rule. The original Irish Republican Army was raised in 1917 from members of the Irish Volunteers and the Irish Citizen Army, later reinforced by Irishmen who returned to Ireland to fight against Britain in the Irish War of Independence. In Irish law, this IRA was the army of the revolutionary Irish Republic as declared by its parliament, Dáil Éireann, in 1919. In the century that followed, the original IRA was reorganised, changed and split on multiple occasions, to such a degree that many subsequent paramilitary organisations have been known by that title – most notably the Provisional Irish Republican Army which was a key participant during the Troubles. The contemporary IRA organisations each claim the sole right to use that name, as they each insist they are the only legitimate descendants of the original IRA.

Saint Patrick was a fifth-century Romano-British Christian missionary and bishop in Ireland. Known as the "Apostle of Ireland", he is the primary patron saint of Ireland, the other patron saints being Brigit of Kildare and Columba. Patrick was never formally canonised, having lived prior to the current laws of the Catholic Church in these matters. Nevertheless, he is venerated as a Saint in the Catholic Church and in the Eastern Orthodox Church, where he is regarded as equal-to-the-apostles and Enlightener of Ireland. He is also regarded as a Saint within the framework of their respective doctrine by the Anglican Communion and the Lutheran Churches.

Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of 209,331 km2 (80,823 sq mi), it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island, and the ninth-largest island in the world. The island is dominated by a maritime climate with narrow temperature differences between seasons. The 60% smaller island of Ireland is to the west – and together these islands, along with over 1,000 smaller surrounding islands and named substantial rocks, form the British Isles archipelago.
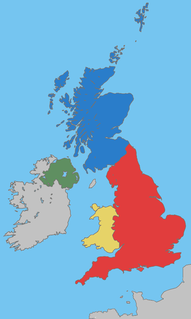
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland (UK), since 1922, comprises four constituent countries: England, Scotland, and Wales, as well as Northern Ireland. The UK Prime Minister's website has used the phrase "countries within a country" to describe the United Kingdom. Some statistical summaries, such as those for the twelve NUTS 1 regions of the United Kingdom, refer to Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland as "regions" of the former EU member state. With regard to Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales particularly, the descriptive name one uses "can be controversial, with the choice often revealing one's political preferences".

Irish is a Goidelic language of the Insular Celtic branch of the Celtic language family, which is itself a part of the Indo-European language family. Irish originated on the island of Ireland and was the population's first language until the late 18th century. Although English has been the first language of most residents of the island since the early 19th century, Irish is spoken as a first language in broad areas of counties Cork, Donegal, Galway, and Kerry, as well as smaller areas of counties Mayo, Meath, and Waterford. It is also spoken by a larger group of habitual but non-traditional speakers, mostly in urban areas where the majority are second-language speakers. Daily users outside the education system number around 73,000, and over 1.85 million people across the island claim to be at least somewhat proficient with the language.
















